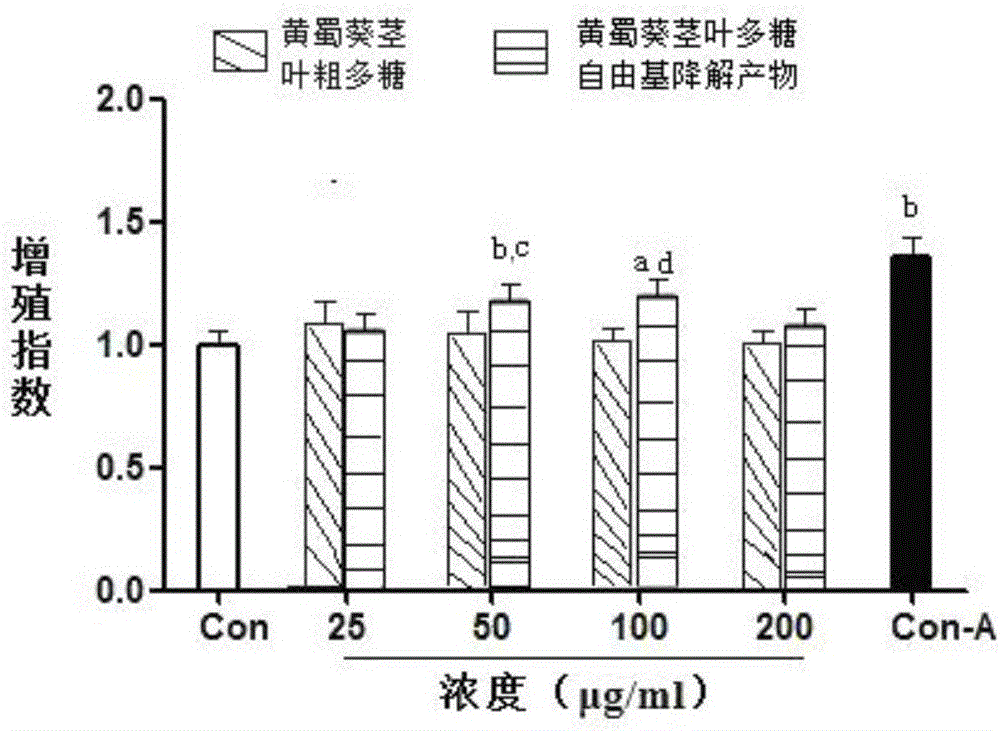
Free radical degradation product of abelmoschus manilhot stem leaf polysaccharide capable of improving immunocompetence and preparation method thereof
A technology of degradation product, hollyhock, applied in the direction of organic active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, etc. The effect of continuous application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The preparation method of the free radical degradation product of the stem and leaf polysaccharide of Abelmoschus manihot according to the present invention includes the following steps:
[0032] (1) Preparation of crude polysaccharides from stems and leaves of Abelmoschus manihot
[0033] 100g of coarse powder of hollyhock stems and leaves were added with 30 times the amount of water, and extracted 3 times with reflux in a water bath at 100°C, each for 1 hour. Filter, combine the filtrates, and concentrate under reduced pressure. Remove protein by Sevag method, centrifuge (4000r / min, 10min), take the supernatant, add four times the volume of absolute ethanol, precipitate with alcohol overnight, filter with suction, and wash the precipitate three times with absolute ethanol, acetone, and ether, 50℃ After drying, crude polysaccharides from stems and leaves of hollyhock are obtained.
[0034] (2) Grading of crude polysaccharides from hollyhock stems and leaves
[0035] Weigh 3g...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Determination of the total sugar and uronic acid content of the free radical degradation products of the stem and leaf polysaccharide of Abelmoschus manihot
[0039] 1. Experimental method: Using D-anhydrous glucose as the standard product, the total sugar content of hollyhock stem and leaf polysaccharides before and after sulfation modification was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method; the uronic acid content was determined by the meta-hydroxybiphenyl method, and D-glucose Aldehydic acid is the standard product.
[0040] 2. Experimental results: The total sugar content of hollyhock stem and leaf polysaccharide prepared in Example 1 was 99.76%. The total sugar content of free radical degradation products of hollyhock stem and leaf polysaccharide decreased to 95.53%; the hollyhock stem and leaf polysaccharide was not degraded before degradation. Contains uronic acid and no uronic acid after degradation, which is consistent with the result of monosaccharide ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Analysis of monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides from stems and leaves of Abelmoschus manihot and its free radical degradation products
[0042] 1. The experimental method uses trifluoroacetic acid to hydrolyze polysaccharide samples, with mixed monosaccharides as the standard, PMP-derived polysaccharide samples and mixed standards, using high performance liquid chromatography to determine the composition of monosaccharides according to the peak time, and draw each monosaccharide based on the peak area The standard curve of sugar measures the monosaccharide content of the sample.
[0043] 2. Experimental results: analysis of monosaccharide composition
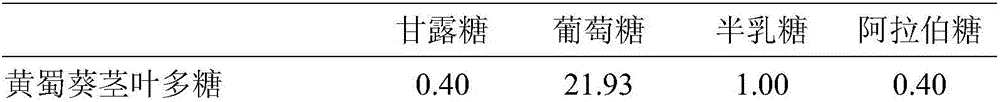
[0044] The molar ratio of the monosaccharide composition of the stem and leaf polysaccharide of hollyhock and its degradation products prepared in Example 1 is shown in Table 1. The stem and leaf polysaccharide of hollyhock is composed of mannose, glucose, galactose and arabinose. Among them, the content of g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com