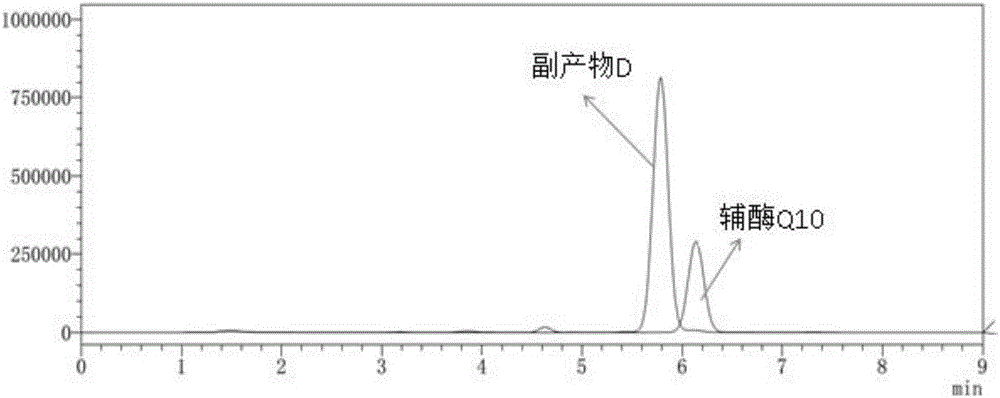
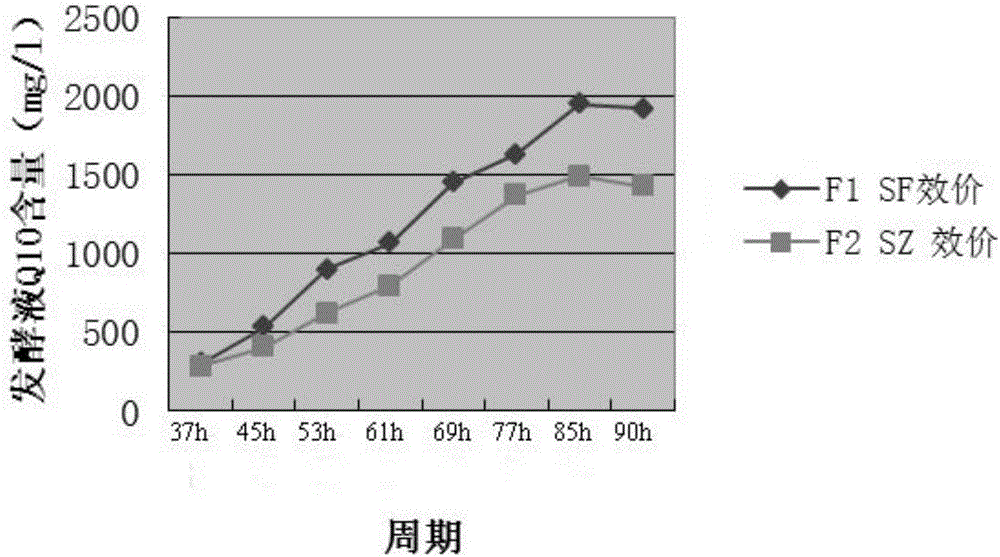
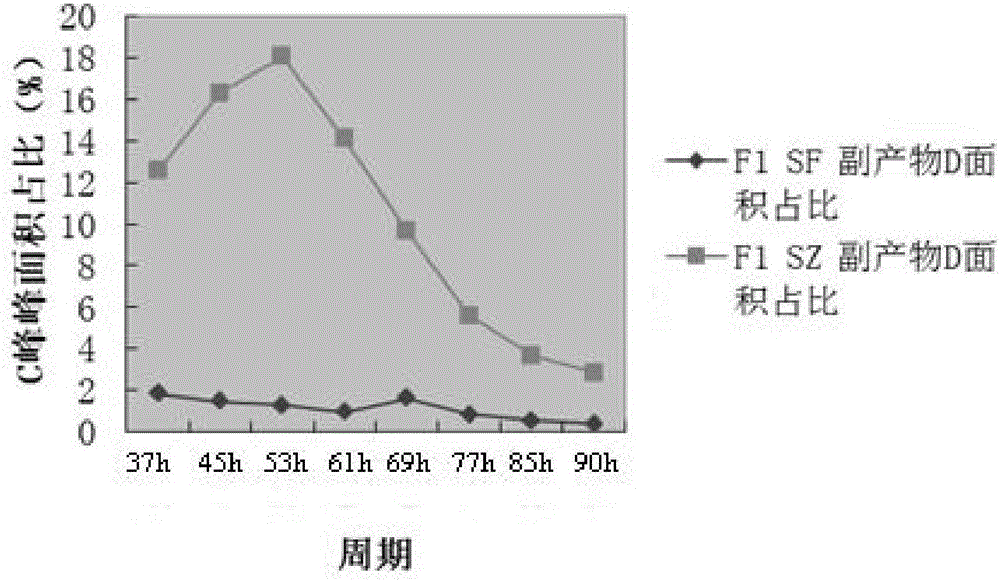
Method for reducing or eliminating by-product D in coenzyme Q10 producing strain SZ, coenzyme Q10 high-yield strain and application thereof
A technology for producing strains and high-yielding strains, applied in the field of modern biology, can solve problems such as restricting large-scale production, no effect, and inability to obtain transformation, and achieve the effects of low by-products, high yield, and stable genetic traits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Construction of expression plasmids
[0043] (a) Preserve pCL1920_pTrc in this laboratory ( www.synthesisgene.com ) and pMG160 (Inui, M, et al AEM 69 (2003) 725-733) as templates to construct Rhodobacter sphaeroides expression vector pBM03;
[0044] (b) Using E.coli W3110 as a template, primers UbiF-F and UbiF-R amplify the UbiF (Genbank: NC_000913.3) fragment; using the genome of coenzyme Q10 production strain-Rhodobacterium sphaeroides SZ as a template, using primer UbiH1 -F and UbiH1-R were amplified to obtain UbiH1 (Genbank: NC_007493, Rsp_1492), and primers UbiH2-F and UbiH2-R were used to amplify to obtain UbiH2 (Genbank: NC_007493, Rsp_1869). The corresponding primer series are shown in the sequence listing as SEQ ID NO : as shown in 1;
[0045] (c) The constructed expression plasmids are pBM03-UbiF, pBM03-UbiH1, and pBM03-UbiH2, respectively.
[0046] Both steps (a) and (c) were obtained by EZ fusion method (Generay GR6086). Rhodobacter sphaeroides SZ has be...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Construction of strain fst△(Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1ΔrshI)
[0049] (a) Using pK18mobSacB preserved in our laboratory as a vector, using the coenzyme Rhodobacter sphaeroides2.4.1 genome as a template, and using primers rshI-5'-F / R and rshI-3'-F / R, construct plasmid pK18mobSacB_rshI;
