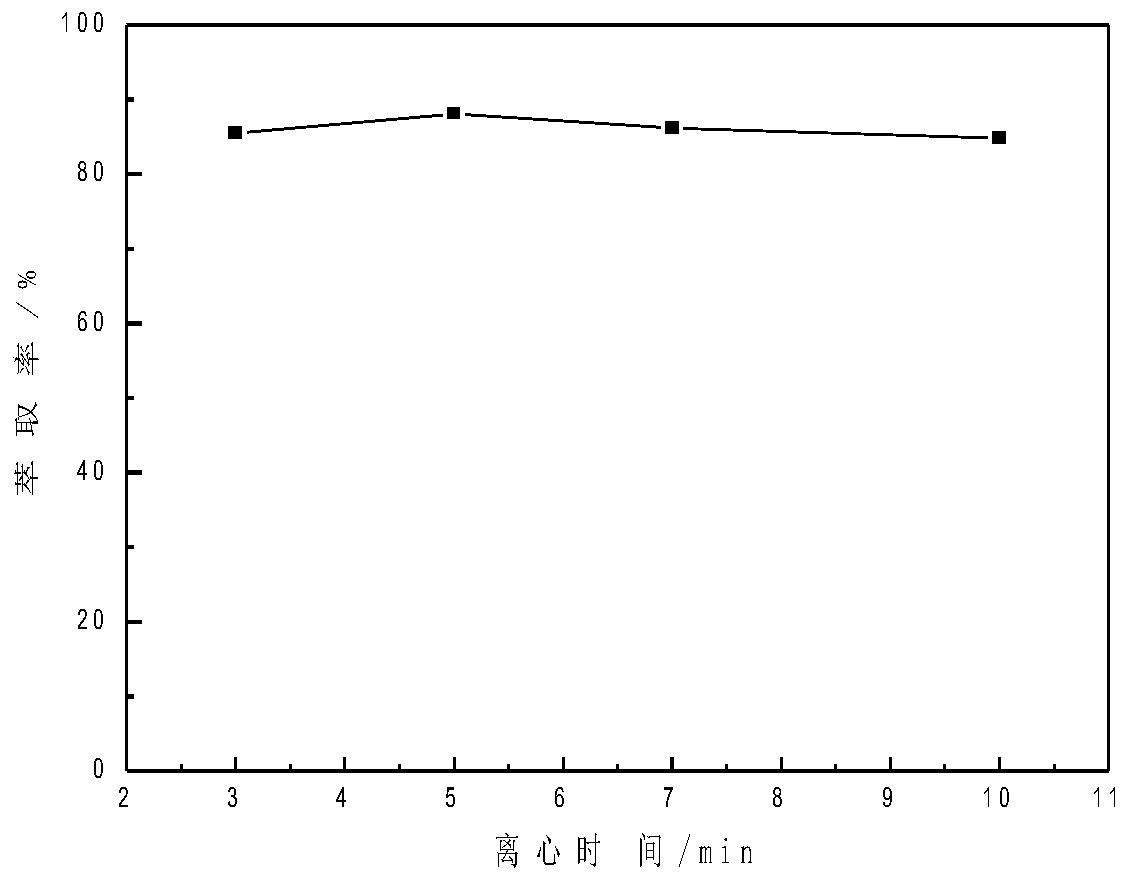
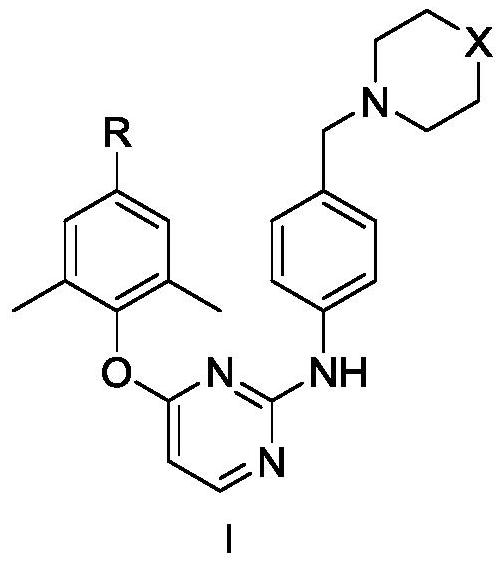
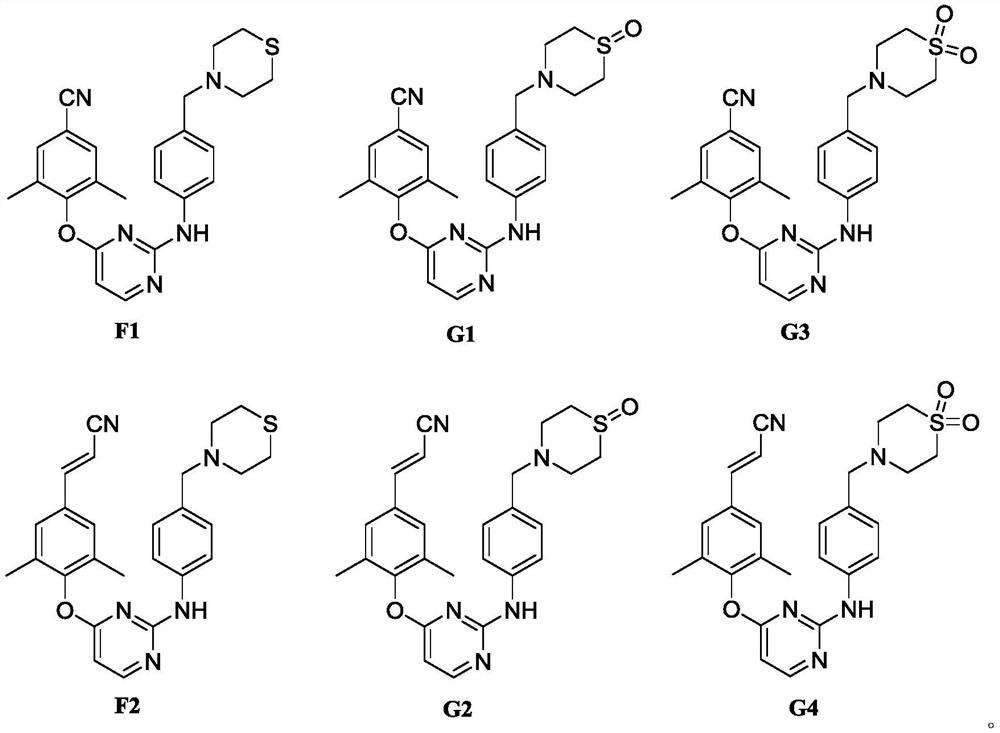
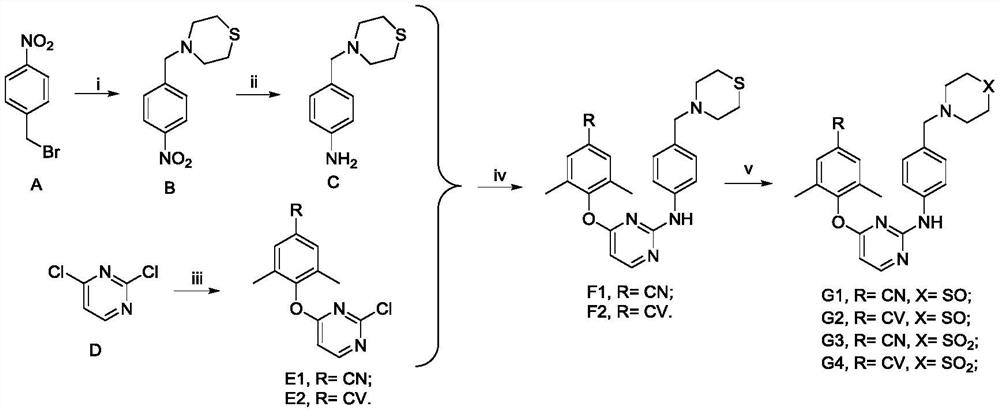
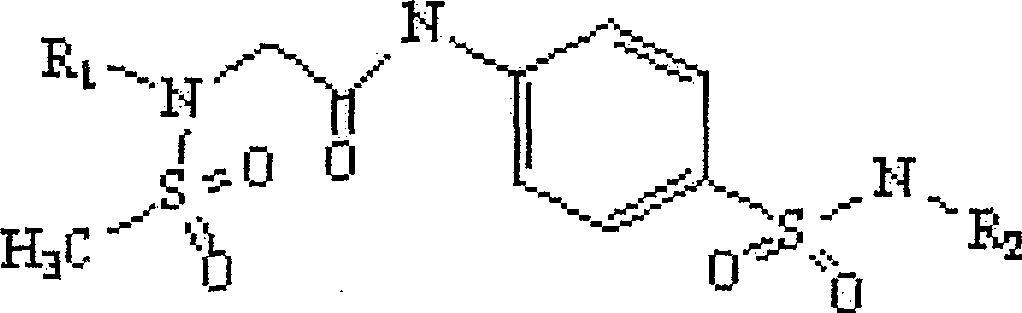
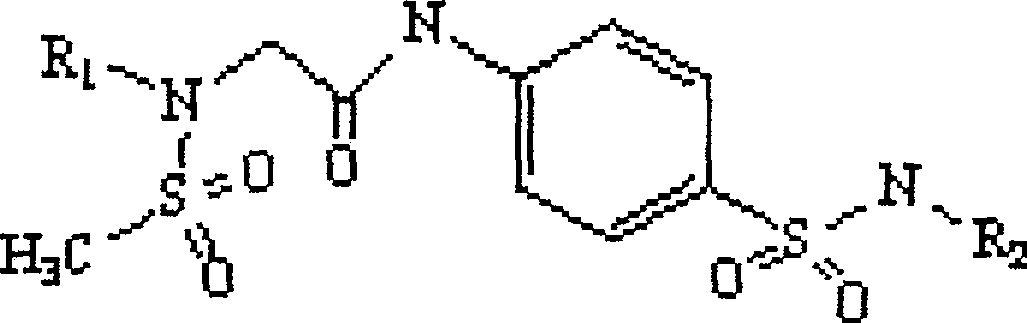
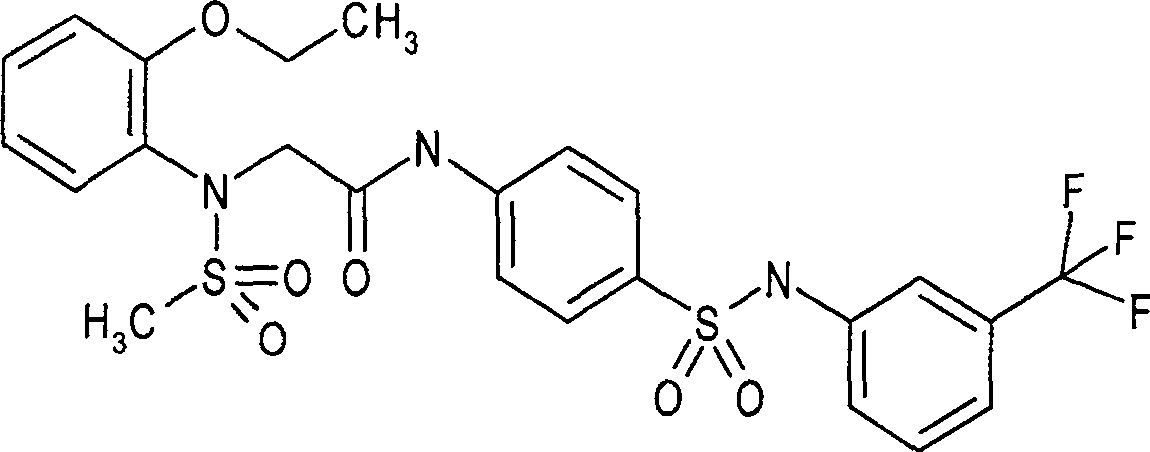
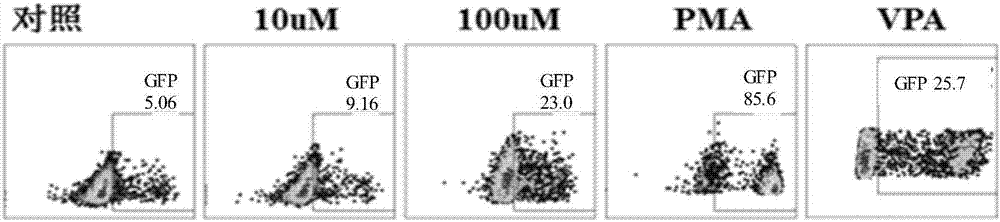
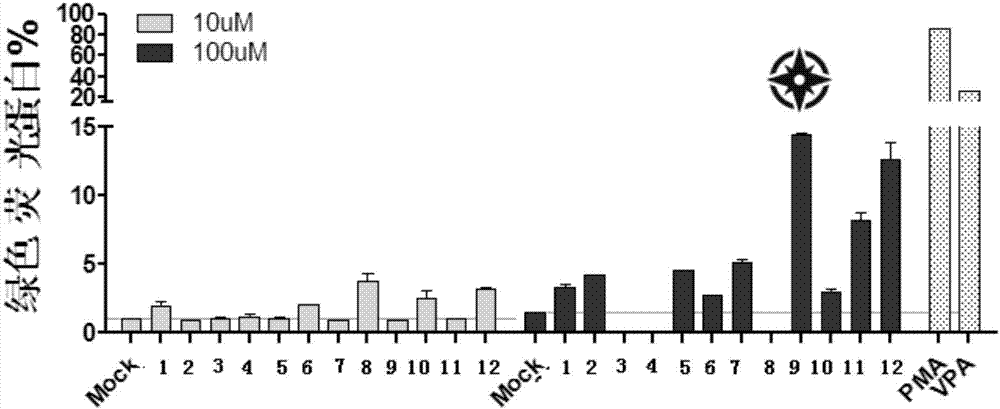
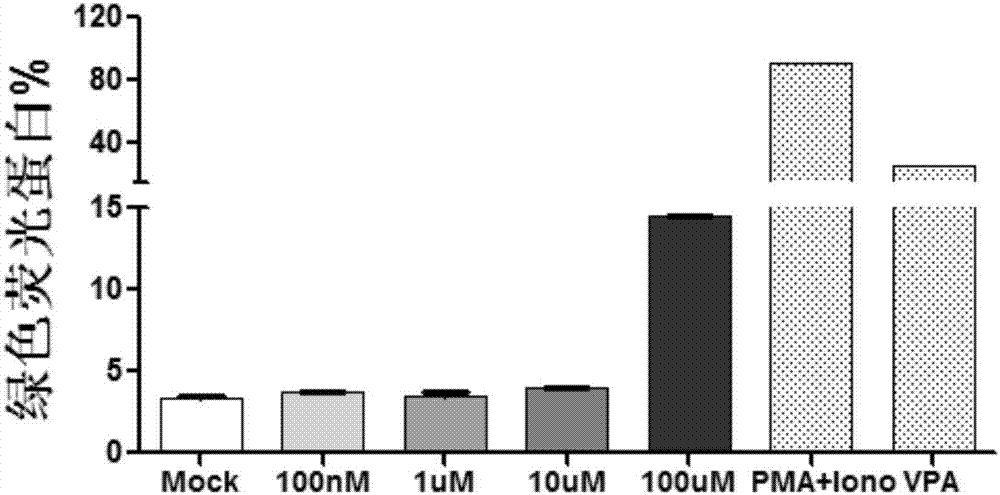
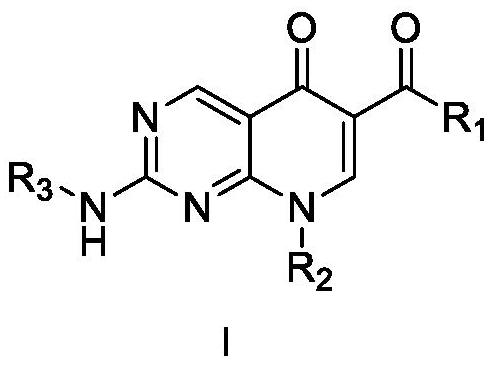
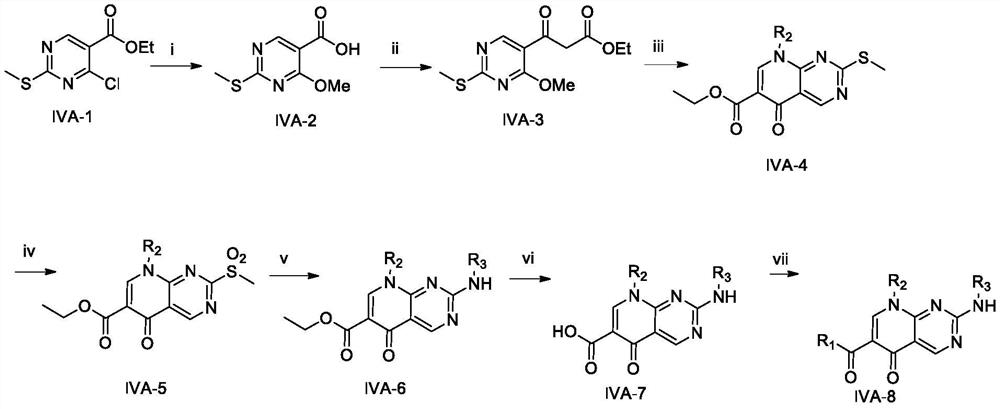
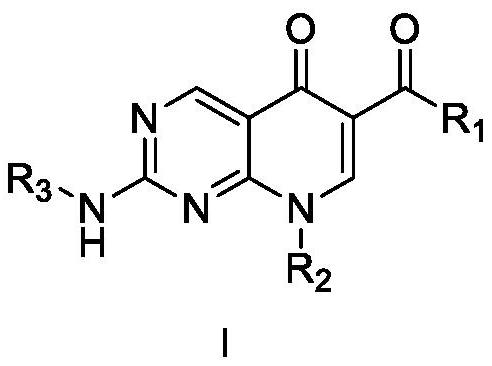
Patents
Literature
74 results about "AIDS drugs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inosine derivatives and production methods therefor
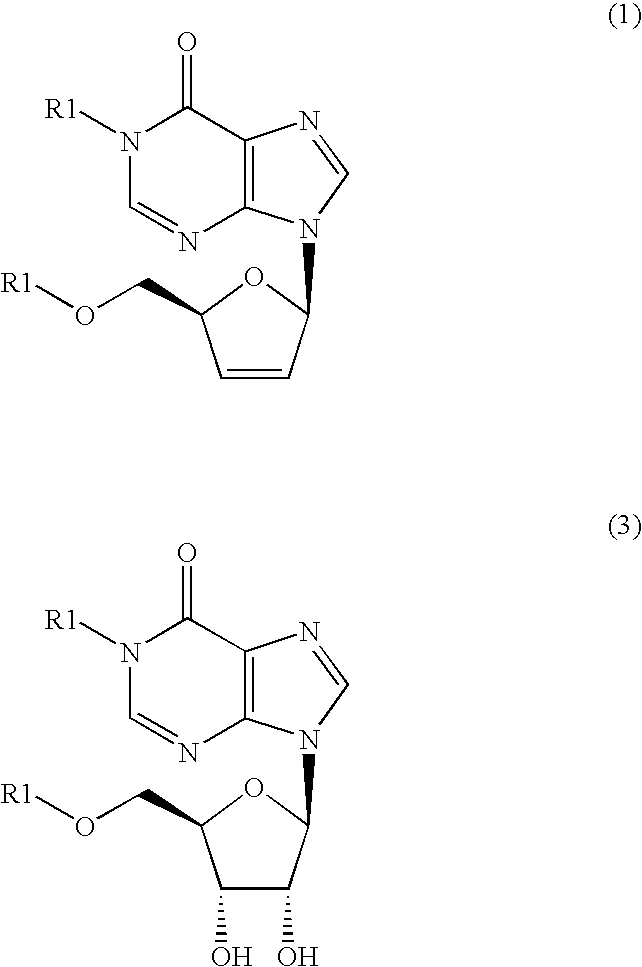
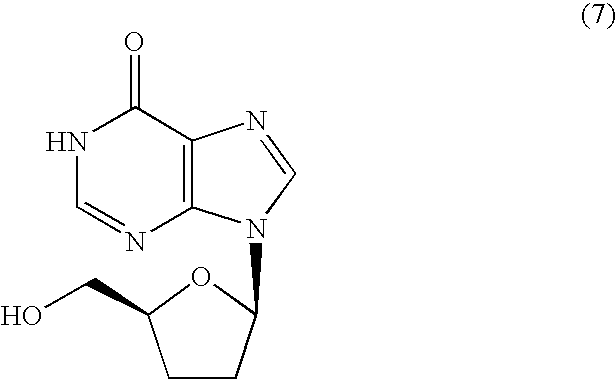
The present invention provides a method for producing an inosine derivative represented by the following general formula (1) including the steps of subjecting an inosine derivative of general formula (3) to dithiocarbonylation and carrying out radical reduction of the obtained compound. According to the present invention there can be produced compounds useful as anti-AIDS drugs on industrial scale. wherein R1 may be the same or different and are each benzyl group, benzhydryl group or trityl group, each of which may have a substituent in general formulas (1) and (3).
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Triazolopyrimidine HIV-1 retrovirus inhibitor and its preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a triazolopyrimidine HIV-1 retrovirus inhibitor and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or prodrug, its preparation method and an application of one compound or a composition of more compounds in the preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Synthetic method of intermediate cyclopropyl acetylene of anti-aids drug efavirenz
InactiveCN103664465AProcess raw materials are easy to getSimple processHydrocarbon from halogen organic compoundsPtru catalystEthyl group
The invention discloses a synthetic method of intermediate cyclopropyl acetylene of an anti-aids drug efavirenz, and relates to the technical field of synthesis of cyclopropyl acetylene. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: reacting in an organic solvent to produce alpha, alpha-ethyl dichloride cyclopropane by taking cyclopropyl methyl ketone as a raw material and taking phosphorus pentachloride as a chlorinating agent; and obtaining the cyclopropyl acetylene by adding the alpha, alpha-ethyl dichloride cyclopropane into strong base aqueous liquor through a phase transfer catalyst. The synthetic method has the beneficial effects that