GS (glutamine synthetase) gene specific identification crRNA and application thereof
A specific and genetic technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, application, genetic engineering, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and complicated knockout process, and achieve high transfection efficiency, reduced number of clones, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1: Construction of CRISPR-Cas9 expression system for GS gene
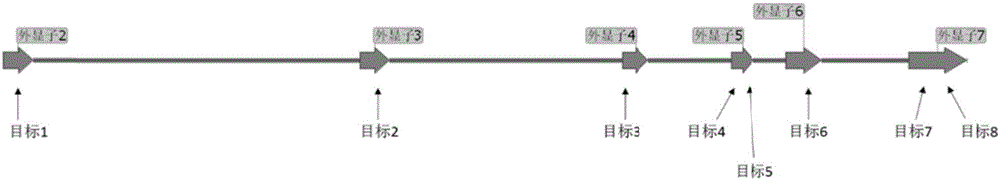
[0065] The GS gene of Chinese hamster ovary cells contains 7 exons, of which exons 2-7 code for the expression of GS protein ( figure 1 ), which play a vital role in normal function. The crRNA sequences were designed for exons 2-7 of the GS gene. Using these crRNA sequences and Cas9 protein can render the expressed GS protein non-functional. The partial sequence of exons 2-7 of GS is as follows (exons are marked with an underline "_____"):
[0066] SEQ ID NO.17:
[0067] TGCCTCTTACGCAATTCCTGCAGGGGACCCCCTTCAGAGTAGATGTTAATGAAATGACTTTTGTCTCTCCAGAGCACCTTCCACC ATGGCCACCTCA GCAAGTTCCCACTTGAACAAAAACATCAAGCAAATGTACTTGTGCCTGCC CCAGGGTGAGAAAGTCCAAGCCATGTATATCTGGGTTGATGGTACTGGAG AAGGACTGCGCTGCAAAACCCGCACCCTGGACTGTGAGCCCAAGTGTGTA GAAG GTGAGCATGGGCAGGAGCAGGACATGTGCCTGGAAGTGGGCAAGCAGCCTGAGATTTGACCTTCCTTCTGTTTTGTTTGCAAAGTCTTTCAAAAGCAGGTCTCTTCAGGCCTCAGTCAGTCACCCGTAAGCTGCCGAGTAGTCTGGAGG
[0068] SEQ ID ...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Knockout and verification of GS gene in CHO-K1 cells
[0082] The designed crRNA and Cas9 protein expression vectors were transfected into CHO-K1 cells acclimated by CD medium, and a total of 16 kinds of transfection or transfection combinations from A to P were designed.
