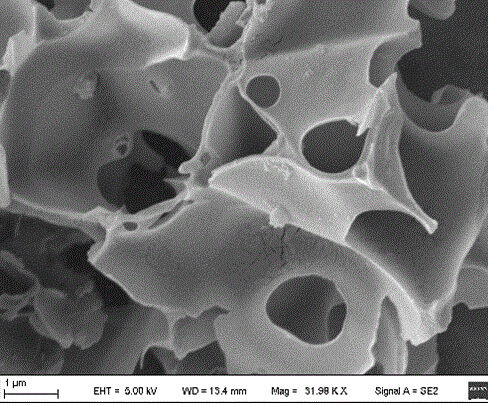
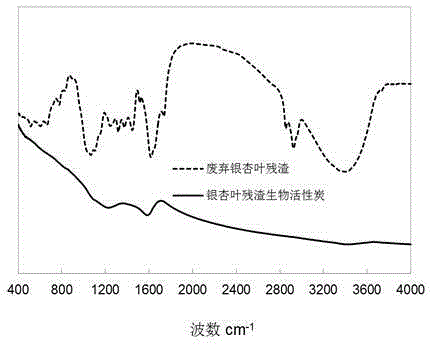
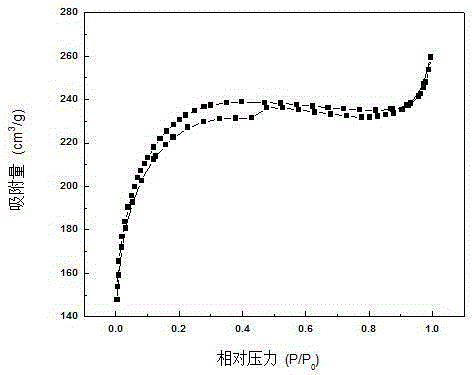
Method for preparing biological activated carbon from waste maidenhair tree leaves and folium ginkgo herb residue
A biological activated carbon, ginkgo tree technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve problems such as perishability, achieve the effects of developed pores, solve the shortage of carbonaceous raw materials, and good adsorption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The collected natural fallen leaves of the ginkgo tree are firstly washed with water for 5 times until the water quality becomes clear, then washed with distilled water, dried and crushed to obtain the ginkgo leaf powder. Take 10 g of ginkgo leaf powder, add 100 mL of 95% ethanol solution, soak for 12 hours, filter, dry, pulverize, and pass through a 300-mesh sieve to obtain ginkgo leaf residue powder.
[0036]Weigh 10g of ginkgo leaf residue powder, dip it in 100mL potassium hydroxide solution (0.1~0.5g / mL) for 2h, put it into a crucible, put it in a muffle furnace, and raise the temperature to 600°C (the heating rate is 10°C / min ), carbonized for 1 h, and cooled to room temperature; first washed with 300 mL of hydrochloric acid solution (1-3 mol / L), then washed with distilled water until neutral, dried and ground to obtain the discarded ginkgo leaf residue bioactivated carbon material.
[0037] The biological activated carbon material has a decolorization rate of 97.6...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The collected natural fallen leaves of the ginkgo tree are firstly washed with water for 3 times until the water quality becomes clear, then washed with distilled water, dried and pulverized to obtain the ginkgo leaf powder. Take 20g of ginkgo leaf powder, add 200mL of 95% ethanol solution, soak for 12h, filter, dry, pulverize, and pass through a 300-mesh sieve to obtain ginkgo leaf residue powder.
[0040] Weigh 20g of ginkgo leaf residue powder, soak it with 200mL potassium hydroxide solution (0.1~0.5g / mL) for 12h, put it into a crucible, place it in a muffle furnace, and raise the temperature to 700°C (the heating rate is 10°C / min ), carbonized for 3 hours, and cooled to room temperature; first washed with 300mL hydrochloric acid solution (1~3mol / L), then washed with distilled water until neutral, and dried to obtain the discarded ginkgo leaf residue bioactivated carbon material.
[0041] The decolorization rate of biological activated carbon material for simulated w...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Wash the collected ginkgo leaf dregs (residue after extracting small molecule active ingredients from ginkgo leaves) with water until the water quality becomes clear, then wash twice with distilled water, dry, pulverize, and pass through a 300-mesh sieve to obtain ginkgo leaf dregs powder .
[0044] Weigh 20g of ginkgo biloba powder, soak it with 200mL potassium hydroxide solution (0.1~0.5g / mL) for 8h, put it into a crucible, put it in a muffle furnace, and raise the temperature to 500°C (the heating rate is 10°C / mL) min), carbonized for 2 hours, and cooled to room temperature; first washed with 300mL hydrochloric acid solution (1~3mol / L), then washed with distilled water until neutral, dried and ground to obtain bioactive carbon material of ginkgo biloba leaves.
[0045] The biological activated carbon material has a decolorization rate of 99.3% for simulated wastewater containing methylene blue, and an adsorption capacity of 595.8mg / g; a removal rate of 96.5% for simu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com