First lens for Tokamak type magnetically-confined nuclear fusion device
A tokamak and magnetic confinement technology, applied in the field of the first mirror, can solve the problems of high price, difficult processing and polishing, and poor sputtering resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
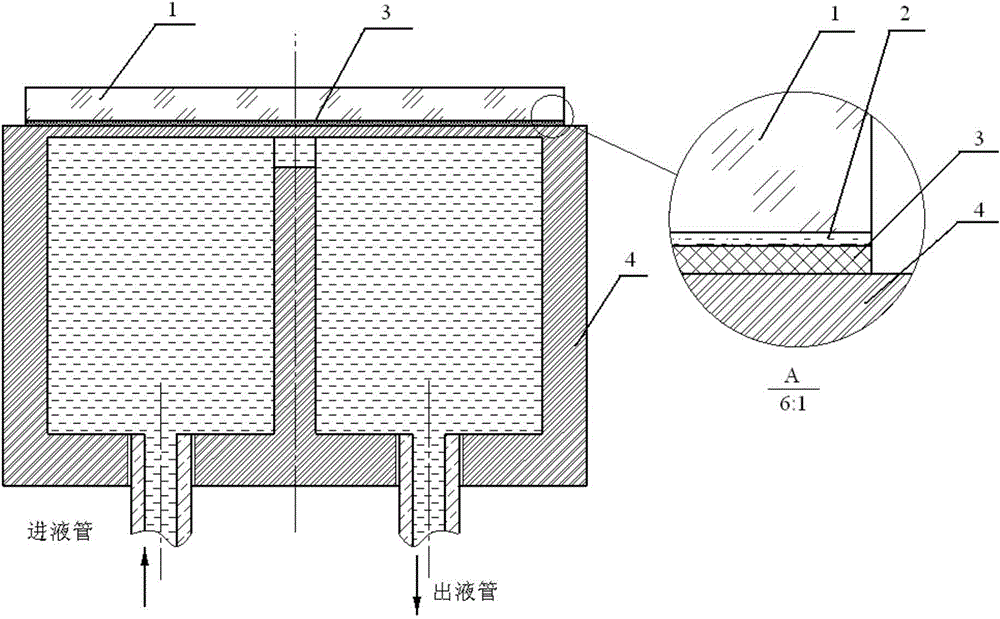
[0009] In the invention, sapphire, white sapphire, SiC crystal, single crystal germanium, single crystal silicon, CaF, quartz, yttrium aluminum garnet crystal and other sputtering-resistant and light-transmitting materials are used as alternative materials for the protective layer 1 (substrate). The surface is polished so that both sides of the protective layer reach the optical mirror surface, and the surface roughness of both sides is less than 10nm. The thickness of the protective layer 1 is less than 500 μm. The thinner the thickness, the more beneficial it is to reduce the temperature of the protective layer, reduce the heat deposition of the protective layer, and reduce the thermal stress damage of the protective layer. The thinner the protective layer 1 is, the more difficult it is for optical processing. Before the microchannel cooler 4 is welded with the functional film, the welding surface of the microchannel cooler (which can also be called a microchannel heat sink; ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com