Method for extracting beta-thymidine from fermentation liquid
A fermented liquid and thymidine technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of relatively large safety and environmental protection hazards, complex chemical synthesis process, and less thymidine extraction process , to achieve a high degree of automation, improve the extraction yield, and ensure the quality of the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
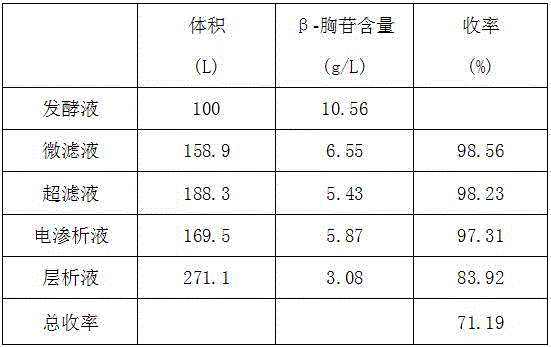
[0022] Heat 100L β-thymidine fermentation broth to 65°C with steam; pass through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 1000nm, the membrane entry pressure is 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure is 0.1MPa, and the operating temperature is 25°C. After the fermentation broth is concentrated 8 times, add The top wash water volume is 60L. The filtrate passes through the ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane molecular weight cut-off of 3000, the operating pressure is 1.4MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the microfiltrate is concentrated by 12 times, 30L of dialysis water is added. The ultrafiltrate passes through electrodialysis equipment at a flow rate of 600L / h to separate anions and cations. When the conductivity of the filtrate is ≤100us / cm, the filtrate is collected for vacuum concentration. Concentrate the filtrate until the content of β-thymidine reaches 30g / L, enter the chromatographic column for separation, collect the chromatographic ...
Embodiment 2
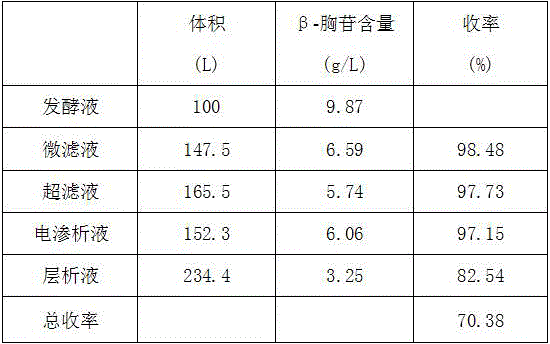
[0025] Heat 100L of β-thymidine fermentation liquid in a fermenter to 65°C by steam; pass through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 500nm, the membrane entry pressure is 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure is 0.1MPa, the operating temperature is 25°C, and the fermentation liquid is concentrated for 9 After doubling, add 70L of top wash water. The filtrate passes through the ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane molecular weight cut-off of 1000, the operating pressure is 1.4MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the ionized liquid is concentrated 15 times, 40L of dialysis water is added. The ultrafiltrate passes through the electrodialysis equipment at a flow rate of 500L / h to separate anions and cations. When the conductivity of the filtrate is ≤100us / cm, the filtrate is collected for vacuum concentration, and the filtrate is concentrated until the content of β-thymidine reaches 35g / L, and then enters the chromatography separation 1. Colle...
Embodiment 3
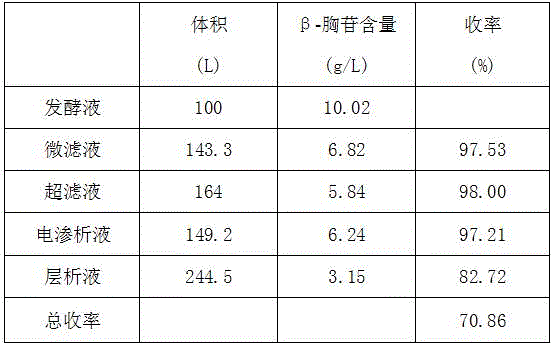
[0028] Heat 100L of β-thymidine fermentation liquid in a fermenter to 65°C by steam; pass through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 200nm, the membrane entry pressure is 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure is 0.1MPa, and the operating temperature is 25°C, and the fermentation liquid is concentrated for 6 After doubling, add 60L of top wash water. The filtrate passes through the ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane molecular weight cut-off of 2000, the operating pressure is 1.4 MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the ionized liquid is concentrated by 10 times, 35 L of dialysis water is added. The ultrafiltrate passes through the electrodialysis equipment at a flow rate of 500L / h to separate anions and cations. When the conductivity of the filtrate is less than or equal to 100us / cm, the filtrate is collected for vacuum concentration. The filtrate is concentrated until the content of β-thymidine reaches 40g / L, and then enters the chromatog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com