[0083]CHO-K1 cells were purchased from ATCC, and the cells were cultured using DMEM / F12 basal medium, supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum. The expanded CHO-K1 cells were cultured in suspension in CD CHO medium, supplemented with glutamine and HT additives.
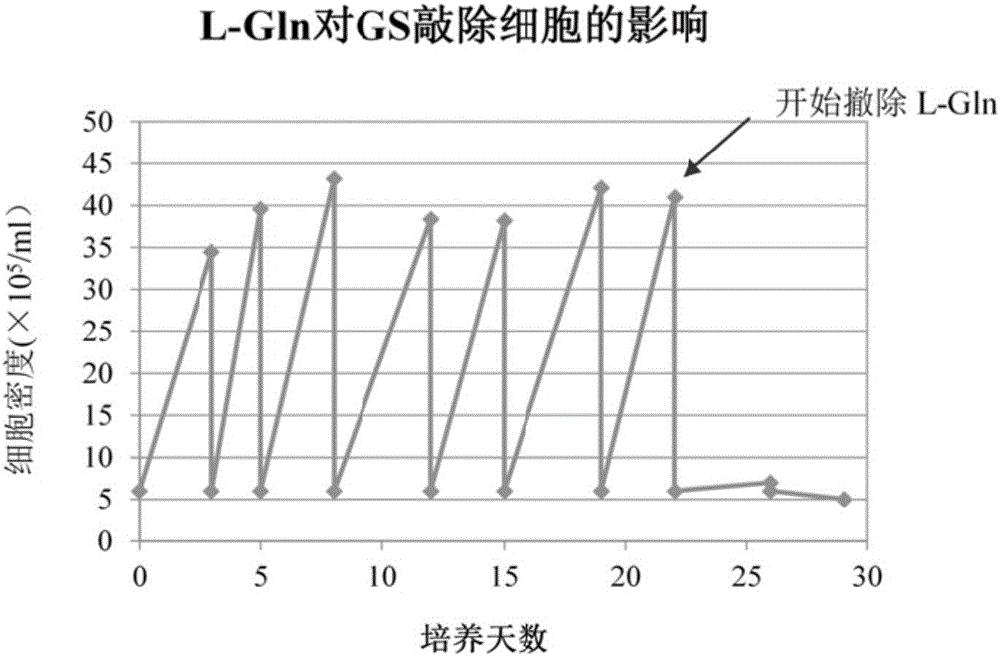
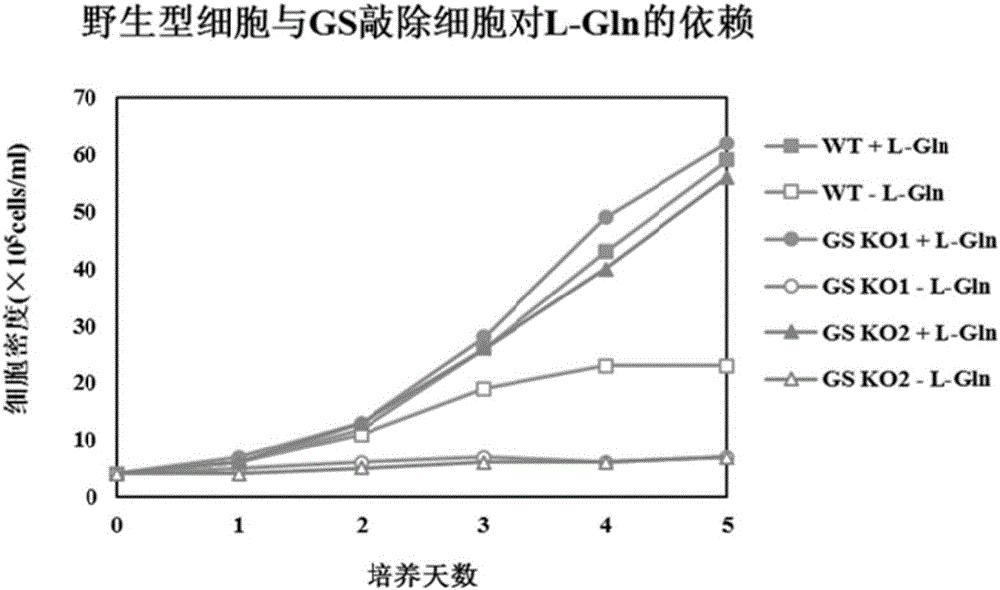
[0084] After the cells were adapted to suspension culture, the crRNA and Cas9 protein expression vectors were transfected into the cells. After 48 hours of transfection, Puromycin was added to the cell culture medium, and after 4 days of culture, the surviving cells were selected for subcloning culture. After the subcloned cells grew out, the cells were transferred to medium containing L-Gln and medium without L-Gln for culture. ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3: GS gene-deficient cell expression antibody experiment
[0091] Antibody expression transfection experiments were performed on the selected GS KO1 and GS KO2 cells, and wild-type CHO-K1 cells were used as control hosts. KJ015 was transfected into GS KO1, GS KO2, and CHO-K1 cells by exactly the same method. 48 hr after transfection, 25 μM MSX was added as selection pressure. After 2 weeks of static culture, clones grew out, and the number of grown clones and the 25 clones with the highest antibody expression in 24 hours were compared, and the results are shown in Table 3. The differences in the number of clones grown among the three were small, and the expression levels of GS KO1 and GS KO2 host clones were significantly higher.
[0092] table 3
[0093]
[0094]
[0095] Cells with better expression levels were amplified and cultured, and expression products were collected, and the quality of expressed antibodies was analyzed using IEC as a key qualit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com