Chinese traditional medicine water extract for treating diabetic nephropathy as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for diabetic nephropathy and extracts, applied in the field of traditional Chinese medicine extracts, can solve problems such as lack of specific means for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, and achieve the effects of reducing urinary protein excretion rate, content and urea content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1, the extraction of Chinese medicine extract
[0029] Weigh the following prescription:
[0030] Dijincao 120g, Salvia 160g, Raw Astragalus 120g, Anemarrhena 80g, Coptis 48g.
[0031] After mixing the traditional Chinese medicines, add them to 8 times the mass of water, soak for 60 minutes, then decoct and extract twice for 1 hour each time, filter, combine the filtrates, concentrate, and evaporate to dryness, which is the Chinese medicine extract of the present invention.
[0032] The Chinese medicine extract prepared in this example is in the form of extract, 182g in total, so 1g of the Chinese medicine extract is equivalent to 2.90g of the Chinese medicine composition.
Embodiment 2
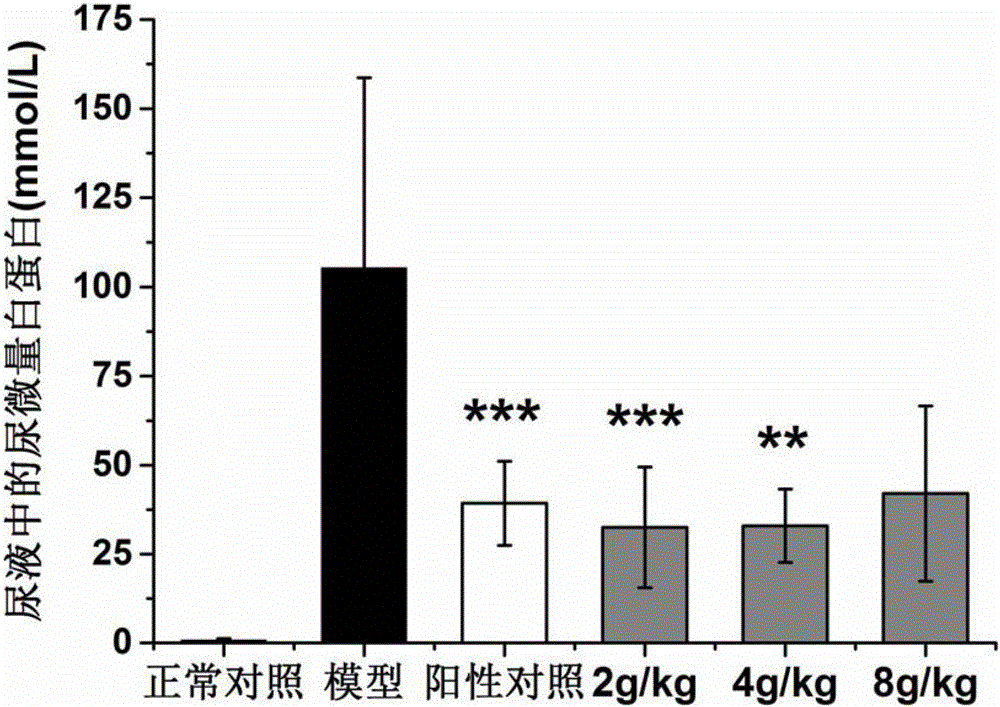
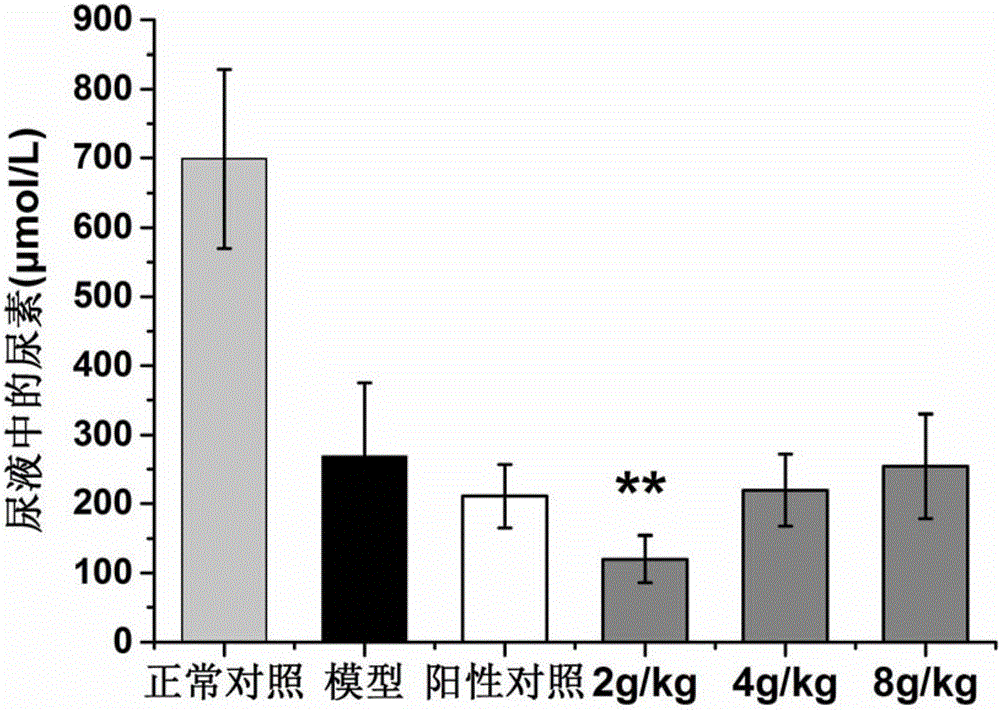
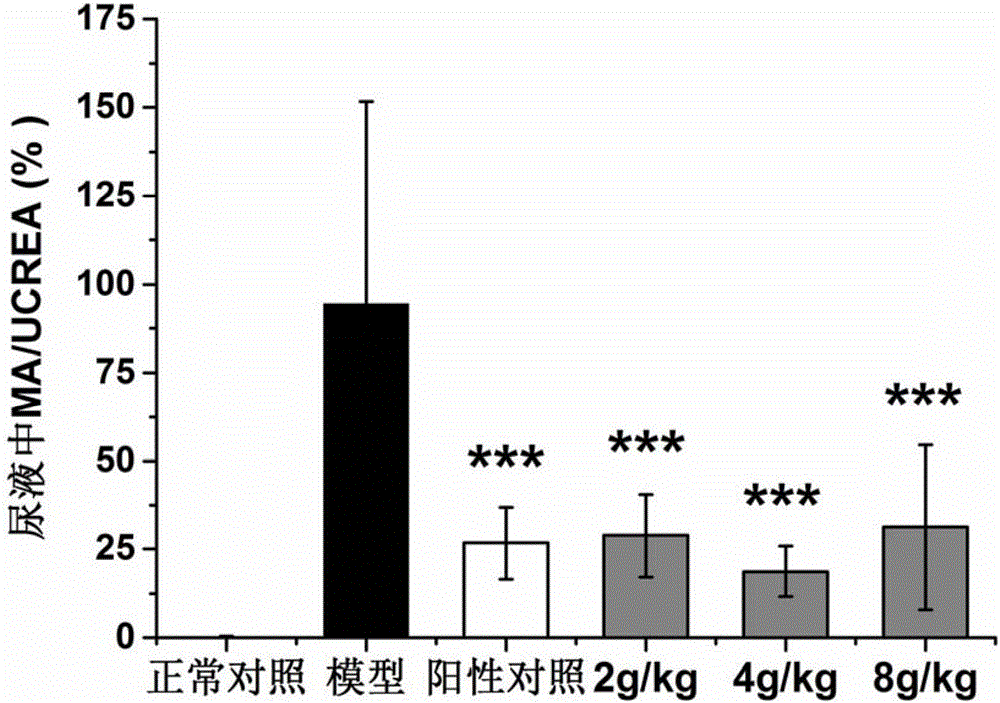
[0033] Embodiment 2, the influence of Chinese medicine extract of the present invention on blood sugar and renal function
[0034] 1. Animals
[0035] 40 male spontaneous type 2 diabetes model KK-Ay mice, 8w old, Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2014-0004; 10 healthy male C57BL / 6J mice, 8w old, Beijing Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co., Ltd., license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2012-0001. KK-Ay mice were fed with high-fat diet, Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2014-0008; C57BL / 6J mice were fed with normal diet. All animals had free access to water, and were adaptively fed for 1 week at room temperature (22±1)°C in an SPF environment with a 12-h photoperiod. Take blood from the tip of the tail to measure the random blood glucose of KK-Ay mice ≥11.1mmol·L -1 Or fasting blood glucose (FBG) ≥ 7.0mmol·L -1 That is, as a model of diabetes.
[0036] 2. Dosage of mice in each group
[003...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com