[0050] (b) Transform pK18mobSacB_rshI into the E.coli S17-1 host preserved in our laboratory to obtain E.coli S17-1 / pK18mobSacB_rshI;
[0051] (c) Transfer pK18mobSacB_rshI from E.coli S17-1 / pK18mobSacB_rshI to Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Fst bacteria through conjugation transfer experiment, and obtain the zygote of single exchange strain Fst_rshI by screening with nalidixic acid + resistance marker. For detailed conjugation transfer methods, see Porter SL, et al Methods Enzymol 423:392-413 (2007).
[0052] (d) A non-resistant double-crossover strain-Rhodobacterium sphaeroides Fst△ was obtained by screening with 20% sucrose. After using rshI-5'-F / rshI-3'R primers to amplify the geno...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Preparation of Fst△ and SZ Competent
[0056] (a) Separate 20 ul from the glycerol tubes containing Fst△ bacteria and SZ bacteria, streak on LB plates, and culture overnight at 34°C in the dark;
[0057] (b) Pick a single bacterium into a 4ml LB test tube, and activate overnight at 34°C in the dark until the cell OD ≤ 1.0;
[0058] (c) Transfer 4ml of the bacterial solution in (b), inoculate into a 500ml shake flask containing 100ml LB medium, culture at 34°C, 220rpm, in the dark for 4-6h;
[0059] (d) But when the OD of the above-mentioned culture solution reaches 0.6, collect the bacteria by centrifuging at 6000rpm for 3min;
[0060] (e) Wash the thalline 3 times with sterile water subsequently, centrifuge at 6000rpm, 3min;
[0061] (f) Add 0.5-1ml of the E2 preparation solution to the prepared cells to suspend the cells, divide each 80ul cells into eppendrof tubes, and store at -80°C for later use.
[0062] Rhodobacter sphaeroides SZ in step (a) is a coenzyme Q10 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com