Rosin esters and compositions thereof
A technology of rosin ester and composition, which is applied in the field of rosin ester and its composition, and can solve the problems that rosin ester does not have proper performance, poor stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
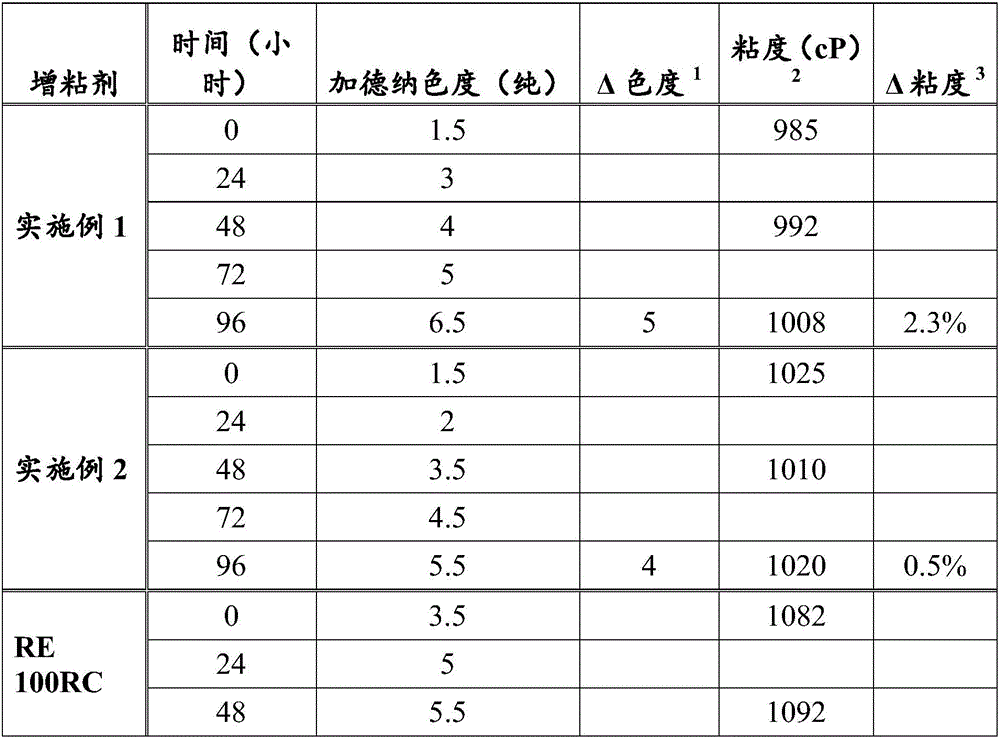
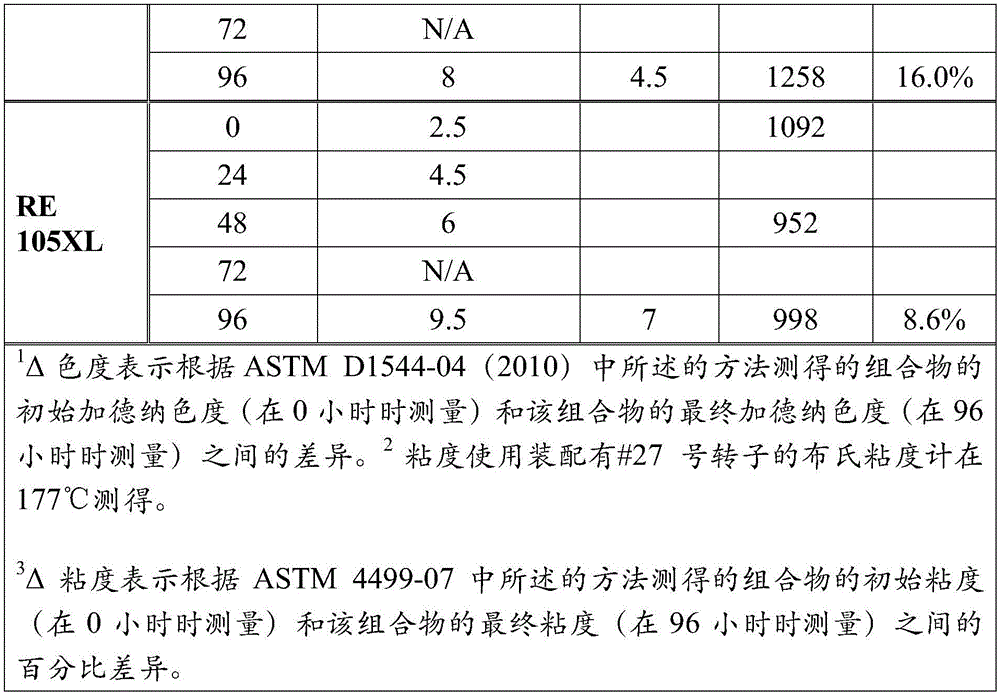
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] 500 g of tall oil rosin having a Gardner color (pure) of 5.5 and an acid number of 180.7 ( HYR, commercially available from Arizona Chemical) was charged to a four-necked flask (2 L) and heated to 200°C under a nitrogen atmosphere. After the rosin was completely melted, the rosin was stirred, and pentaerythritol (57.4 g) and 1425 (1.98 g) was added. The reaction mixture was heated to 275°C (heating rate 30°C / hour) and maintained at this temperature for 7.5 hours. The crude rosin ester was withdrawn and analyzed to have a Gardner color (pure) of 5.6, an acid value of 13.8, a softening point of 97.1° C. and an oxidation induction time of 0.5 minutes.
[0088] Without further purification, the crude rosin ester was hydrogenated at 650 psi and 260°C for 6 hours using 2 wt% palladium on carbon (5 wt% palladium). The catalyst was then removed by filtration to yield a rosin ester having a Gardner color (pure) of 1.4, an acid value of 11.2, a softening point of 98.0°C, and...
Embodiment 2
[0090] The procedure in Example 1 was repeated except that solvent was added during the hydrogenation reaction.
