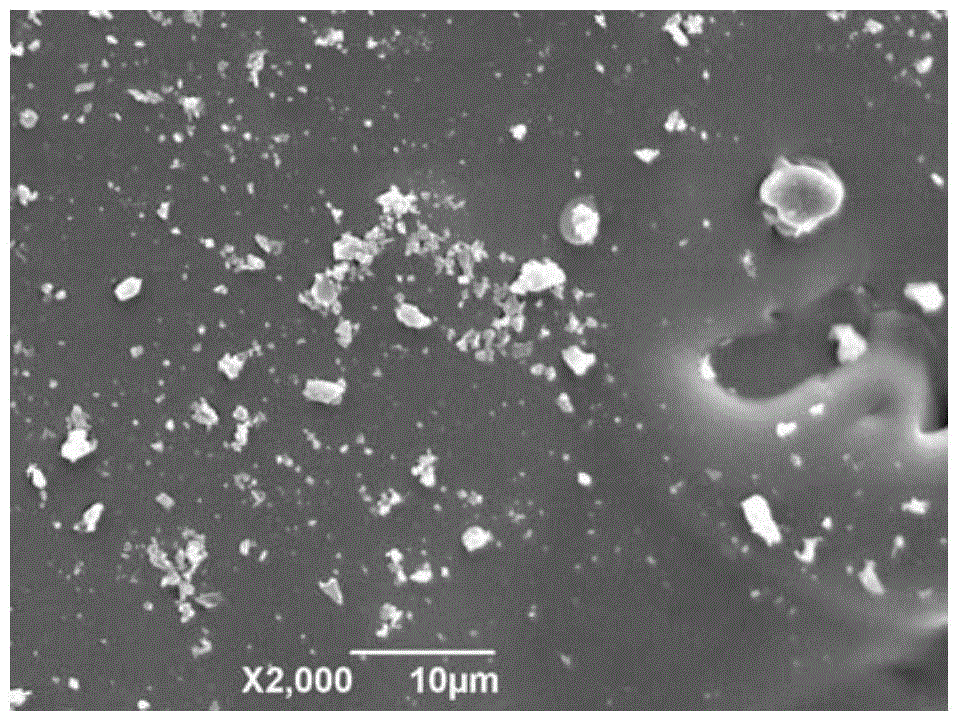
Preparation method of carbon fiber reinforced MoSi2-SiC ceramic matrix composite
A composite material and ceramic matrix technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of carbon fiber reinforced MoSi2-SiC ceramic matrix composite materials, can solve the problems of decreased fiber reinforcement strength, low matrix densification speed, low composite material stability, etc., and achieves increased density. , low cost, improve the effect of interface combination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1) Choose commercially available molybdenum disilicide powder (after wet ball milling for 48 hours, the average particle size is 0.8-1 μm), Si-Mo alloy powder (after wet ball milling for 24 hours, the average particle size is 1-2 μm), Al 2 o 3 The powder has been wet ball milled for 24 hours, the average particle size is 100-200nm), low-density C / C composite material (density is about 0.5g / cm 3 ), glucose (purity ≥ 99%) is raw material;
[0027] 2) According to mass percentage, 80% of molybdenum disilicide powder with an average particle size of 0.8-1 μm, 16% of Si-Mo alloy with an average particle size of 1-2 μm, and 4% of an average particle size of 100-200nm Al 2 o 3 The powders were mixed, and mixed with a planetary ball mill for 6 hours, and the speed of the ball mill was set at 440 rpm;
[0028] 3) Set the density to 0.4g / cm 3 The porous carbon / carbon composite material (Jiangsu Tianniao High-tech Co., Ltd.) was cut into circular sheets with a diameter of 1 c...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1) Choose commercially available molybdenum disilicide powder (after wet ball milling for 48 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 0.8-1 μm), Si-Mo alloy powder (after wet ball milling for 24 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 1-2 μm), Al 2 o 3 The powder is wet ball milled for 24 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 100-200nm), and the low-density C / C composite material (density is about 0.5g / cm 3 ), glucose (purity ≥ 99%) is raw material;
[0036] 2) According to mass percentage, 60% of molybdenum disilicide powder with an average particle size of 0.8-1 μm, 32% of Si-Mo alloy powder with an average particle size of 1-2 μm, and 8% with an average particle size of 100 -200nm Al 2 o 3 The powders were mixed, and mixed for 3 hours with a planetary ball mill, and the speed of the ball mill was set at 500 rpm;
[0037] 3) Set the density to 0.8g / cm 3 The porous carbon / carbon composite material is cut into circular slices with a ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 1) Choose commercially available molybdenum disilicide powder (after wet ball milling for 48 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 0.8-1 μm), Si-Mo alloy powder (after wet ball milling for 24 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 1-2 μm), Al 2 o 3 The powder is wet ball milled for 24 hours, the average particle size is controlled at 100-200nm), and the low-density C / C composite material (density is about 0.5g / cm 3 ), glucose (purity ≥ 99%) is raw material;
[0045] 2) According to mass percentage, 70% of molybdenum disilicide powder with an average particle size of 0.8-1 μm, 25% of Si-Mo alloy powder with an average particle size of 1-2 μm, and 5% with an average particle size of 100 -200nm Al 2 o 3 The powders were mixed, and mixed with a planetary ball mill for 3 hours, and the speed of the ball mill was set at 540 rpm;
[0046] 3) Set the density to 0.6g / cm 3 The porous carbon / carbon composite material is cut into circular slices with a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com