the organic solvent and inorganic strong base are not needed to be adopted, expensive reagents such as the organic solvent and potassium tert-butoxide are avoided; moreover, process raw materials are easily available, process is simple, operation is convenient, cost is lowered and the three wastes are reduced, and therefore, the synthetic method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIUJIANG ZHONGTIAN PHARMA
Drug for resisting HIV latency and applications thereof
The invention relates to a drug for resisting HIV latency and applications thereof, and specifically relates to the HIV latency resisting effect of oxaliplatin and dilazep and the applications of oxaliplatin and dilazep in preparation of drugs for treating AIDS. Oxaliplatin and dilazep both has the HIV latency resisting effect, can be cooperatively used with antiretroviral drugs to eliminate activated cells that has been subjected to latent infection so as to accelerate the elimination of latent virus reservoir, and can be further used to prepared novel anti-AIDS drugs. The invention provides a novel way for radically curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
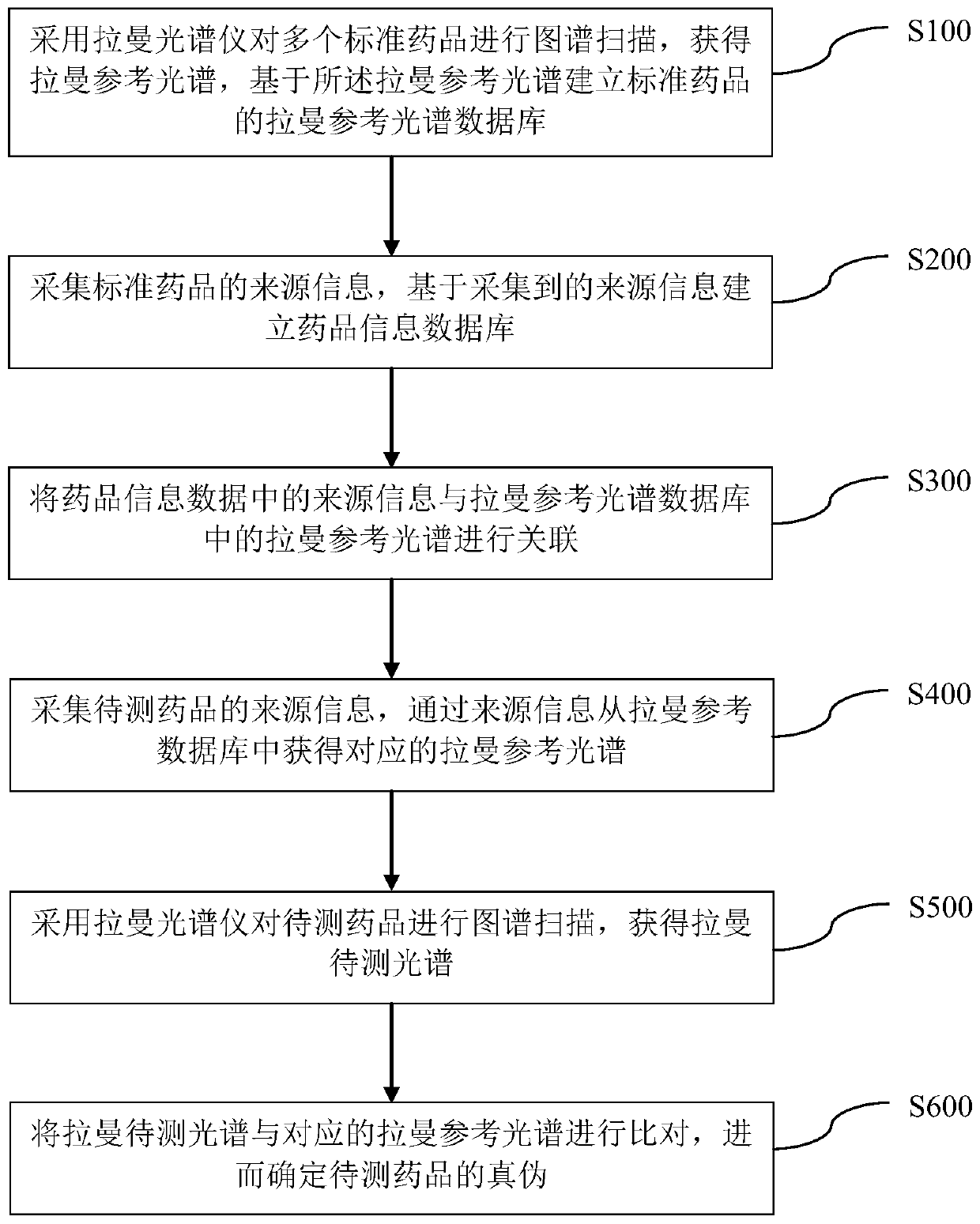
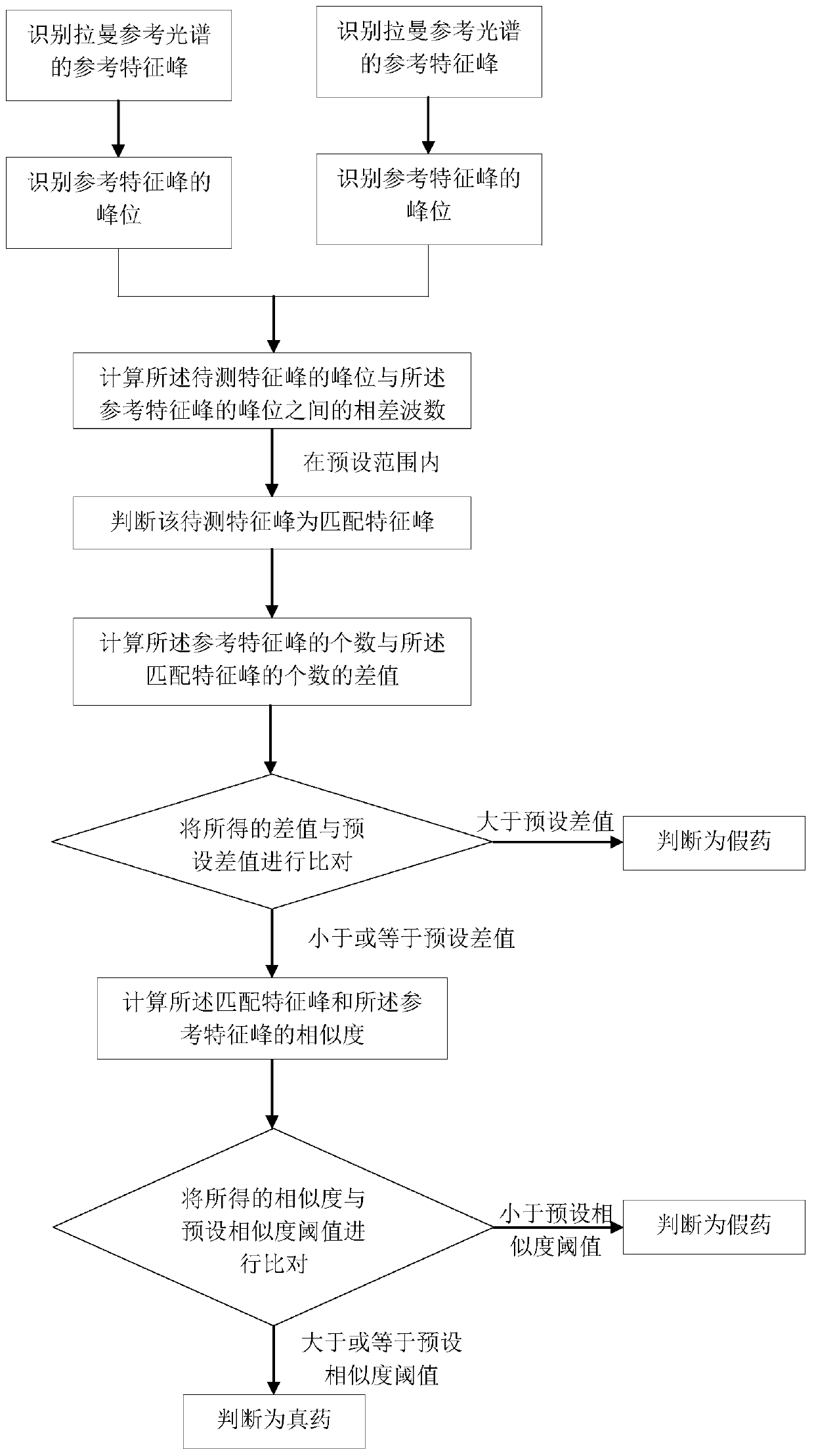
Rapid nondestructive identification method of anti-AIDS drug
PendingCN111141719AFast non-destructive identificationDifferential scienceRaman scatteringAnti aids drugPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a rapid nondestructive identification method of an anti-AIDS drug. According to the method, the Raman reference spectrum database of a standard drug and a drug information database associated with the Raman reference spectrum database are established; a corresponding Raman reference spectrum is obtained according to the source information of a to-be-detected drug, spectrumscanning is performed on the to-be-detected drug by using a Raman spectrometer, so that a Raman to-be-detected spectrum can be obtained; and the Raman to-be-detected spectrum is compared with the corresponding Raman reference spectrum, so that the authenticity of the to-be-detected drug can be determined. The method provided by the invention can scientifically, accurately, simply, conveniently andquickly identify the anti-AIDS drug, will not damage the sample, causes no pollution to the environment, and realizes the rapid nondestructive detection of the drug. The identification method provided by the invention can qualitatively analyze traces and anti-AIDS drugs in order to obtain a stable and reliable analysis result, and is of great significance in the drug research field and the medical health field.
