Degradable zinc alloy material, and preparation method and application thereof
A zinc alloy and alloy technology, applied in the field of degradable zinc alloy materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of inflammation, low mechanical properties of biopolymer materials, and limited application prospects, etc., to improve tensile strength and processing parameters Optimized, wide-ranging application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
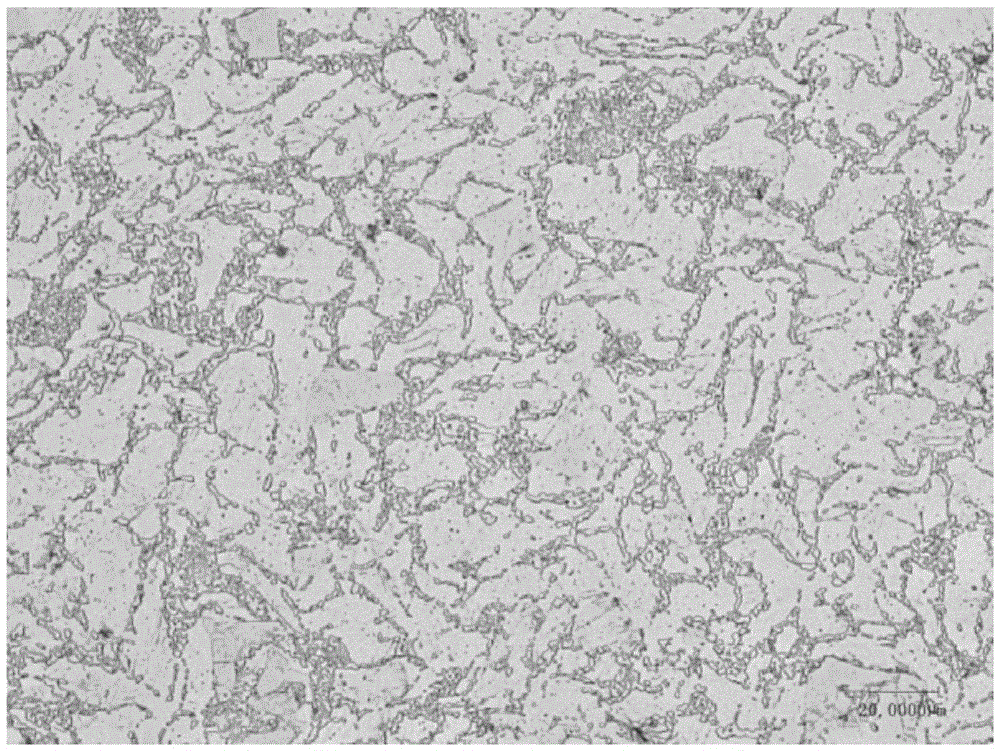
[0049] A zinc alloy containing 1% magnesium and 0.14% calcium was melted at 650°C for 10 minutes, and cast into shape. A 30mm diameter ingot was extruded into a 2mm rod. The tensile strength of the obtained bar was 252 MPa, the yield strength was 187 MPa, and the elongation was 5.1%. Metallographic and SEM characterizations were carried out on the obtained bars, respectively as image 3 and 4 shown. Continue to heat-treat the bar, at a heating rate of 10°C / min, raise the temperature to 330°C for 1 hour, put it in the air to cool, and then cold draw to obtain a 0.5mm wire.
Embodiment 2
[0051]The zinc alloy containing 1.2% magnesium and 0.16% calcium was smelted at 650°C for 10 minutes and cast into shape. A 30 mm diameter ingot was extruded into a 1.6 mm rod. The tensile strength of the obtained bar was 247 MPa, the yield strength was 189 MPa, and the elongation was 4.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0053] A zinc alloy containing 1.1% magnesium and 0.15% calcium was melted at 650°C for 10 minutes, and cast into shape. A 30mm diameter ingot was extruded into a 1.4mm rod. The tensile strength of the obtained bar was 258 MPa, the yield strength was 193 MPa, and the elongation was 4.9%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com