[0091] Crude rosin esters were prepared as described in Example 1. Without further purification, the crude rosin ester was hydrogenated at 650 psi and 260° C. for 6 hours using 2 wt % palladium on carbon (5 wt % palladium) in 50 wt % dimethylcyclohexane. The catalyst was then removed by filtration and the solvent was removed by distillation. The resulting rosin ester exhibited a Gardner color (pure) of 0.8, an acid value of 11.4, a softening point of 97.4°C, a PAN number of 0, and an oxidation induction time of 43.0 minutes. The color stability of the rosin esters was also tested. Incubated at 160°C for 3 hours, the rosin ester exhibited a Gardner color (pure) of 0.8. It was determined that the weight ratio of esterified dehydroabietic acid and esterified dihydroabietic acid in the obtained rosin ester was 1:1.6.
Embodiment 3
[0093] 500 g of tall oil rosin was charged into a four-necked flask (1 L). Place the flask under vacuum for 10 to 15 minutes. The vacuum was then released with nitrogen, and the flask was heated to 180°C with stirring. Will (Poly-tert-butylphenol disulfide 1.74 g, 0.31 wt%, commercially available from Arkema, Inc) was added to the reaction flask. The reaction flask contents were then stirred for 5 to 10 minutes. Catalyst (bis(((3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl)-ethylcalcium phosphate), 1.98 g) and pentaerythritol (57.4 g) were added, And the reactants were heated to 270°C at a rate of 35°C / hour. The reaction temperature was maintained at 275°C until the acid number of the mixture was less than 15. Take out the crude rosin ester.
[0094] Without further purification, the crude rosin ester was hydrogenated at 450 psi and 260°C for 6 hours using 1.5 wt% palladium on carbon (5 wt% palladium). The catalyst was then removed by filtration in toluene and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com