Owner:WUZHOU INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
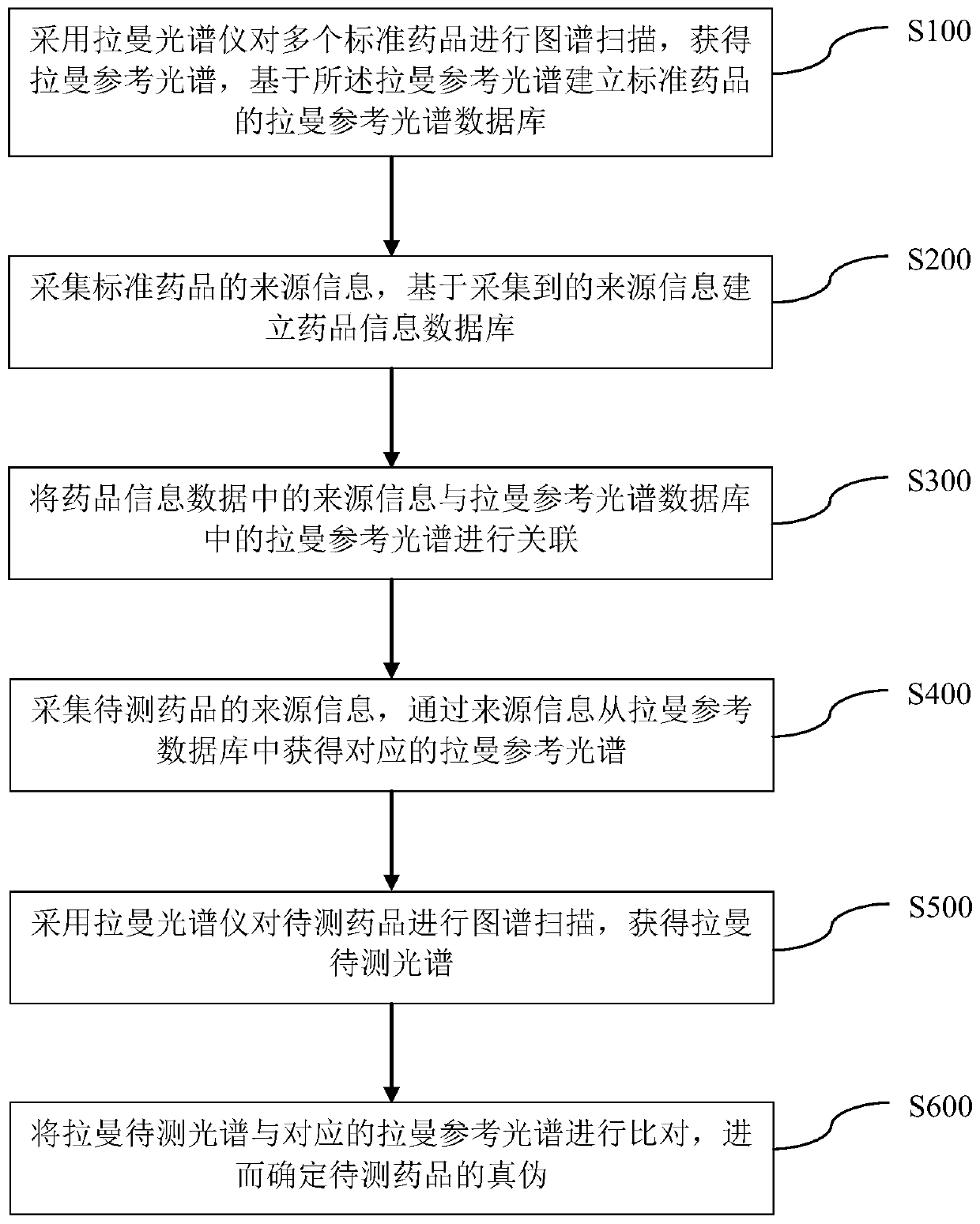
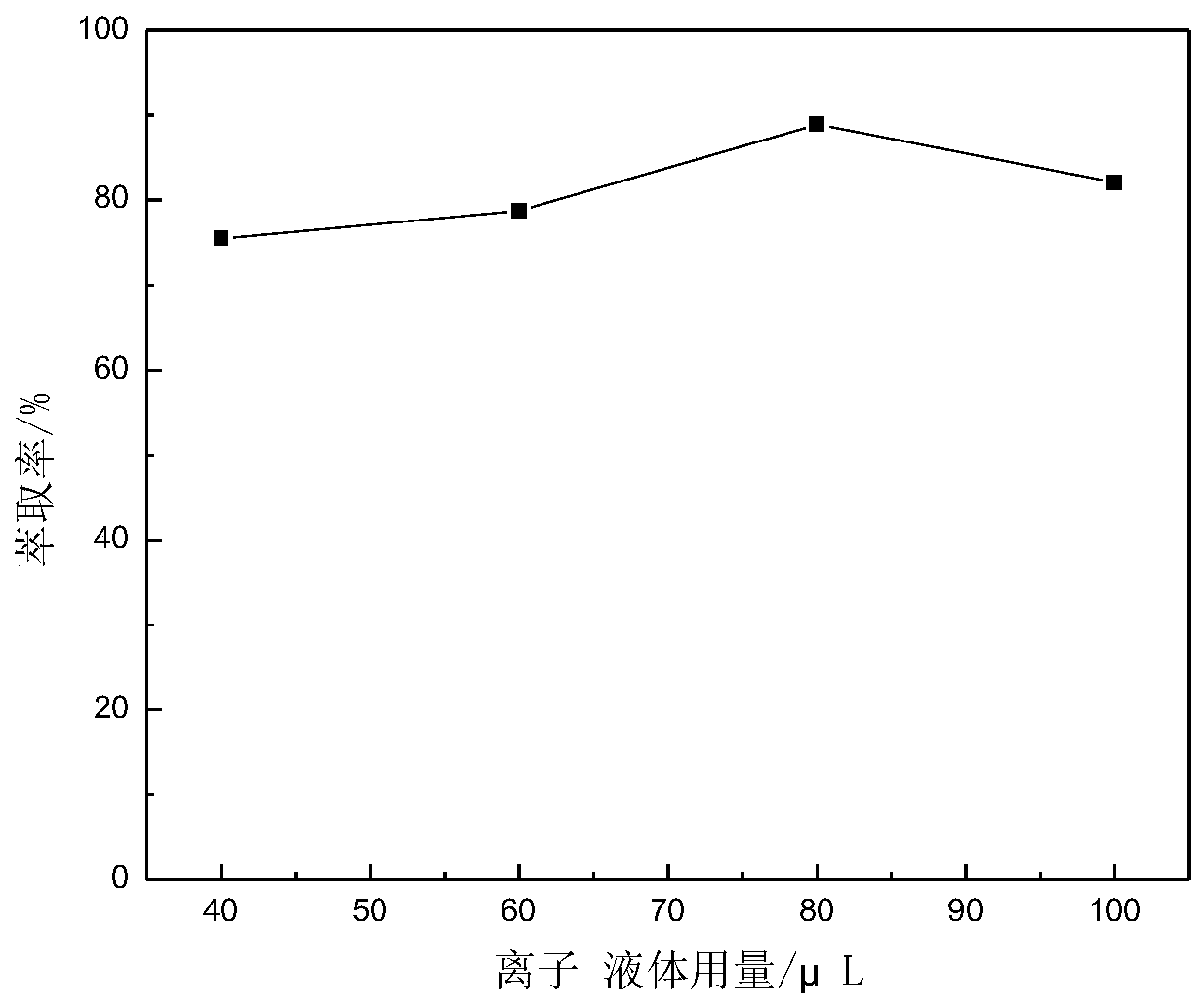
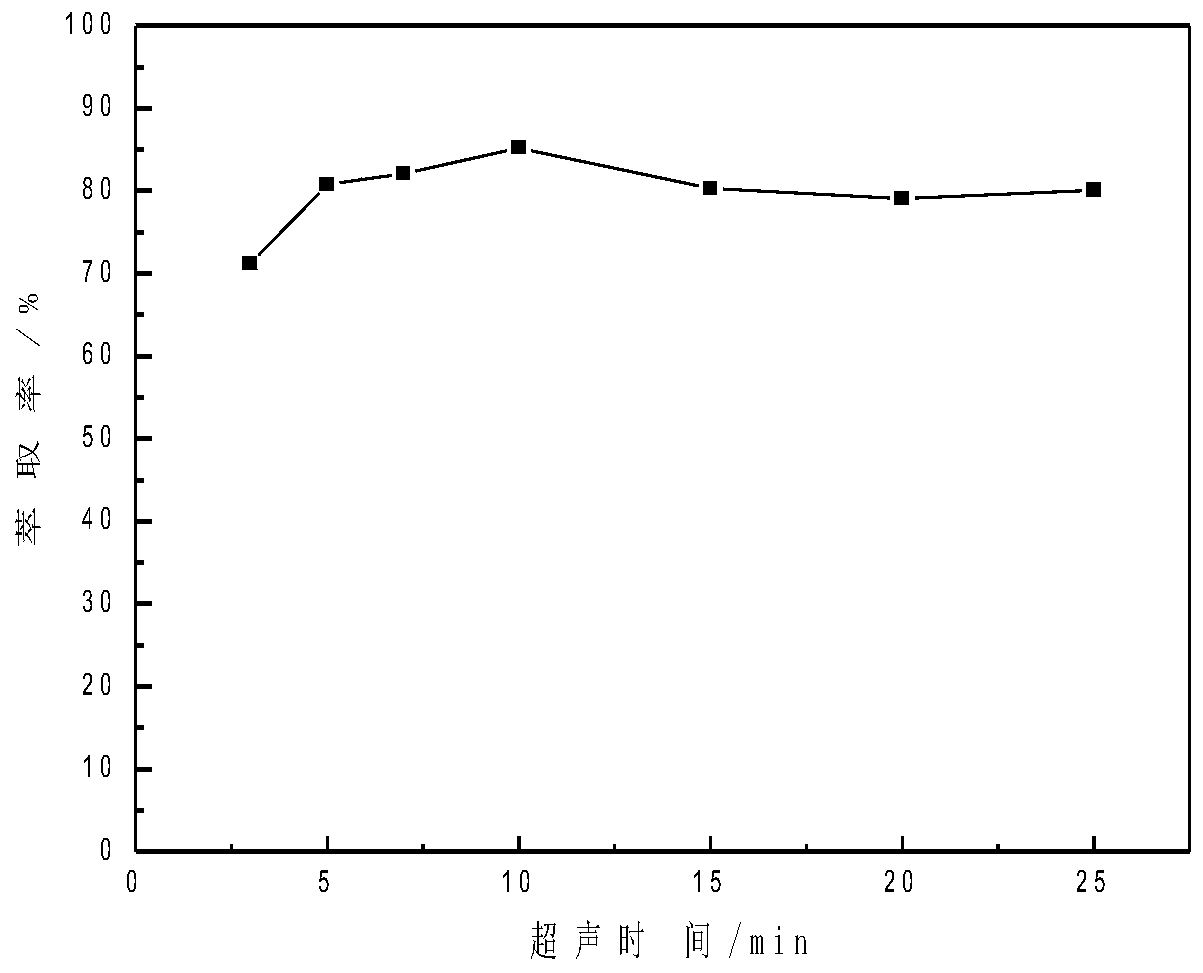
Method for analyzing and detecting new anti-AIDS drug
ActiveCN111504933AStudy bigBig analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium acetateAceticum acidum
The invention relates to a method for analyzing and detecting a new anti-AIDS drug ACC007. The method comprises the following steps of respectively adding 2.0 mL of an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with a pH value of 3.38-5.35, a proper amount of an ACC007 sample solution to be detected and 40-200 [mu] L of an ionic liquid in a centrifuge tube of 10.0 ml ; adding distilled water to scale marks, performing ultrasonic treatment for 3-25min, cooling the centrifuge tube to 0-4 DEG C, keeping the temperature at 0-4 DEG C for 10-20min, centrifuging with a centrifuge for 3-10min, layering, removing an upper-layer aqueous solution, and diluting a lower-layer ionic liquid phase with ethanol to 10mL to obtain a to-be-detected liquid; (2) detecting, taking the to-be-detected liquid obtained in the step (1), and detecting by using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer to obtain absorbance; and (3) calculating the content, substituting the absorbance measured in the step (2) into aworking curve equation to obtain the content of ACC007.
