Method for qualitative and quantitative detection of microorganisms in human body
A technology of microorganisms and target microorganisms, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of inaccurate qualitative and quantitative detection of microorganisms, and achieve the effect of fine detection results, simple detection process, and probability guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1. Identification of human blood microorganisms
[0040] The samples to be tested are human tissues, body fluids and excreta, among which blood microorganisms are the basis for the diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. The sample to be tested in this embodiment is human blood, which is taken from a patient diagnosed with bacteremia by a doctor, and the detection of microorganisms in the blood is to provide a basis for a treatment plan.
[0041] Step 1. Determining the target microbial group in the sample to be tested, target microorganisms and non-target organisms, and reference microorganisms that do not exist in the sample to be tested, the specific method is as follows:
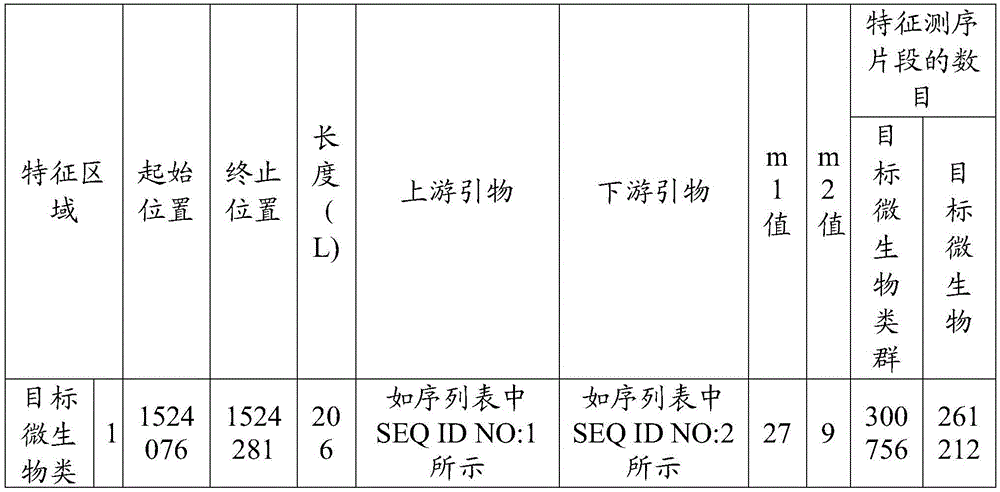
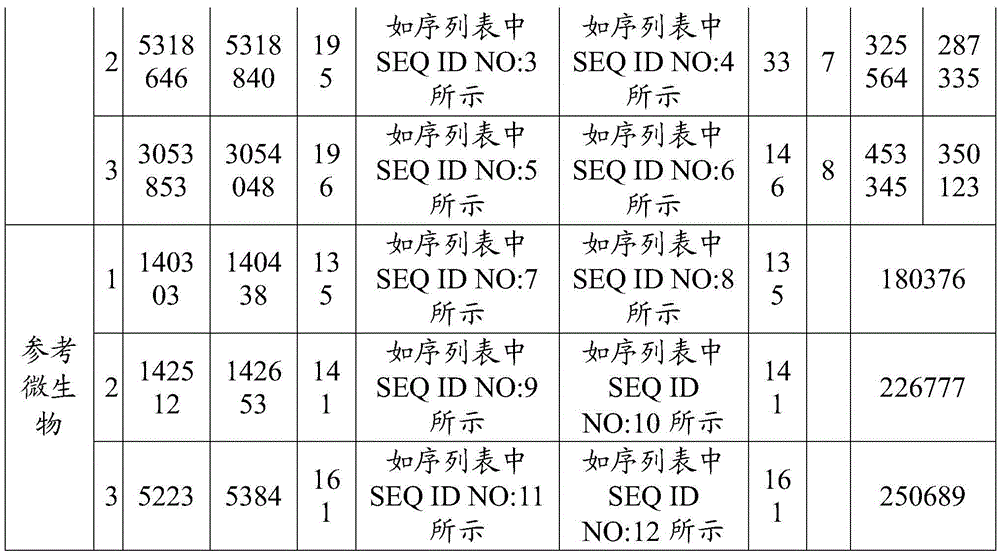
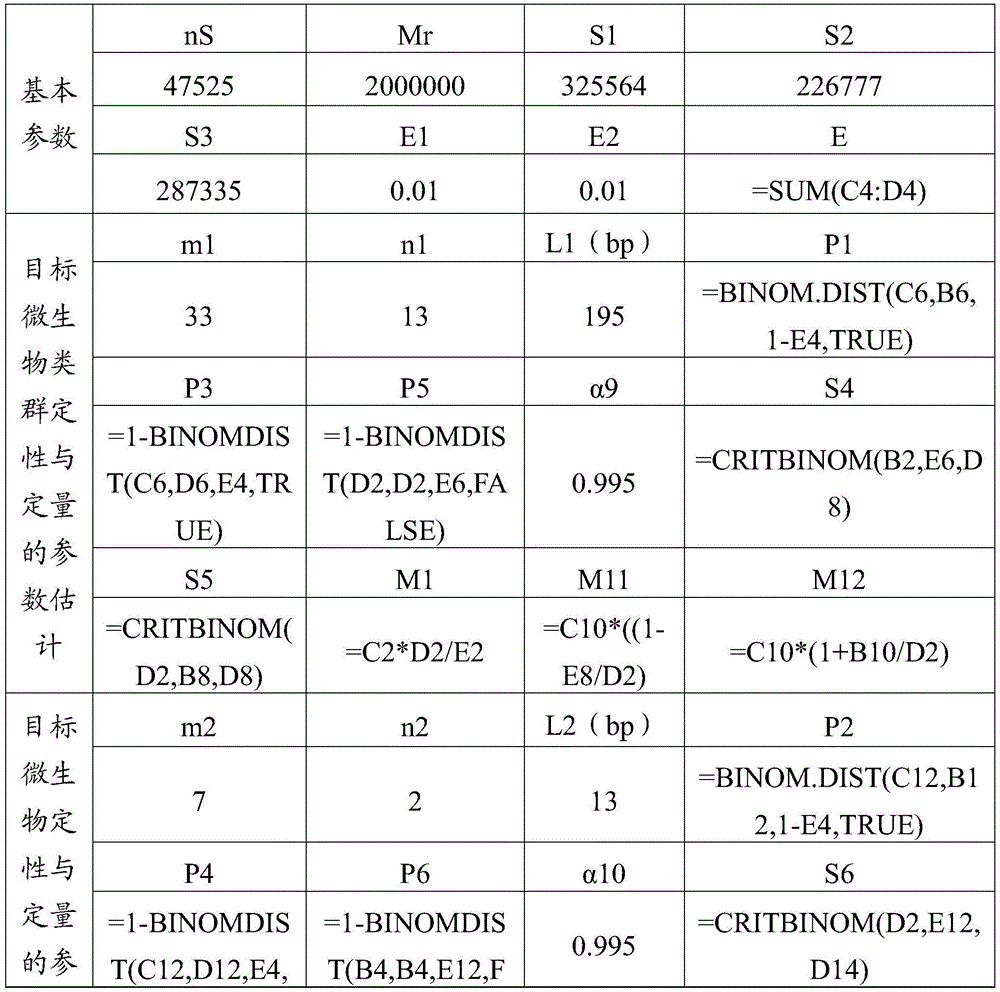
[0042] The number of target microbial groups ≥ 1, and each target microbial group includes ≥ 0 target microorganisms; target microorganisms can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, actinomycetes, rickettsia, mycoplasma, chlamydia, spirochetes and protozoa at least one of . The purpose of t...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment two, the identification of human feces microorganism
[0090] The sample to be tested in this embodiment is human feces, which are taken from patients with intestinal diseases diagnosed by doctors, and the detection of microorganisms in their feces is to provide a basis for treatment plans. This implementation is similar to the method in Example 1, and the methods, parameters and results not mentioned are the same as those in Example 1, so they will not be repeated here.
[0091] Step 1. Determining the target microbial groups, target microorganisms and non-target organisms in the test sample, and reference microorganisms that do not exist in the test sample.
[0092] The purpose of this embodiment is to identify Salmonella enterica in the sample to be tested. Its Latin formal name is Salmonella enterica. On NCBI (Nationalcenterforbiotechnologyinformation, National Center for Biotechnology Information), there are 33 physiological races of Salmonella enterica ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com