Preparation method of slow-release polypeptide growth factor biological material scaffold
A peptide growth factor and biomaterial technology, applied in the field of preparation of slow-release polypeptide growth factor biomaterial scaffolds, can solve the problems of inability to achieve therapeutic effect, short half-life of polypeptide growth factor, influence of polypeptide growth factor biological activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
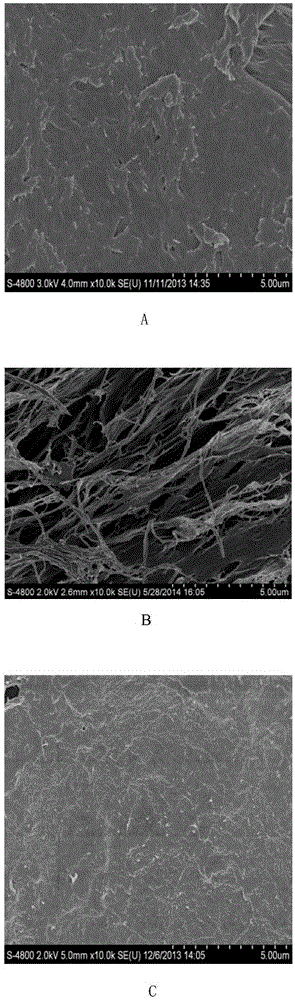
[0033] Embodiment 1, a kind of preparation method of the chitosan sustained-release scaffold of encapsulating nerve growth factor
[0034] Nerve growth factor (NGF) is one of the members of the neurotrophic factor family and is the first discovered neurotrophic factor, which plays a role in neuronal cell survival, axon regeneration, and regulation of Schwanncell (SC) differentiation and Both play an important role in the process of axonal remyelination. The axons of the central nervous system can regenerate under a suitable microenvironment, and can partially restore the function of damaged axons, but the half-life of nerve growth factor in adult rats is only 7.2min. In this example, nerve growth factor was taken as the test object, and a chitosan slow-release scaffold encapsulated with nerve growth factor was prepared to prolong the slow-release time of nerve growth factor. Specific steps are as follows:
[0035] 1. Chitosan material and nerve growth factor blend swelling ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2, Bioactivity Verification of Chitosan Slow-release Scaffold Encapsulating Nerve Growth Factor
[0042] In order to verify whether the chitosan slow-release scaffold encapsulating nerve growth factor prepared according to the method in Example 1 destroys the activity of nerve growth factor and whether it also has the effect of nourishing neurons, the present invention uses chicken embryo dorsal root nerve The nerve growth factor activity of the chitosan slow-release scaffold encapsulating nerve growth factor obtained in Example 1 was verified by using chicken embryo dorsal root ganglion (DRG) culture method as the test object. Specific steps are as follows:
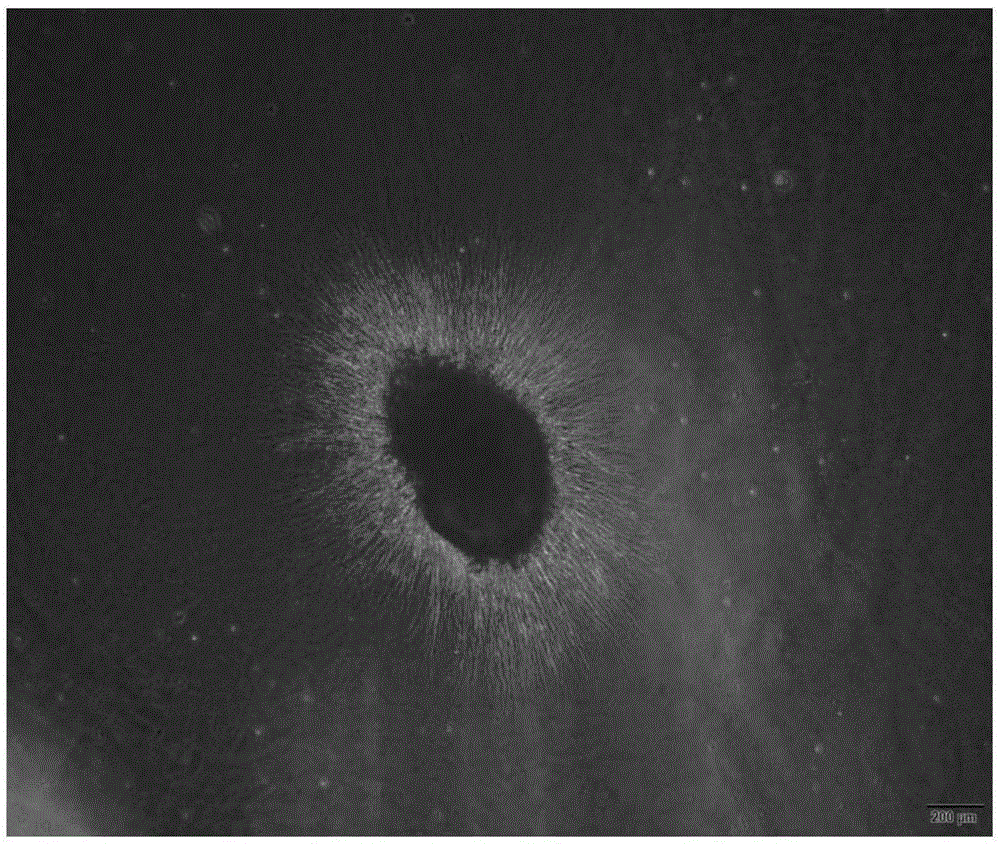
[0043] Chitosan sustained-release scaffolds encapsulated with nerve growth factor were co-cultured with dorsal root ganglion extracted from 8-day-old chicken embryos. After 48 hours, the growth of DRG axons was observed under an optical microscope.