Owner:西安昊洋药业科技有限公司
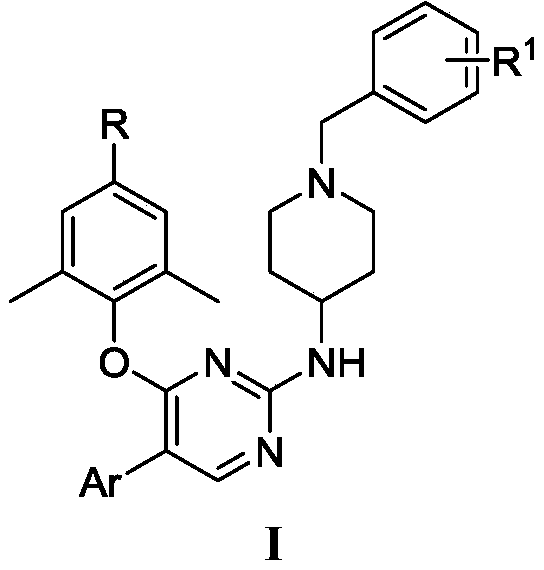
Diarylpyrimidine derivative containing six-membered nitrogen heterocyclic ring as well as preparation method and application of diarylpyrimidine derivative
The invention discloses a diarylpyrimidine compound containing a six-membered nitrogen heterocyclic ring as well as a preparation method and application of the diarylpyrimidine compound. The compoundhas a structure as shown in a general formula I in the specification. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound with the structure shown in the formula I. Activity screening experiments show that the compound provided by the invention has good anti-HIV1 activity, so that the invention also provides application of the compound in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
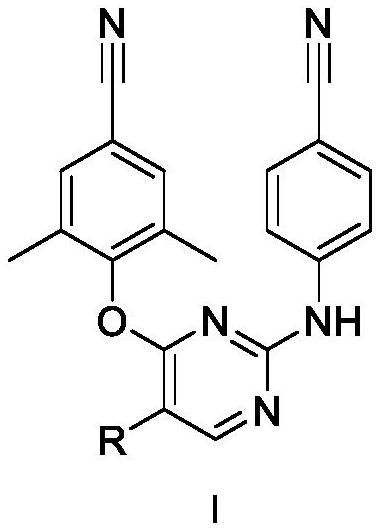
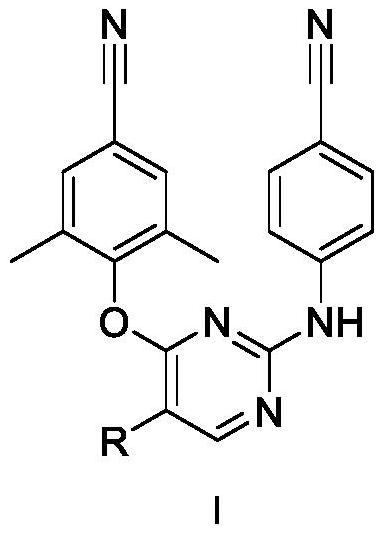
5-site aromatic ring substituted diarylpyrimidine derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a diarylpyrimidine derivative substituted by a 5-site aromatic ring. The diarylpyrimidine derivative has a structure as shown in a general formula I which is described in the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the derivative and application of the derivative as an HIV inhibitor in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
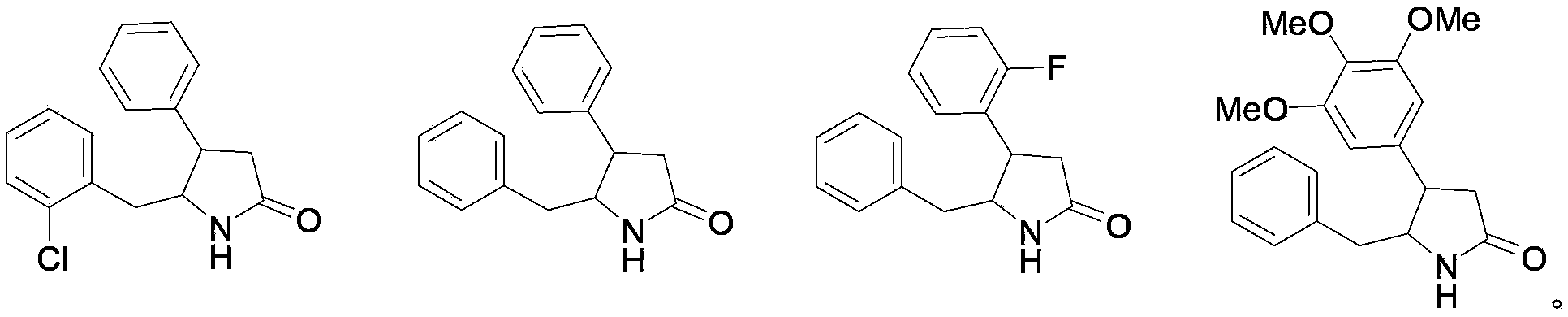
New use of 4, 5-disubstituted-2-pyrrolidone compound
InactiveCN103877080AGood anti-HIV-1 activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsNew medicationsSide effect
The invention discloses application of a 4, 5-disubstituted-2-pyrrolidone compound in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs and preparation of reverse transcriptase inhibitor drugs. Test on the anti-HIV-1 activity of the compound provided by the invention by an international general experimental method finds that the compound has good anti-HIV-1 activity, small toxic and side effect, and has good new drug development prospects.
Owner:THE KEY LAB OF CHEM FOR NATURAL PROD OF GUIZHOU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
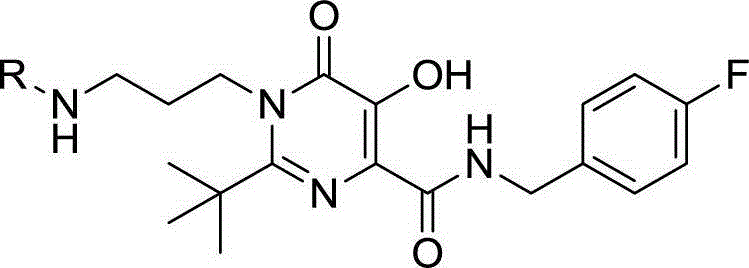
Hydroxy-pyrimidone compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102911124AStrong inhibitory activityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydrogenAnti aids drug
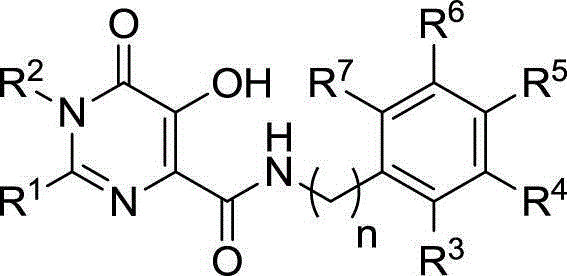
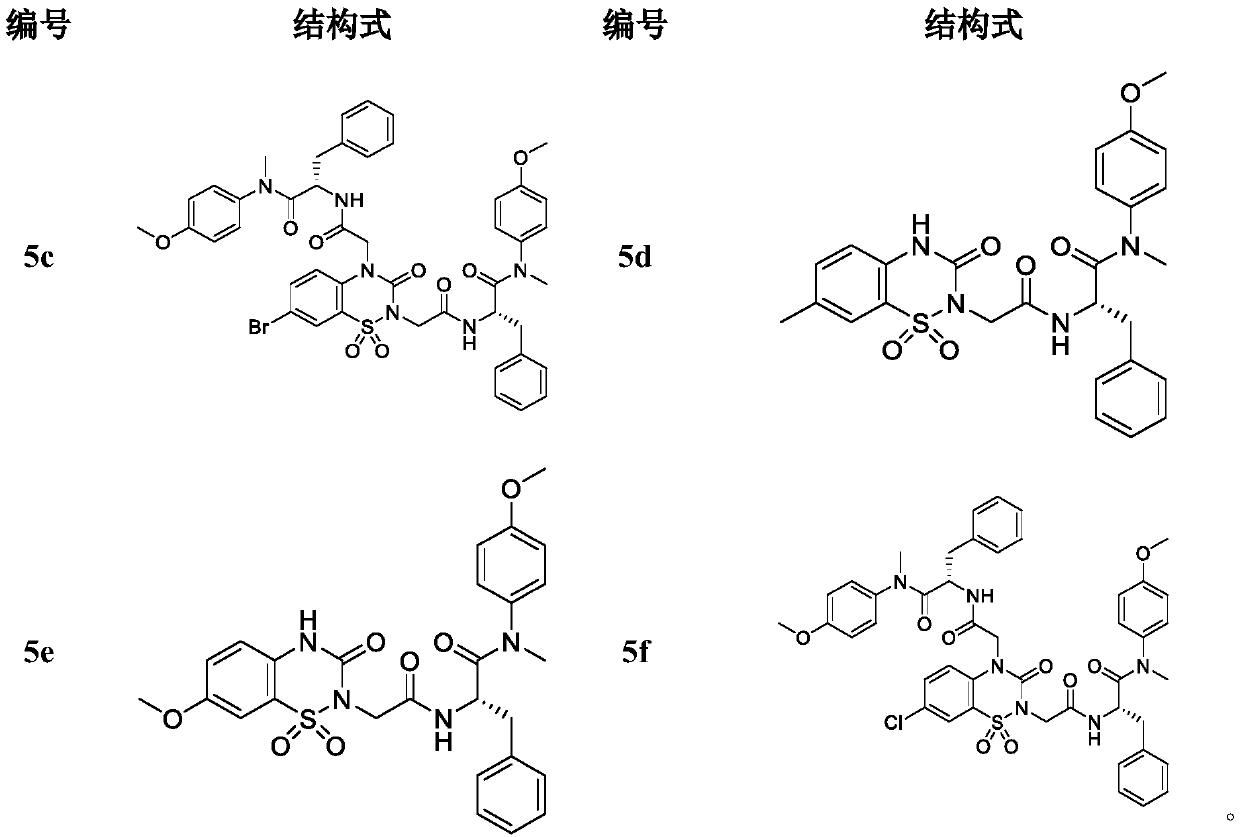
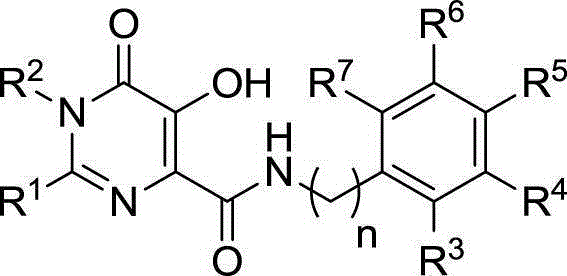
The invention discloses a hydroxy-pyrimidone compound shown as the general formula (I). In the general formula (I), the R1 represents tertiary butyl, phenyl or substituent phenyl and benzyl; the R2 represents hydrogen or substituent propyl, the R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 respectively represent hydrogen, methyl, methoxy, hydroxyl or halogen individually, and the n is equal to one or two. The hydroxy-pyrimidone compound has good HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus) integrase inhibitory activity and HIV-1 antiviral activity, wherein integrase inhibitory activities IC50(inhibitory concentration) of compounds 5a, 5b, 5c, 5d, 5e, 5i, 5n and 5q are all lower than or equal to 1 micromole, compounds 5a, 5h and 5s have high antiviral activity, and EC50(effective concentration) of the compounds 5a,5h and 5s are respectively 1.72 micromoles, 1.91 micromoles and 1.3 micromoles, and accordingly, the hydroxy-pyrimidone compound can be used for preparing anti-AIDs drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
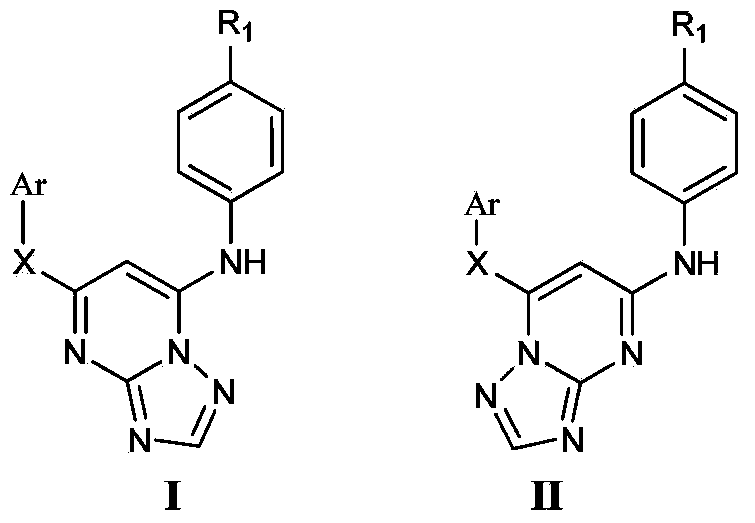
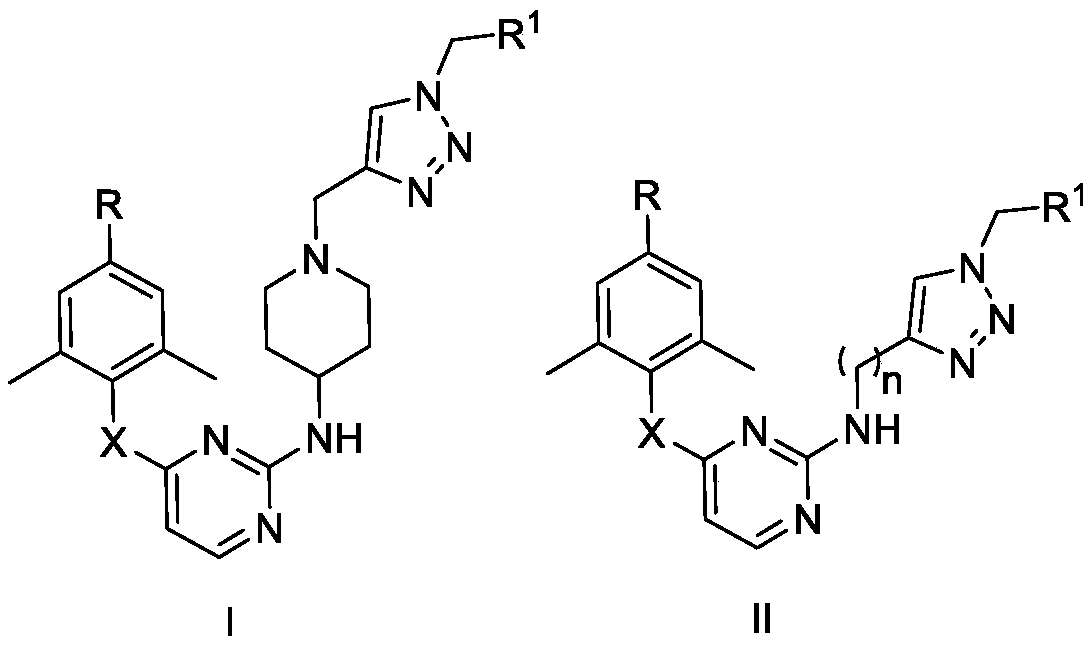
Monoaromatic miazine HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor containing triazole rings and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a monoaromatic miazine HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor containing triazole rings and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has the structure shown as the formula I or II. The invention further relates to a drug composition containing the compound of the formula I or II. The compound and the application of the composition containing one or more compounds of this kind in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs are further provided.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
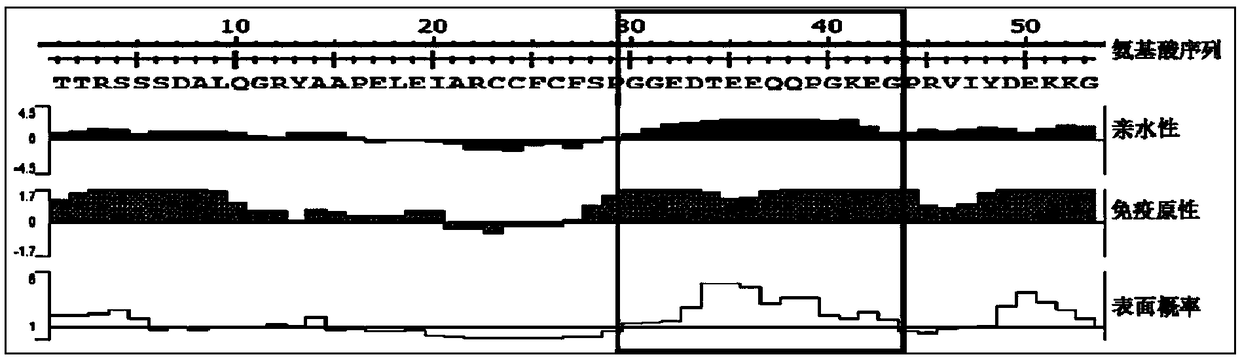
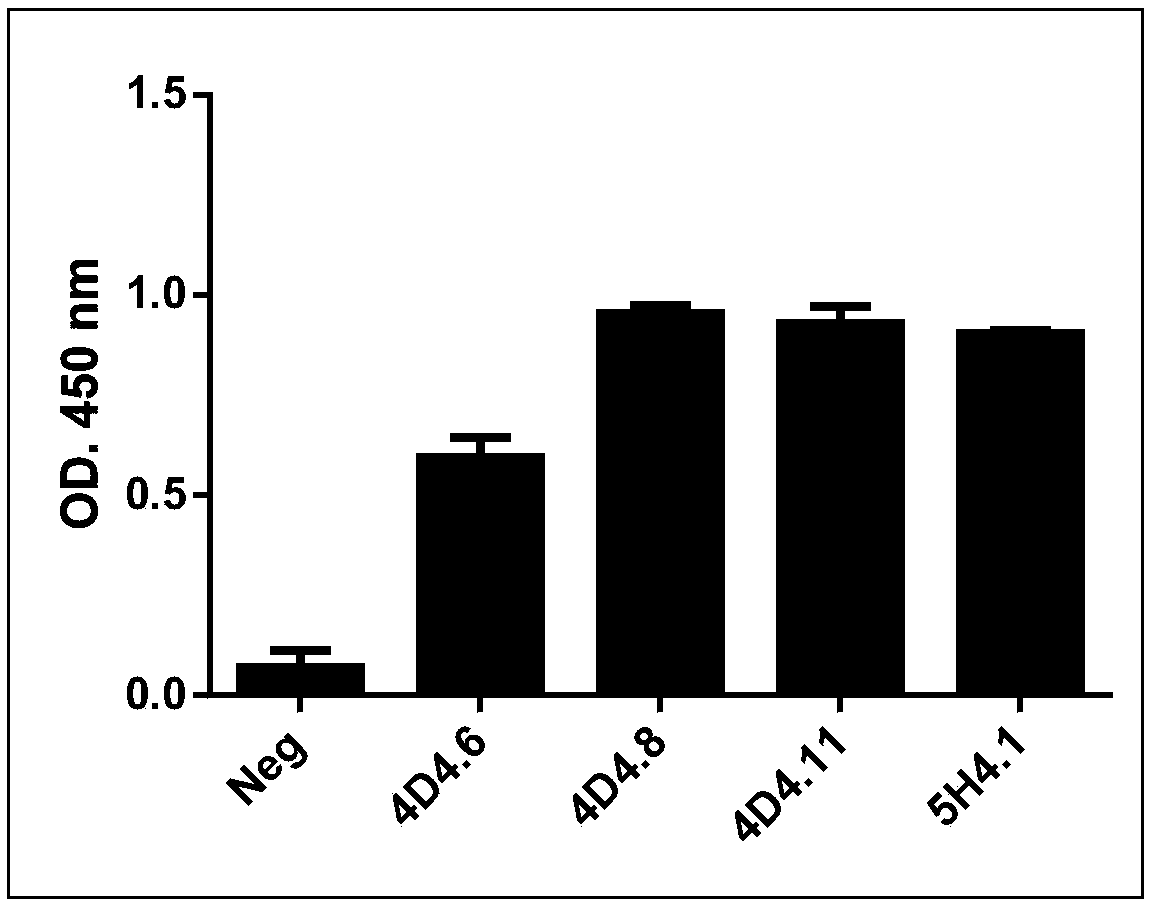
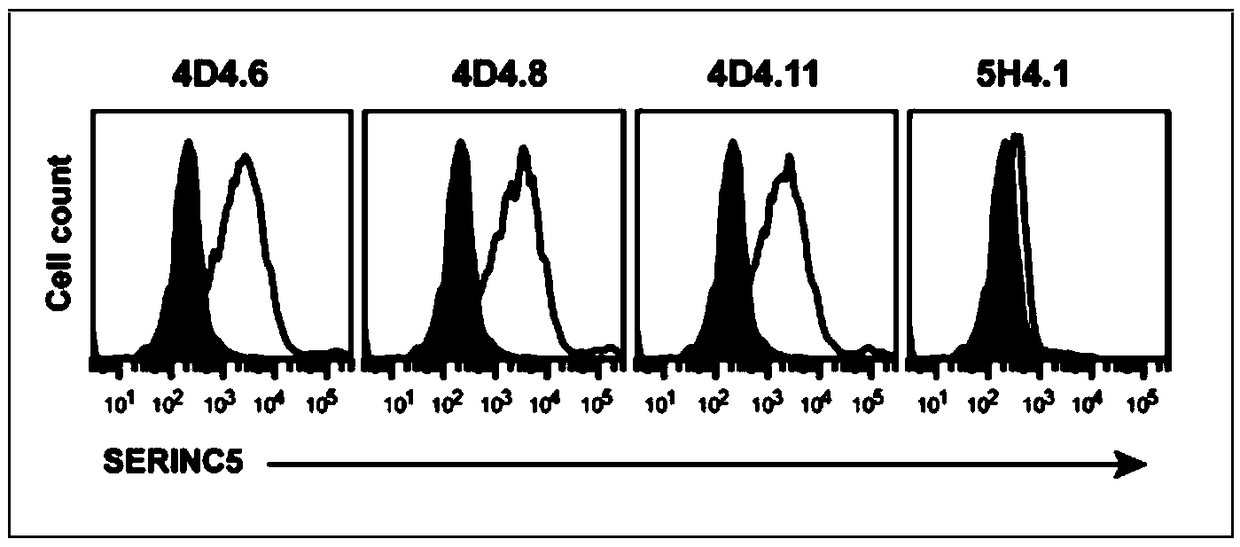
Anti-SERINC5 antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN108929382APromote research progressBiologically activeImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHybrid cell preparationHIV ProteinsAntiviral mechanism
