Phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dot and electrochemistry preparing method thereof
A graphene quantum dot, electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of uneven size of graphene quantum dots, a large amount of use of dangerous strong acid and strong oxidant, etc., to achieve good ability to scavenge free radicals, simple and low cost The effect of cost preparation method and preparation process convenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
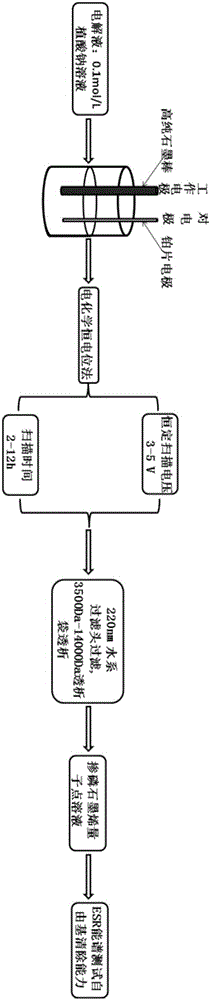
[0023] Such as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dot and an electrochemical preparation method thereof. Using an electrochemical constant potential method, by controlling the voltage, selecting a suitable electrolyte, and electrolysis time to prepare a graphene quantum dot with a high doped phosphorus content. Dots, and the quantum dots have excellent ability to scavenge free radicals, which is a new idea and method for scavenging free radicals.
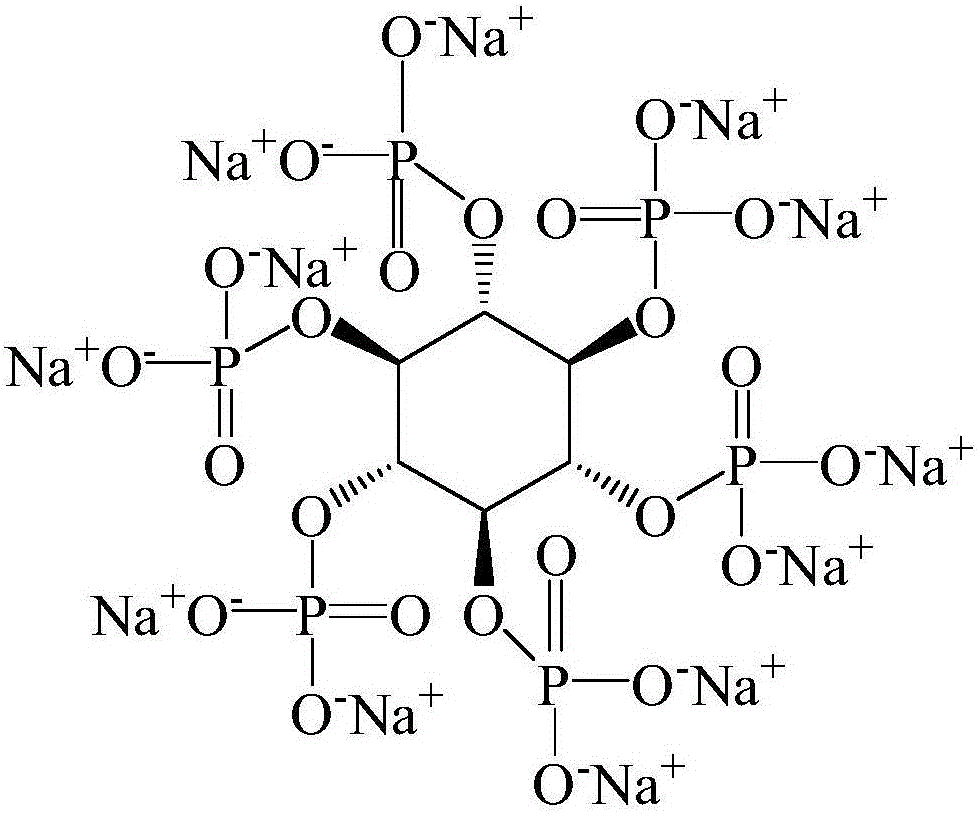
[0024] The core of preparing phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dots by constant potential electrochemical method is to select a suitable electrolyte. This electrolyte must be a phosphorus-containing, water-soluble macromolecular organic compound, and it is non-toxic and easy to prepare. No toxic substances are produced in the process, so we chose sodium phytate, which is a green food additive, see molecular structure figure 1, in the sodium phytate molecule, the phosphoru...
Embodiment 1
[0027] A sodium phytate solution (NaP) with a concentration of 0.1mol / L was prepared, and a high-purity graphite rod and a platinum sheet electrode were inserted into the solution as the working electrode and the counter electrode. The constant potential was set to 5V, and the sweep time was set to 12h. The brown aqueous solution obtained from this solution was filtered with a 220nm filter head, and then dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500-14000Da to remove excess ions, and the obtained light brown solution was designated as sample 1. Afterwards, the same concentration of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) was configured, and the control was the same as the above-mentioned condition parameters, except that the electrolyte was changed, and the quantum dots prepared by this method were counted as sample 2.
[0028] The GQDs aqueous solutions prepared above were respectively drip-coated on the surface of a clean silicon wafer of 0.5 × 0.5 cm. The inf...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A sodium phytate (NaP) solution with a concentration of 0.1mol / L was prepared, a high-purity graphite rod and a platinum sheet electrode were inserted as the working electrode and the counter electrode, and the electrochemical constant potential method was used for scanning. The scanning voltage was set to 3V, and the scanning time was 12h. Then the obtained brown aqueous solution was filtered with a 220nm filter head, and then dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500-14000Da to remove excess ions.
[0031] Take the above-prepared GQDs aqueous solution, drop-coat it on the surface of a 0.5×0.5 cm clean silicon wafer, test whether it is successfully doped with phosphorus by infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and then conduct free radical scavenging experiments by ESR spectroscopy. Tested to see if it has high free radical scavenging capacity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com