[0044] The result is as image 3Shown: the dorsal root...
Embodiment 3
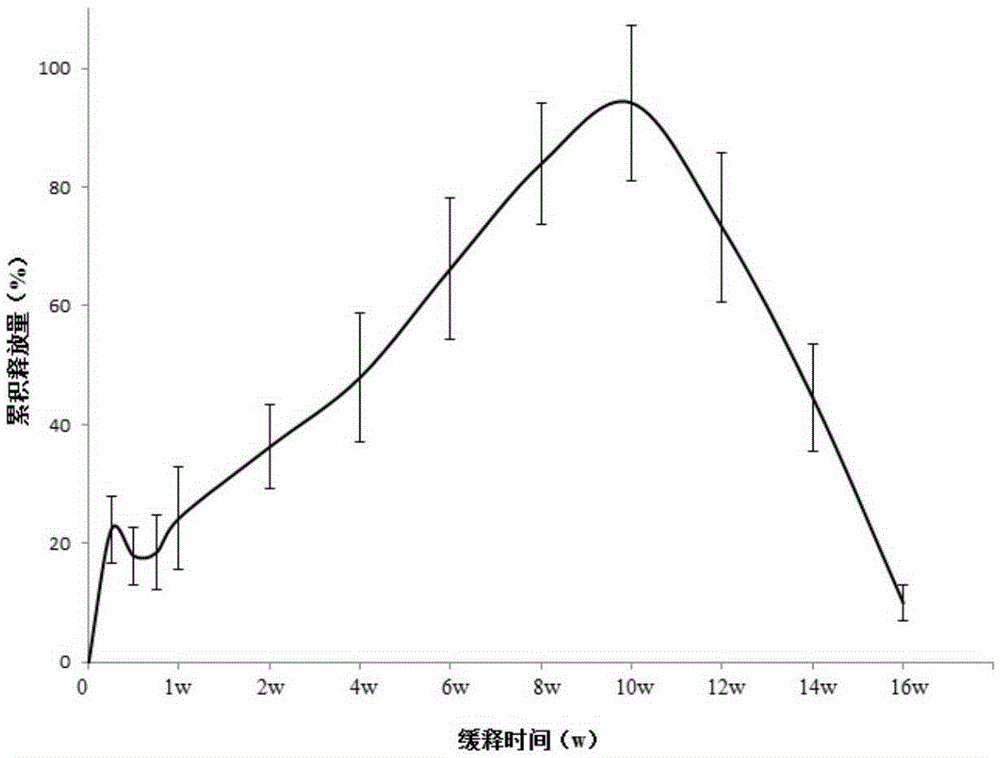
[0045] Embodiment 3, the sustained-release curve of the chitosan sustained-release stent encapsulating nerve growth factor
[0046] After spinal cord injury, the important cause of nerve regeneration impairment after injury is the formation of glial scar. The barrier effect of glial scars on axon regeneration is mainly reflected in two aspects: 1. The mechanical barrier formed by astrocytes; 2. The chemical barrier composed of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. The mechanical barrier that hinders axon regeneration begins to enter a stable period 2 months after spinal cord injury, and finally reaches a stable level at 3 months after injury; the chemical barrier that hinders axon regeneration begins to relax 1 month after injury, And reached stability in 3 months. Once the spinal cord injury enters the stage of old spinal cord injury, the stable glial scar and the local environment of the injury tend not to change, and it becomes more difficult to repair the damaged part at thi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com