The invention relates to an anti-SERINC5 antibody and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an anti-SERINC5 antibody and functional fragment, a nucleotide, a carrier, a monoclonalantibody, a kit and application thereof in detection of SERINC5 protein or polypeptide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:9. At the same time, the invention also provides a preparation method of the monoclonalantibody and a preparation method of a monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line. The antibody and functional fragment prepared by the method provided by the invention can be effectively used for reaction with SERINC5 protein, like flow cytometry detection of SERINC5 molecules on cell surfaces and SERINC5 expressed in combination with cells, study of virus amplification mechanism, etc., thus providing an effective research tool for studying the antiviral mechanism of SERINC5, being conducive to accelerating the research progress in the field, and providing a new idea for further development ofnovel HIV protein Nef targeted AIDS drugs.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Application of a compound in preparing anti-virus medicament
InactiveCN101108186AInhibition of replicationSuitable for life-long medication needsAntiviralsPill deliveryChemical industryAnti virus
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical industry, in particular to a preparation method and application of micromolecule compound with HIV resisting activity. CyPA is able to combine with the Gag polymer protein in HIV-1. Silence or inhibit the activity of CypA with RNAi technology and disturb the replication of virus. The micromolecule compound in the invention refers to a CyPA inhibitor that has the effect of resisting HIV-1 virus. Besides, as the micromolecule compound is designed while aiming at cellular target, the invention is not easy to develop drug resistance, thus meeting the demands of lifetime medication for AIDS patients. Therefore, the micromolecule compound in the invention, which can be developed as a new type anti-AIDS drug, provides a new means for treating and curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
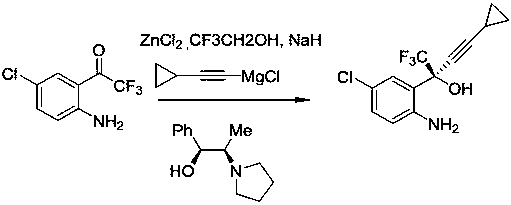
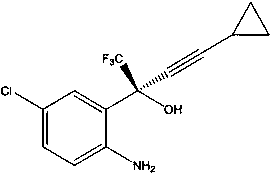
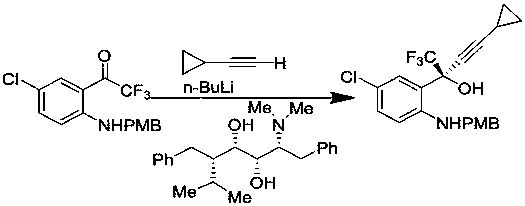
Method for asymmetric synthesis of anti-Aids drug, namely efavirenz key intermediate
InactiveCN110746312AHigh yieldHigh ee valueOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPharmacologyEfavirenz
The invention discloses a method for asymmetric synthesis of an anti-Aids drug, namely an efavirenz key intermediate. The method comprises the following steps that in an organic solvent, fluoride, anorganic ligand (9S)-6'-methoxy-deoxidized cinchonine-9-ol and cyclopropyl acetylene are evenly stirred, an organic zinc solution is slowly added at the temperature of 15-25 DEG C, after constant-temperature stirring is conducted for 3-5 hours, tetraisopropyl titanate is added, stirring is continued to be conducted for 2-3 hours, then the temperature is decreased to minus 20 DEG C to 0 DEG C, 5-chloro-2-amino-trifluorobenzophenone is added, a mixture is stirred at the temperature of minus 20 DEG C to 0 DEG C for 5-12 hours, after a reaction is completed, a proton source is added for a quenchingreaction, then a certain amount of activated carbon is added, a mixture is stirred for 0.5 hour and filtered, an organic phase and a water phase are separated in an extraction mode, the organic phaseis washed, dried and subjected to vacuum concentration, and after purification, the efavirenz key intermediate is obtained. The technological process is short, the technological condition is mild, operation is easy, environmental protection is achieved, the cost is low, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:湖北随州双星生物科技有限公司 +1
2,4,5-trisubstituted pyrimidine compound taking HIV-1 reverse transcriptase as target spot as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111285859AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptasePharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a 2,4,5-trisubstituted pyrimidine compound taking HIV-1 reverse transcriptase as a target spot as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has a structure as shown in a general formula I in the specification. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound with the structure shown in the formula I. Activity screening experiments show that the compound provided by the invention has good anti-HIV-1 activity, so that the invention also provides application of the compound in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Application of a compound in preparing anti-virus medicament
InactiveCN100502879CInhibition of replicationSuitable for life-long medication needsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsChemical industryPolymer
