A kind of spore-producing medium of maize leaf spot fungus and its application
A technology of maize leaf spot fungus and culture medium, which is applied in the field of plant pathogenic fungus research, can solve the problems of low spore production, limited breeding of disease-resistant varieties and screening of resistant resources, and achieves convenient material collection, good growth and operability strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
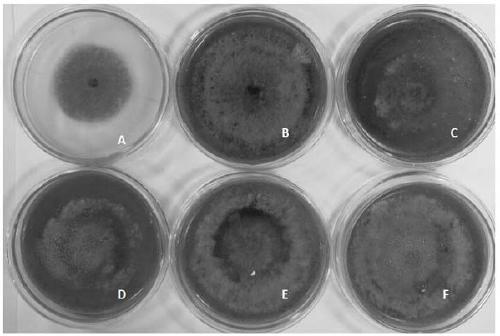
[0018] (1) Use clean water to prepare the following formula of spore-producing culture medium for maize leaf spot fungus (proportion 1), and each liter contains the following raw material components: 20 g of mannitol, 3 g of peptone, 40 g of fresh corn leaves, and 30 g of sorghum grains g, agar powder 14 g.
[0019] (2) Grind the sorghum grains with a cooking machine for later use, wash the fresh corn leaves with water, add water 20 times the weight of the corn leaves, boil for 30 minutes, and filter, then add crushed sorghum grains, mannitol, and peptone to the supernatant and agar powder, heated to dissolve, added water to make the volume to 1 L, adjusted the pH value to 7.0, sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min, and cooled to obtain a large amount of spore-producing medium for S. maize.
[0020] (3) Take out the Pseudomonas spp. stored in the refrigerator at 4°C, transfer it to PDA medium (PDA medium: 200 g potato, 20 g glucose, 15 g agar powder, 1 L water) for activation, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0022] (1) Use clean water to prepare the following formula of spore-producing culture medium for maize leaf spot fungus (proportion 2), which contains the following raw material components per liter: 25 g of mannitol, 5 g of peptone, 60 g of fresh corn leaves, and 50 g of sorghum grains g, agar powder 16 g.
[0023] (2) Grind the sorghum grains with a cooking machine for later use, wash the fresh corn leaves with water, add water 20 times the weight of the corn leaves, boil for 40 minutes, and filter, then add crushed sorghum grains, mannitol, and peptone to the supernatant and agar powder, heated to dissolve, added water to make the volume to 1 L, adjusted the pH value to 7.0, sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min, and cooled to obtain a large amount of spore-producing medium for S. maize.
[0024] (3) Take out the Pseudomonas spp. stored in the refrigerator at 4°C, transfer it to PDA medium (PDA medium: 200 g potato, 20 g glucose, 15 g agar powder, 1 L water) for activation, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] (1) Use clean water to prepare the following formula of spore-producing medium for S. maize leaf spot (proportion 3), which contains the following raw material components per liter: 20 g of mannitol, 5 g of peptone, 40 g of fresh corn leaves, and 40 g of sorghum grains g, agar powder 15 g.
[0027] (2) Grind the sorghum grains with a cooking machine for later use, wash the fresh corn leaves with water, add water 20 times the weight of the corn leaves, boil for 35 minutes, filter, and add crushed sorghum grains, mannitol, and peptone to the supernatant and agar powder, heated to dissolve, added water to make the volume to 1 L, adjusted the pH value to 7.0, sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min, and cooled to obtain a large amount of spore-producing medium for S. maize.
[0028] (3) Take out the Pseudomonas spp. stored in the refrigerator at 4°C, transfer it to PDA medium (PDA medium: 200 g potato, 20 g glucose, 15 g agar powder, 1 L water) for activation, and then put Use a h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com