Method for fermentation production of isoprenoid compound via peanut shell degradation sugar
A technology of isoprenoid and peanut shells, applied in the field of production of emerging renewable fuels, to achieve the effect of increasing production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
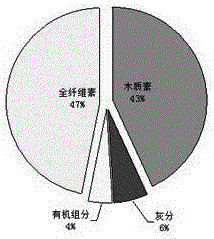
[0037] Embodiment 1, carry out component identification to peanut shell by different methods
[0038] 1.1 Identification of peanut shell components
[0039] Weigh 0.3 g of peanut shell sample, Soxhlet extract completely with 200 ml of ethanol in a water bath at 95 °C, and air-dry.
[0040] Weigh 0.3 g of sample into a pressure-resistant tube, add 3 mL of 72% H 2 SO 4 , fully stirred and mixed, placed in a water bath at 30°C for 60 minutes, then added 84 mL of deionized water, placed in an autoclave, and hydrolyzed at 121°C for 1 hour.
[0041] 1.1.1 Determination of lignin content
[0042] The hydrolyzed sample was placed in a filter crucible for suction filtration, and the filtrate and residue were collected. Determination of lignin by ashing method: put the residue and the crucible in a drying oven at 105°C and dry to constant weight, record the weight m 1 , put the residue and crucible in a box-type resistance furnace, ash at 575±25°C for 10h, cool to room temperature ...
Embodiment 2
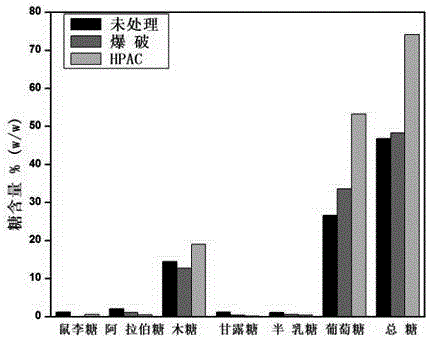
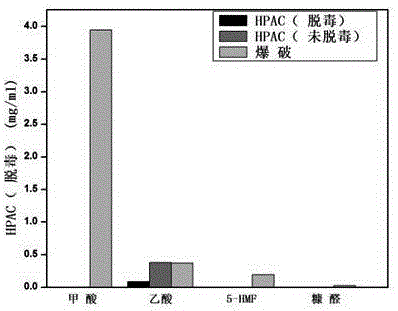
[0078] Example 2. Fermentative production of isoprenoid compounds by degrading sugar from peanut shells
[0079] 1. Peanut shell pretreatment
[0080] Rinse the peanut shells with running water and air dry them for later use.
[0081] 1.1 Pretreatment of peanut shells by blasting method
[0082] Get the cleaned peanut shells and process it with distilled water to keep its humidity at 75% and place it in the blasting device, heat the blasting tank at a heating rate of 15-20 °C / min, when the temperature rises to 220 °C, the pressure rises When it reached 1.47 MPa, quickly open the lid of the explosion tank, collect the processed peanut shells in the tank and place them at room temperature to cool.
[0083] 1.2 HPAC pretreatment of peanut shells
[0084] HPAC solution: a solution obtained by mixing hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid at a ratio of 1:1.
[0085] 10 g of washed and air-dried peanut shells were treated with 100 ml of HPAC solution at 80 °C for 2 h, then the treatm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com