Foam water drainage treatment process
A treatment process, soaking and drainage technology, applied in water/sewage treatment, mining wastewater treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of peculiar smell, high degree of emulsification, slow defoaming speed, etc., to achieve economical and environmental The effect of win-win, protecting the ecological environment and accelerating the pace of construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
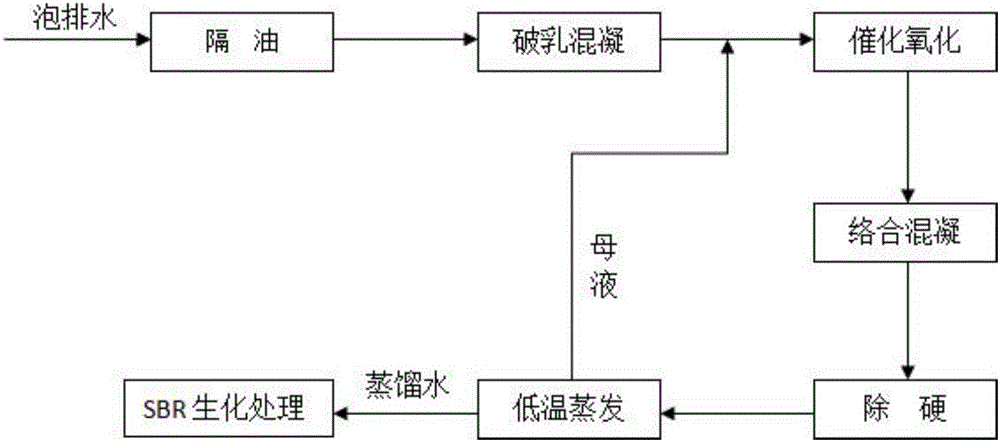
[0028] like figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a bubble drainage treatment process, which includes the following steps in sequence:
[0029] Oil separation: after the soaked water to be treated is static, the liquid is separated, the oil layer is removed, and the water sample of the lower layer is obtained;
[0030] Demulsification and coagulation: take the lower water sample, adjust its pH value to 8, then add demulsifier and coagulant in turn to the lower water sample to produce a large number of flocs, and the lower water sample changes from milky white to khaki, the flocs Floating, the lower layer liquid is turbid, after a period of time, the flocs sink and filter to obtain the filtrate; wherein, the addition amount of the demulsifier is 3g / L; the addition amount of the coagulant solution is 8ml / L, and the amount of the coagulant solution The mass percentage content is 10%;
[0031] Catalytic oxidation: take the filtrate in the demulsification coagulation...
Embodiment 2
[0040]In this embodiment, various parameters in the demulsification coagulation step are screened.
[0041] 1. Screening of pH value
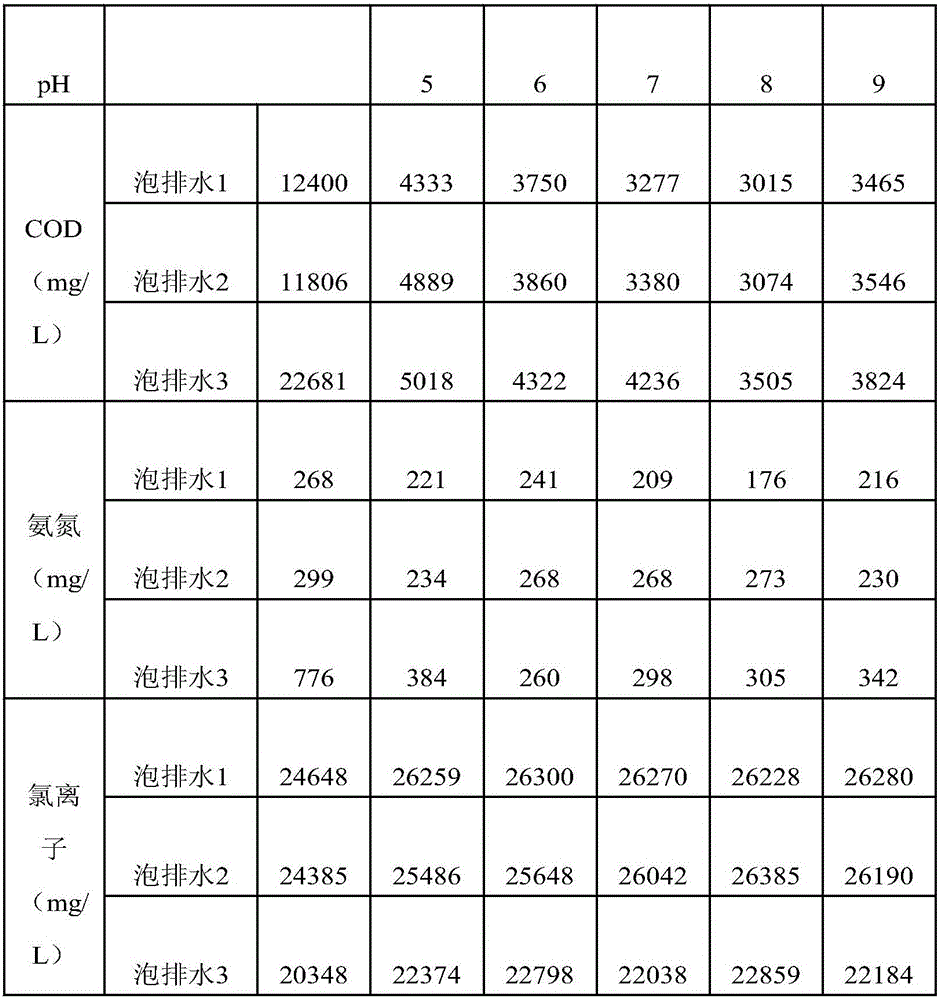
[0042] For beakers numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively take the lower layer water samples treated by the oil separation step, and adjust the pH values of the lower layer water samples in each numbered beaker to 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9; , the addition of demulsifier is 1g / L, the addition of coagulant solution is 3ml / L, and the mass percentage of coagulant solution is 10%; detection. Among them, the relationship between pH and demulsification coagulation effect is shown in Table 1 below.
[0043] Table 1 Relationship between pH and demulsification coagulation effect
[0044]
[0045]
[0046] It can be seen from the above results that COD first decreases and then increases as the pH value increases. Taking bubble drainage 1 as an example, when pH=9, COD is 3465mg / L, which is higher than 3015mg / L when pH=8, therefore, the optimal pH val...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In this embodiment, various parameters in the catalytic oxidation step are screened.
[0054] 1. Screening of pH value
[0055] For the beakers numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4, take the filtrate obtained in the demulsification and coagulation step respectively, and adjust the pH value of the filtrate in each numbered beaker to 7.5, 8.5, 9.5, and 10.5; then press the mass ratio of 1:20 Add catalyst and oxidant to carry out oxidation reaction, filter after the reaction is complete, and detect the treatment results under different pH conditions. Among them, the catalytic oxidation effects of different pHs are shown in Table 3 below.
[0056] Table 3 Catalytic oxidation effect of different pH
[0057]
[0058] It can be seen from the test results that when the pH is 9.5, the COD in the treated filtrate is the lowest and the NH3-N is low; when the pH is 8.5, the NH3-N in the treated filtrate is the lowest and the COD is at a medium level.
[0059] Therefore, considering the ov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com