Anti-fuse memory cell
A memory unit and antifuse technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, information storage, etc., can solve problems of manufacturability and reliability, high voltage exposure of MOS switching elements, doubtful manufacturability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
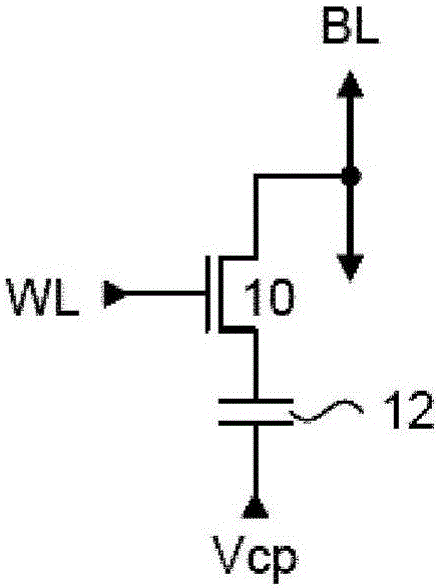
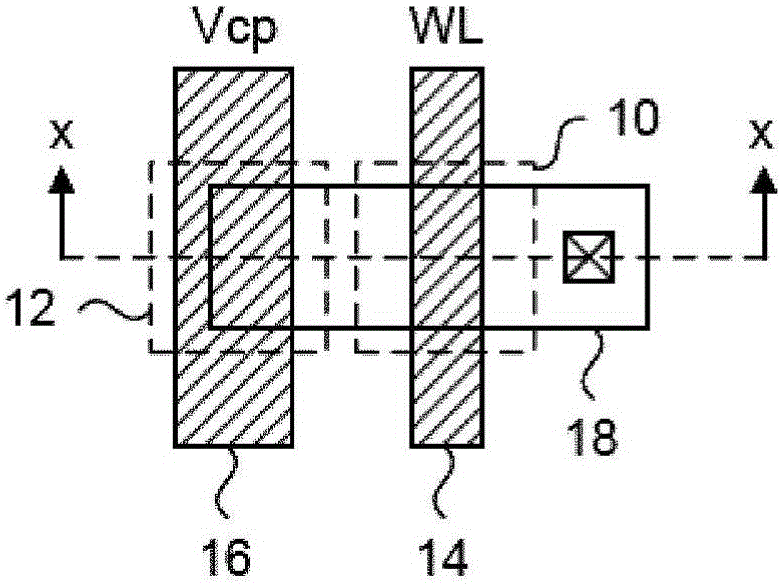
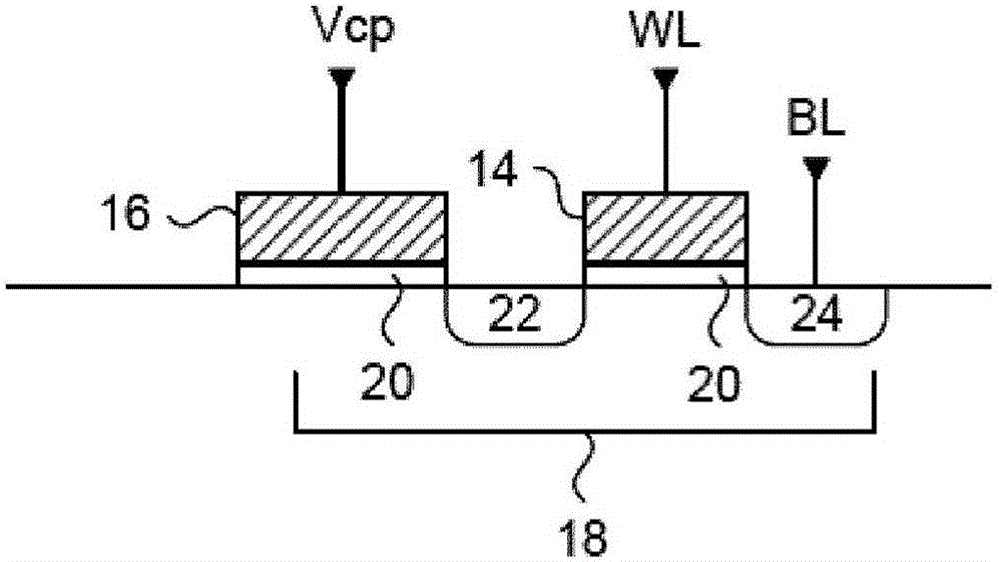
[0059] The present invention generally provides a variable thickness gate oxide antifuse transistor device useful for non-transitory one-time programmable (OTP) memory array applications. The antifuse transistor can be fabricated in standard CMOS technology and configured as a standard transistor element with source diffusion, gate oxide and polysilicon gate. The variable gate oxide under the polysilicon gate consists of a thick gate oxide region and a thin gate oxide region, where the thin gate oxide region acts as a local breakdown voltage region. A conductive path between the polysilicon gate and the channel region may be formed in the local breakdown voltage region during a programming operation. In memory array applications, the word line read current applied to the polysilicon gate can be sensed through the channel of the antifuse transistor through the bit line connected to the source diffusion. More specifically, the present invention provides an efficient method of u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com