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical industry, in particular to a preparation method and application of micromolecule compound with HIV resisting activity. CyPA is able to combine with the Gag polymer protein in HIV-1. Silence or inhibit the activity of CypA with RNAi technology and disturb the replication of virus. The micromolecule compound in the invention refers to a CyPA inhibitor that has the effect of resisting HIV-1 virus. Besides, as the micromolecule compound is designed while aiming at cellular target, the invention is not easy to develop drug resistance, thus meeting the demands of lifetime medication for AIDS patients. Therefore, the micromolecule compound in the invention, which can be developed as a new type anti-AIDS drug, provides a new means for treating and curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
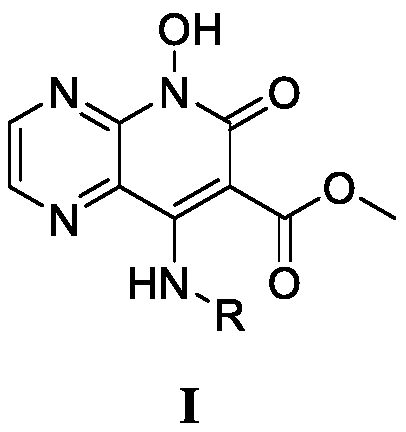
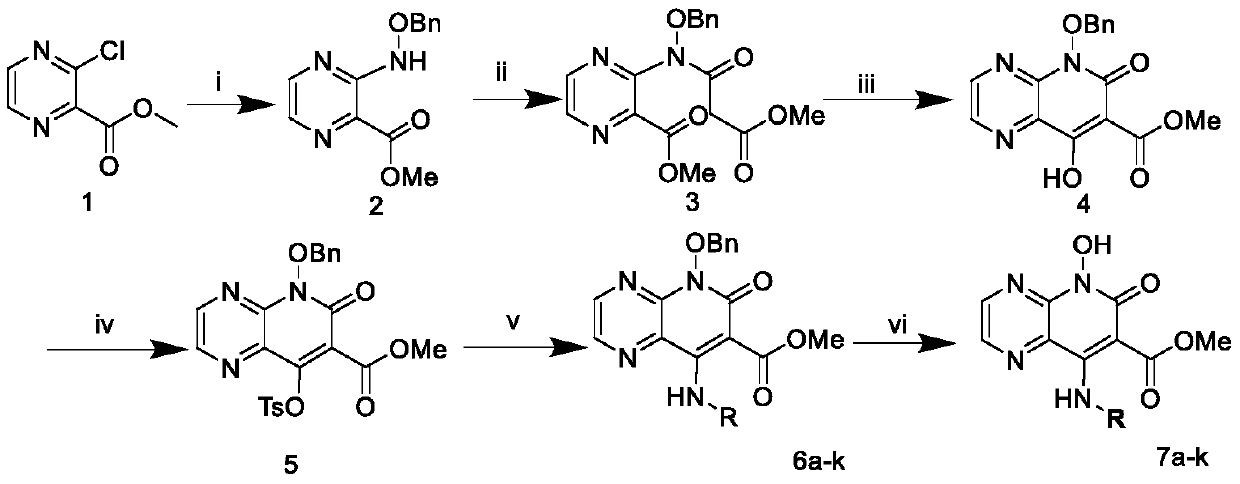
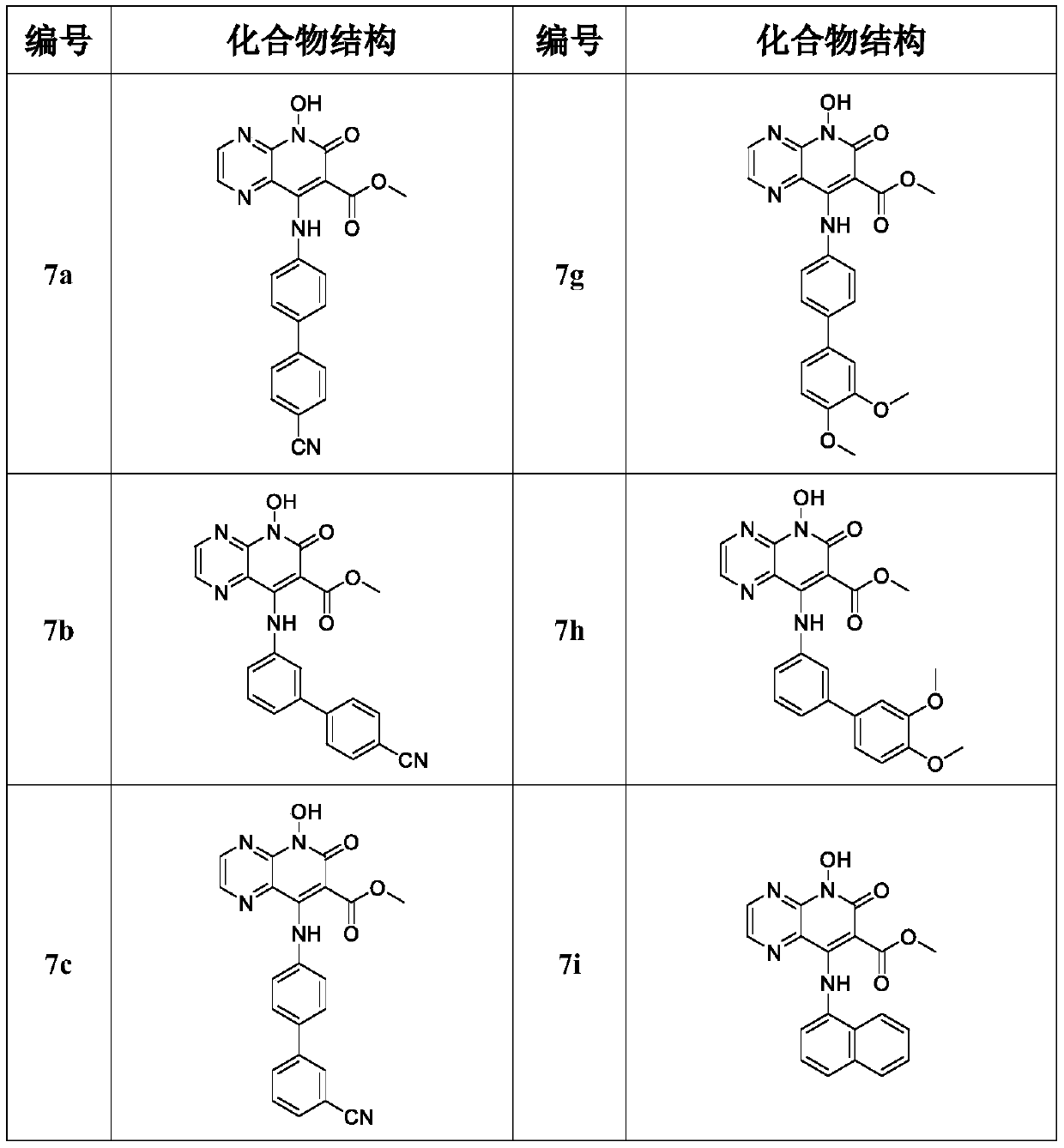
8-Amino-7-formic acid methyl ester-pyrazine-pyridone derivative and its preparation method and application
The invention provides 8-amino-7-methyl formate-pyrazine pyridone derivatives and a preparation method and use thereof. The 8-amino-7-methyl formate-pyrazine pyridone derivatives have a structure shown in the following general formula I, wherein R is 4'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl, 4'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl, 3'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl, 4-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl, 3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl, 3',4'-dimethoxy- 1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl, 3',4'-dimethoxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl, naphthalene-1-yl and [1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl. The invention also relates to a process for the preparation of such derivatives and their use as HIV inhibitors in the preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
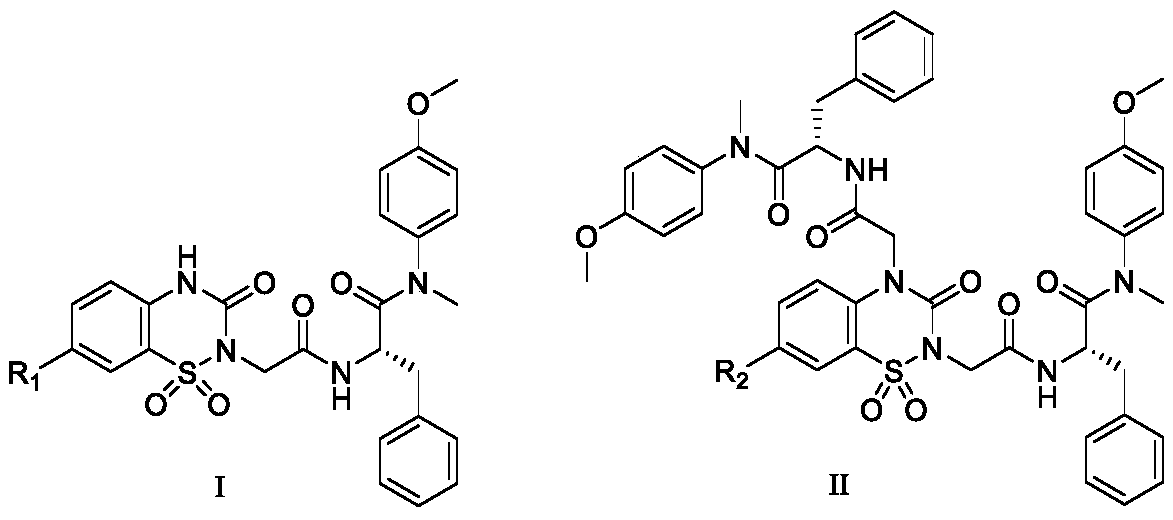
Phenylalanine derivative containing benzothiadiazine-3-ketone 1,1-dioxide and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a phenylalanine derivative containing benzothiadiazine-3-ketone 1,1-dioxide and a preparation method and an application thereof. The derivative has a structure as shown in the following general formula I. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the derivative and the application of the derivative as an HIV-1 inhibitor in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
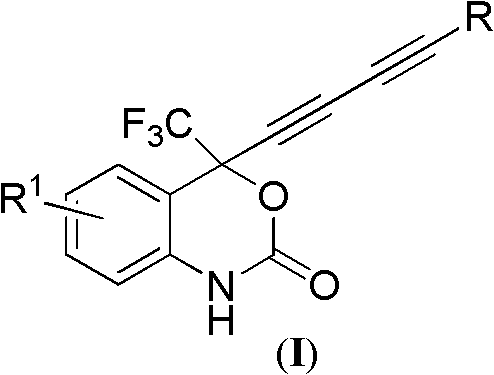
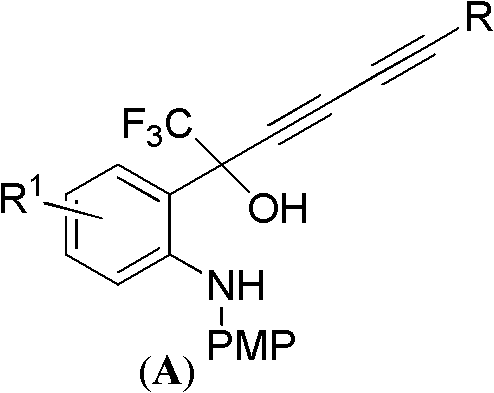
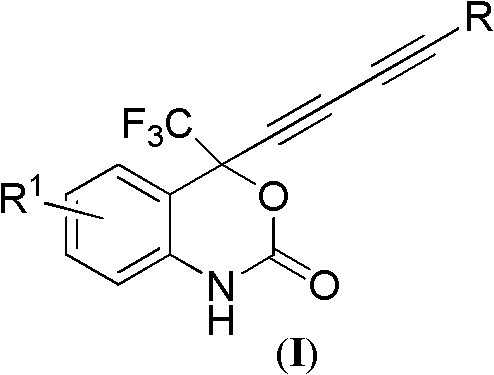
4-(substituted-1,3-dialkynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzo-1,4-dihydroxazole-2-one compounds and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102127030AThe synthesis method is simple and feasibleHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention relates to 4-(substituted-1,3-dialkynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzo-1,4-dihydroxazole-2-one compounds and a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method is as follows: substituted-2-(2-(4-methoxybenzylamino)phenyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-3,5-hexyne-2-ol reacts with phosgene in organic solvent at the temperature ranging from -20 DEG C to 30 DEG C under the action of alkali; after the reaction, the pressure is reduced to remove solvent, and then the obtained product reacts with ammonium ceric nitrate in organic solvent to obtain the target compounds. In the method, bialkynyl group is introduced in 4-trifluoromethylbenzo-1,4-dihydroxazole-2-one, the synthesis method is simple and practical and has high yield; and the compounds are used to prepare anti-HIV drugs oranti-HBV drugs or anti-HCV drugs and have better application value. The anti-HIV drugs are anti-AIDS drugs; the anti-HBV drugs are anti-hepatitis B drugs; and the anti-HCV drugs are anti-hepatitis C drugs. The structural general formula of the compounds of the invention is shown as below.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
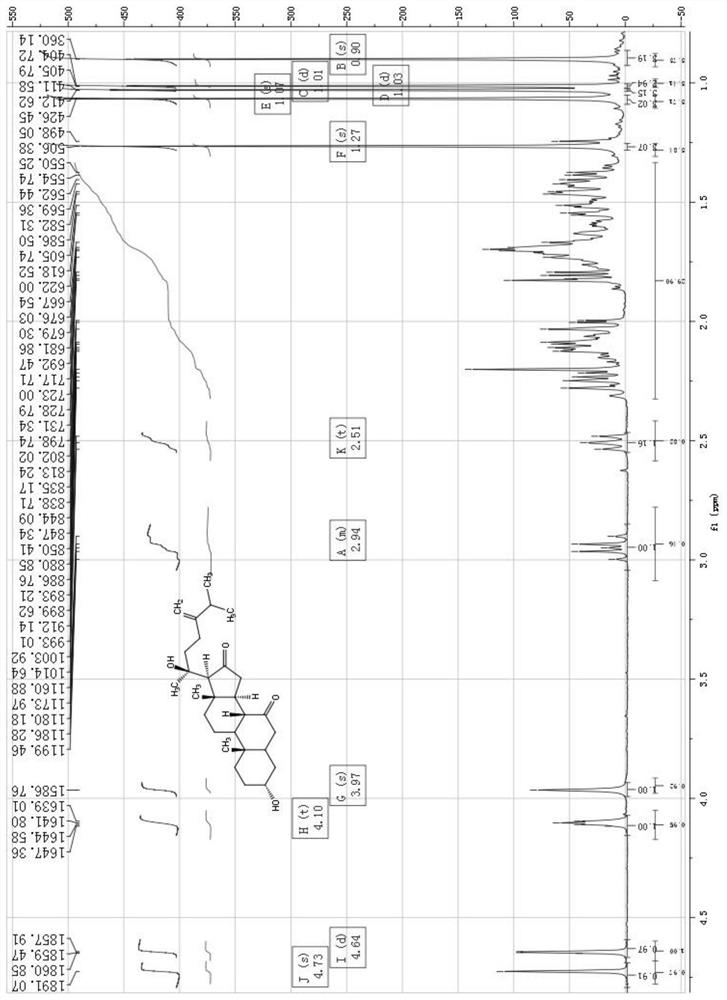
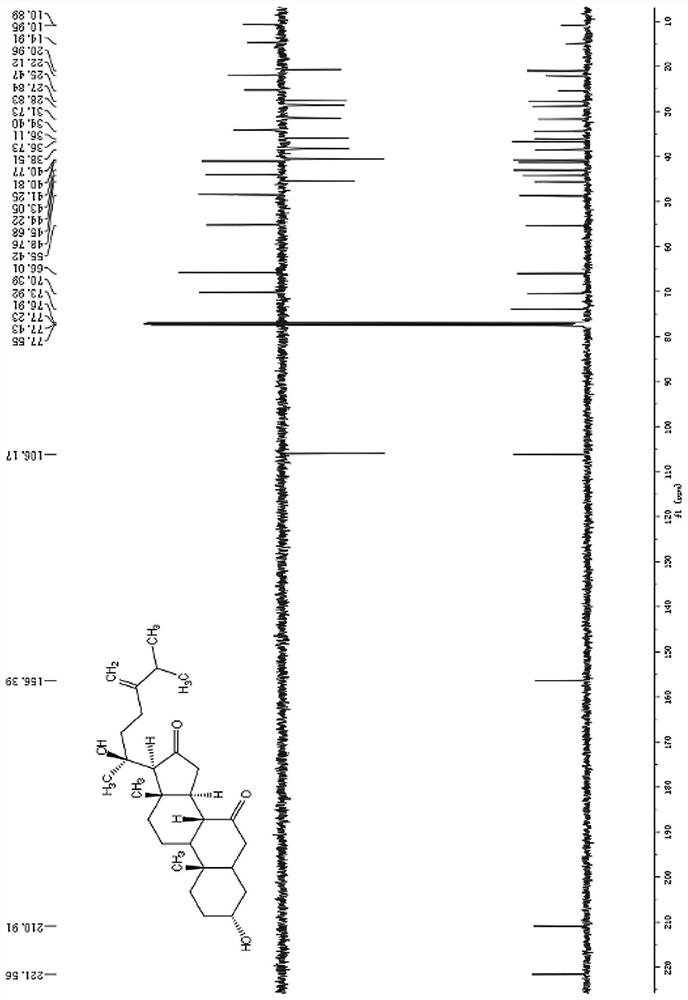
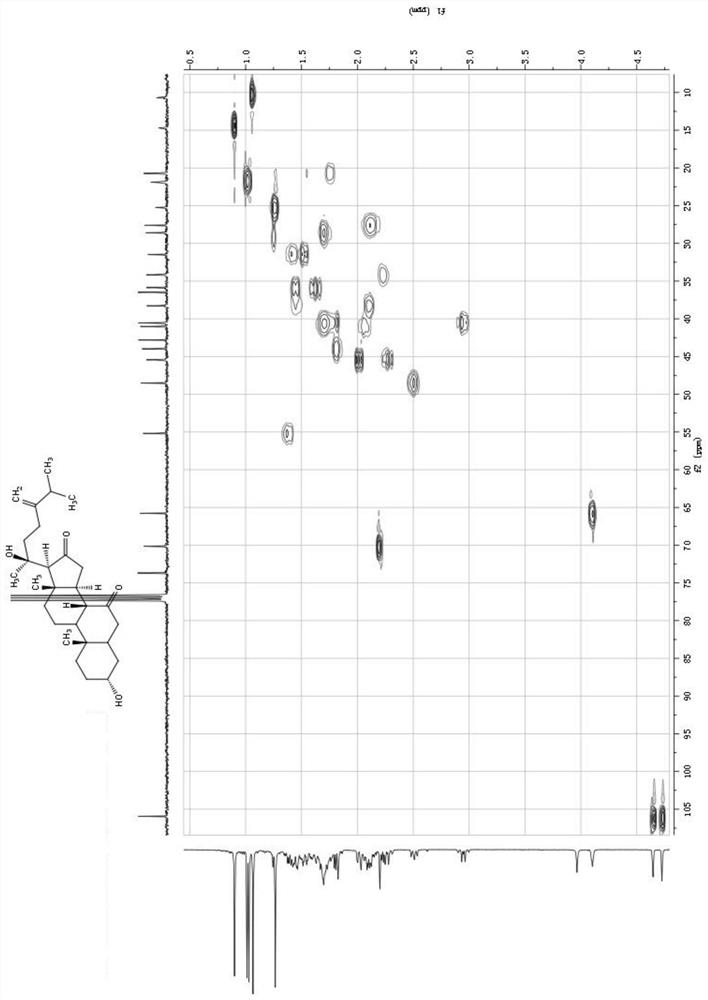
A class of ergostane steroid compound, its preparation method and use
The invention relates to the technical field of anti-aids drugs and an ergostane-type steroid compound and a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to an ergostane-type steroid compound selected from a following compound which is shown in the description and a preparation method and application thereof in preparation of anti-aids drugs. The ergostane-type steroid compound has aremarkable anti-aids effect. At the same time, it is found in a research that there is a certain structure-function relationship between the compound and activity, and a basis is provided for furtherstructural optimization. The compound has a novel chemical structure, remarkable biological activity and a great development prospect and is expected to be developed into a new anti-aids drug withoutdrug resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An antibody against serinc5 and its application
ActiveCN108929382BPromote research progressBiologically activeImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureHIV ProteinsAntiviral mechanism
The invention relates to an anti-SERINC5 antibody and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an anti-SERINC5 antibody and functional fragment, a nucleotide, a carrier, a monoclonalantibody, a kit and application thereof in detection of SERINC5 protein or polypeptide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:9. At the same time, the invention also provides a preparation method of the monoclonalantibody and a preparation method of a monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line. The antibody and functional fragment prepared by the method provided by the invention can be effectively used for reaction with SERINC5 protein, like flow cytometry detection of SERINC5 molecules on cell surfaces and SERINC5 expressed in combination with cells, study of virus amplification mechanism, etc., thus providing an effective research tool for studying the antiviral mechanism of SERINC5, being conducive to accelerating the research progress in the field, and providing a new idea for further development ofnovel HIV protein Nef targeted AIDS drugs.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
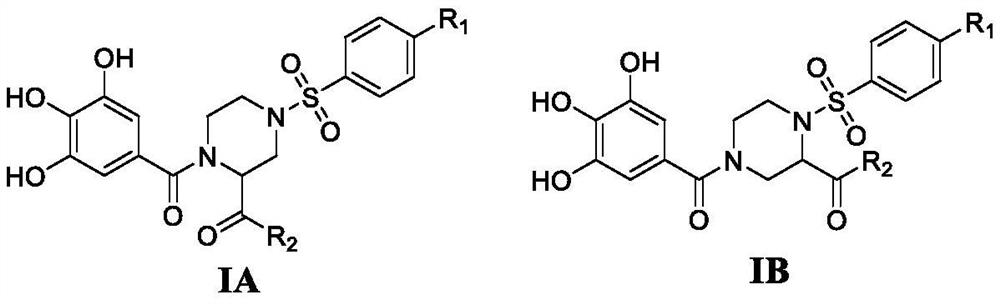
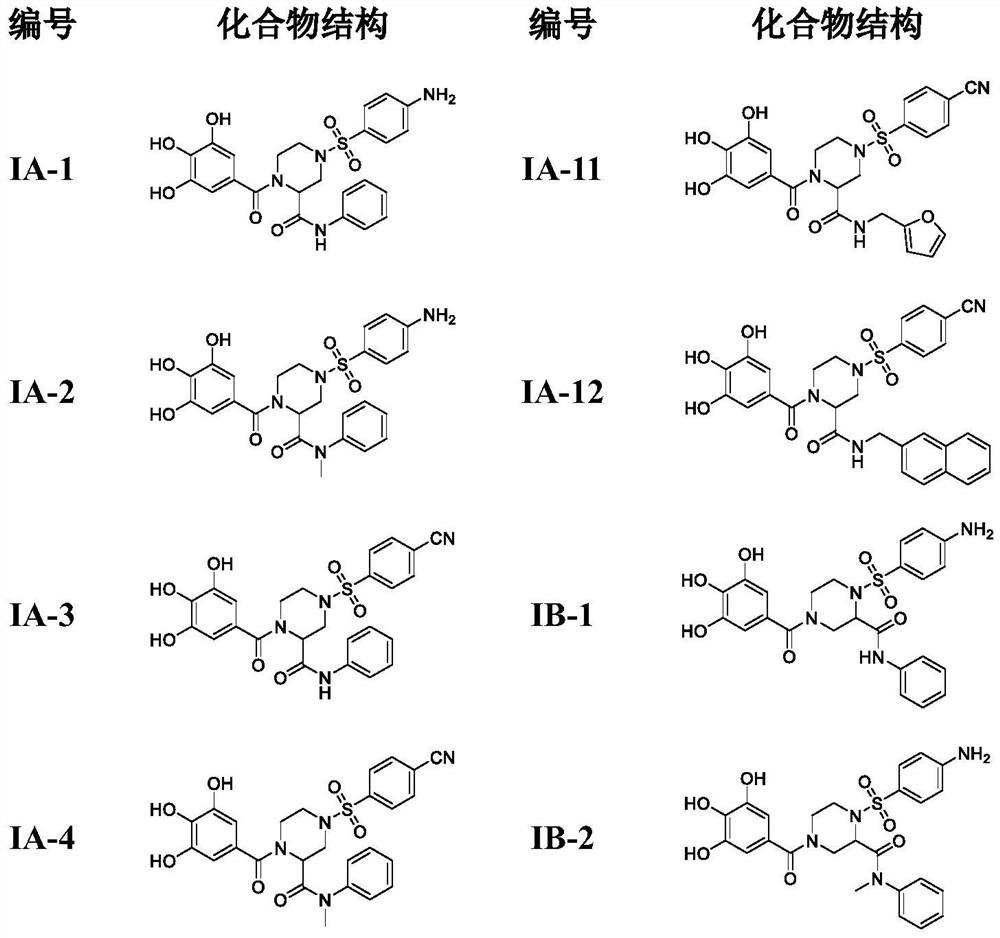
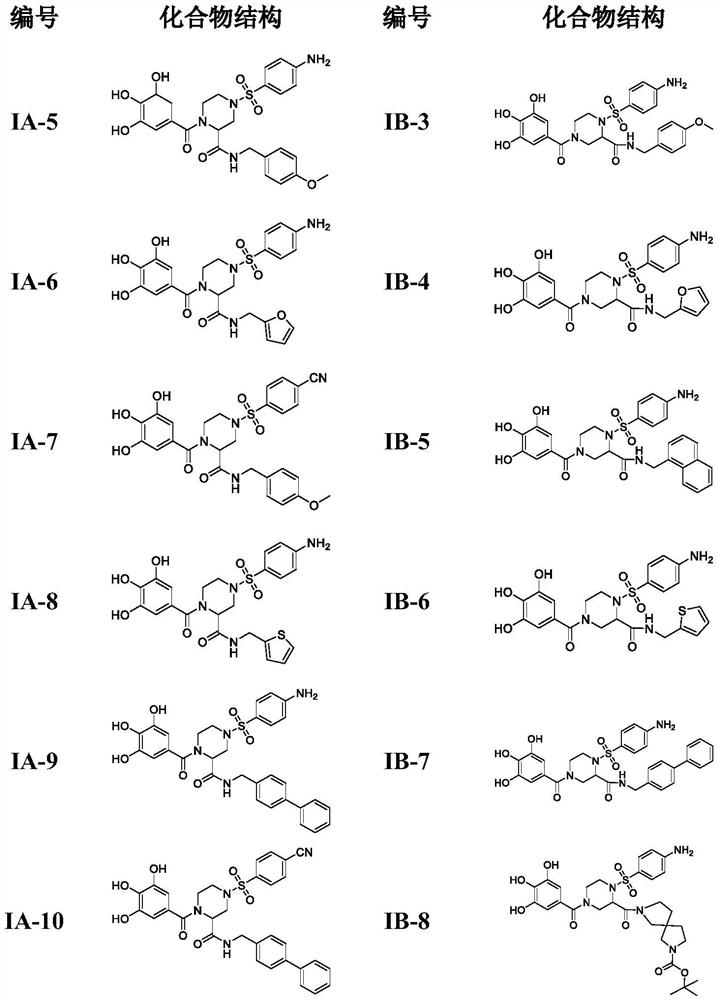
4-phenylsulfonyl-1-trihydroxybenzoylpiperazine-2-carboxamide derivative and its preparation method and application
The present invention provides a 4-phenylsulfonyl-1-trihydroxybenzoylpiperazine-2-carboxamide derivative, which has the structure shown in the following general formula IA or IB. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the derivative and its application as an HIV inhibitor in the preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Artificially synthesized gene of encoding thymidine phosphorylase protein, and application of gene
ActiveCN107287221AIncrease enzyme activityReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThymidine Phosphorylase DeficiencyPhosphorylation
The invention relates to an artificially synthesized gene of encoding thymidine phosphorylase protein, and application of the gene, belonging to the field of biological engineering. By using a gene sequence optimized by the invention to express a thymidine phosphorylase mutant, the total enzyme activity of unit bacteria can be effectively increased, and the production cost of anti-AIDS drug intermediate beta-thymidine can be effectively lowered. The gene can be produced only in a common fermentation workshop (such as an amino acid or a vitamin production workshop) without needing to purchase special equipment, thus being easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:NANJING NUOYUN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Pyranoindole compound as well as preparation method and application thereof in preparation of anti-aids drugs
InactiveCN107286170AEasy to prepareEase of industrial productionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTherapy HIVAnti aids drug
The invention provides a pyranoindole compound as well as a preparation method and an application thereof in preparation of anti-aids drugs. The pyranoindole compound has a structure as shown in a formula I. The pyranoindole compound, or a pharmacologically acceptable salt, isomer, raceme, prodrug cocrystal compound, aquo-complex or solvate thereof is capable of effectively activating an HIV virus repository, can be used for treating aids, and is simple in preparation method and wide in application prospect, and industrialized production is easy to implement.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
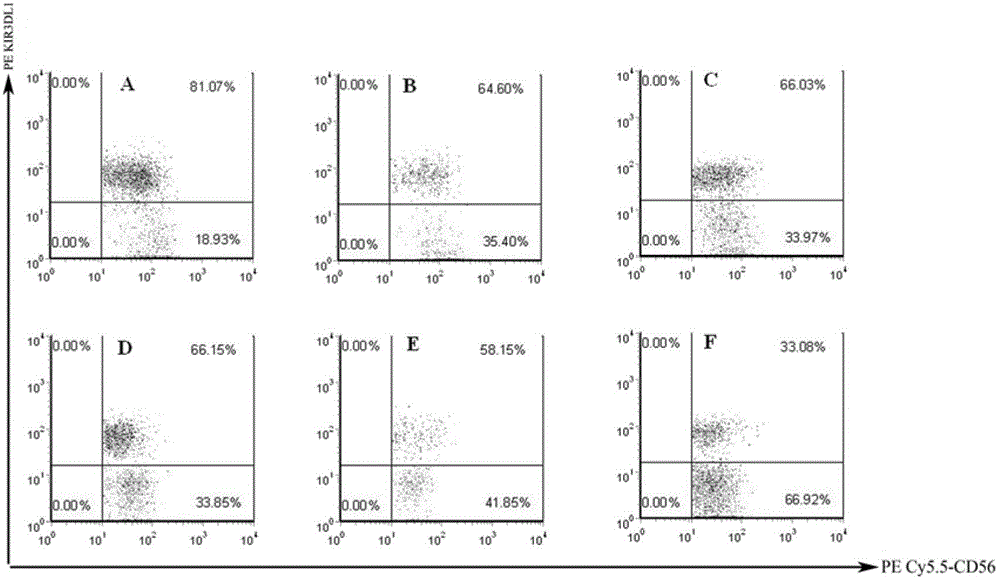
Small ribonucleic acid interference molecule for specifically inhibiting NK (Natural Killer) cell receptor KIR3DL1 and application of small ribonucleic acid interference molecule
InactiveCN102911940ASmall side effectsHigh activityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsKIR3DL1Natural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention discloses a small ribonucleic acid interference molecule for specifically inhibiting an NK (Natural Killer) cell receptor KIR3DL1 and an application of the small ribonucleic acid interference molecule. The genbank login number of the mRNA of the targeted KIR3DL1 of the small ribonucleic acid interference molecule for specifically inhibiting the NK cell receptor KIR3DL1 is NM_013289. A large amount of experiments show that the siRNA fragment can remarkably inhibit the expression of the receptor KIR3DL1 of an NK cell membrane, and the siRNA subjected to various chemical modifications has the same effect of inhibiting the expression of the receptor KIR3DL1. The expression level of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha cell factors in an NK cell can be remarkably increased after the expression of the receptor KIR3DL1 is inhibited. Meanwhile, the killing activity of the NK cell can be remarkably enhanced after the siRNA is transfected. Therefore, the small ribonucleic acid interference molecule for specifically inhibiting the NK cell receptor KIR3DL1 can be applied to preparation of anti-aids drugs.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
Hydroxypyrimidinone compounds and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102911124BStrong inhibitory activityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydrogenChemical compound
The invention discloses a hydroxy-pyrimidone compound shown as the general formula (I). In the general formula (I), the R1 represents tertiary butyl, phenyl or substituent phenyl and benzyl; the R2 represents hydrogen or substituent propyl, the R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 respectively represent hydrogen, methyl, methoxy, hydroxyl or halogen individually, and the n is equal to one or two. The hydroxy-pyrimidone compound has good HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus) integrase inhibitory activity and HIV-1 antiviral activity, wherein integrase inhibitory activities IC50(inhibitory concentration) of compounds 5a, 5b, 5c, 5d, 5e, 5i, 5n and 5q are all lower than or equal to 1 micromole, compounds 5a, 5h and 5s have high antiviral activity, and EC50(effective concentration) of the compounds 5a,5h and 5s are respectively 1.72 micromoles, 1.91 micromoles and 1.3 micromoles, and accordingly, the hydroxy-pyrimidone compound can be used for preparing anti-AIDs drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Diarylpyrimido pyridone derivative, preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a diarylpyrimido pyridone derivative. The diarylpyrimido pyridone derivative has a structure shown as general formula I in the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the derivative and application of the derivative as an HIV inhibitor in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
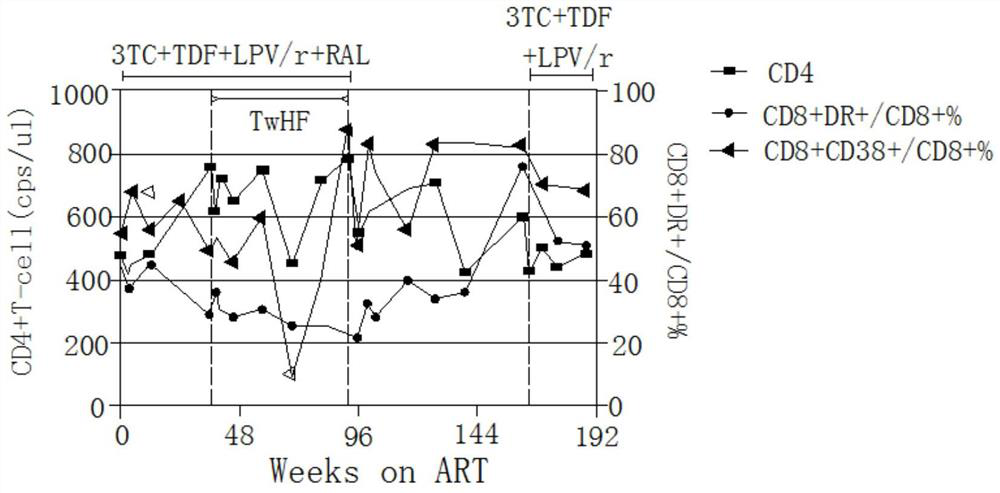
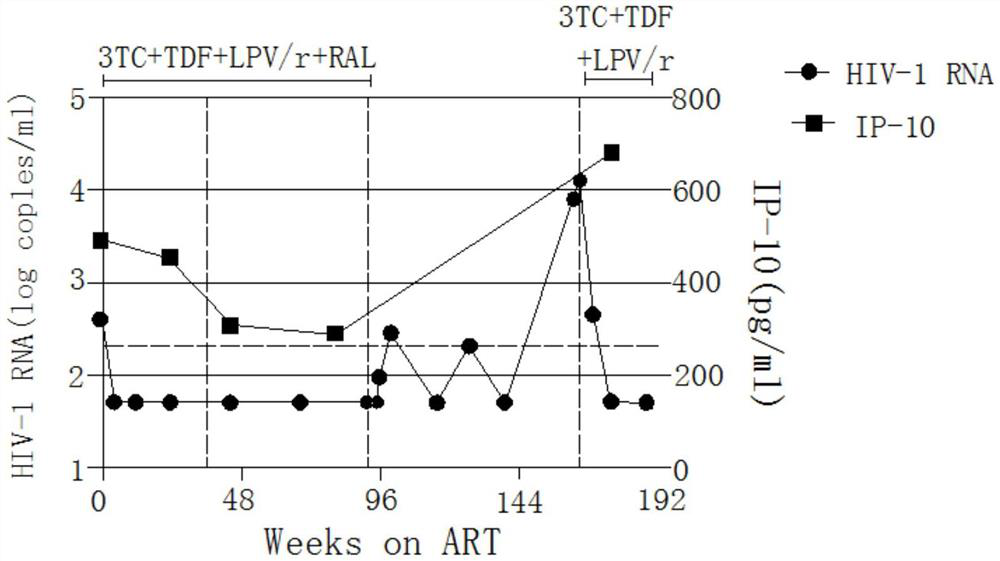
Application of Tripterygium wilfordii in the preparation of functional drugs for curing AIDS
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
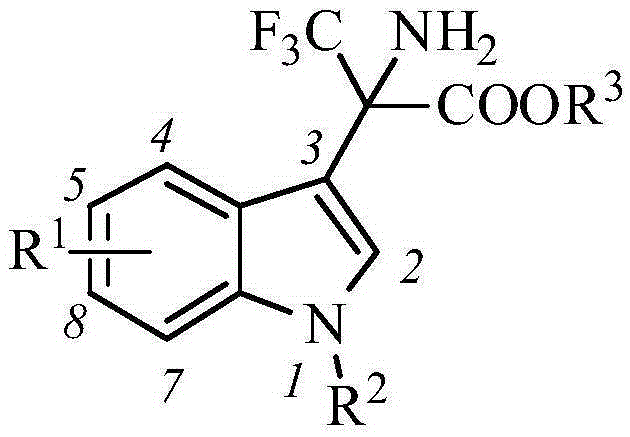
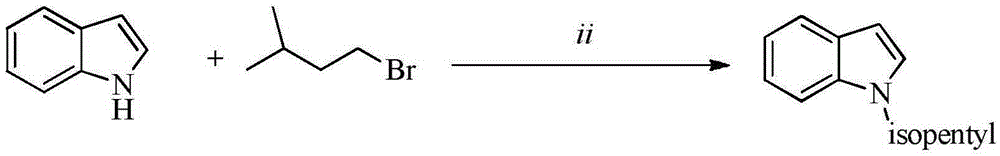
A kind of indole-alpha-amino acid compound and its application in the preparation of anti-AIDS drugs
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and particularly discloses indole-alpha-amino acid compounds. The idole-alpha-amino acid derivatives are prepared by carrying out Friedel-Crafts reaction on indole and trifluoropropionate-imine under the catalytic action of Lewis acid. The invention mainly discloses a method for preparing the compounds and an application of the compounds in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Health care pillow with built-in nerve calming and aid-sleeping medicines
The invention discloses a health care pillow with built-in nerve calming and aid-sleeping medicines. The pillow mainly comprises a pillow main body which is divided into a head pillow area, a neck pillow area and side pillow areas by linings, wherein the side pillow areas are positioned on two sides of the pillow main body, and respectively perpendicularly connected with the two ends of the neck pillows for form a [-shape, and the head pillow area is positioned in a surrounding area formed by the side pillow areas and the neck pillow area. An adjustable air bag layer and a neck pillow bag are arranged in the beck pillow from the bottom up, and massage heating equipment and health care traditional Chinese medicines are arranged in the neck pillow bag. The health care pillow provided by the invention can provide a bolster effect as the common pillow, and can also provide traction, massage, heating and medical functions for people with cervical discomfort.
Owner:胡国芳
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com