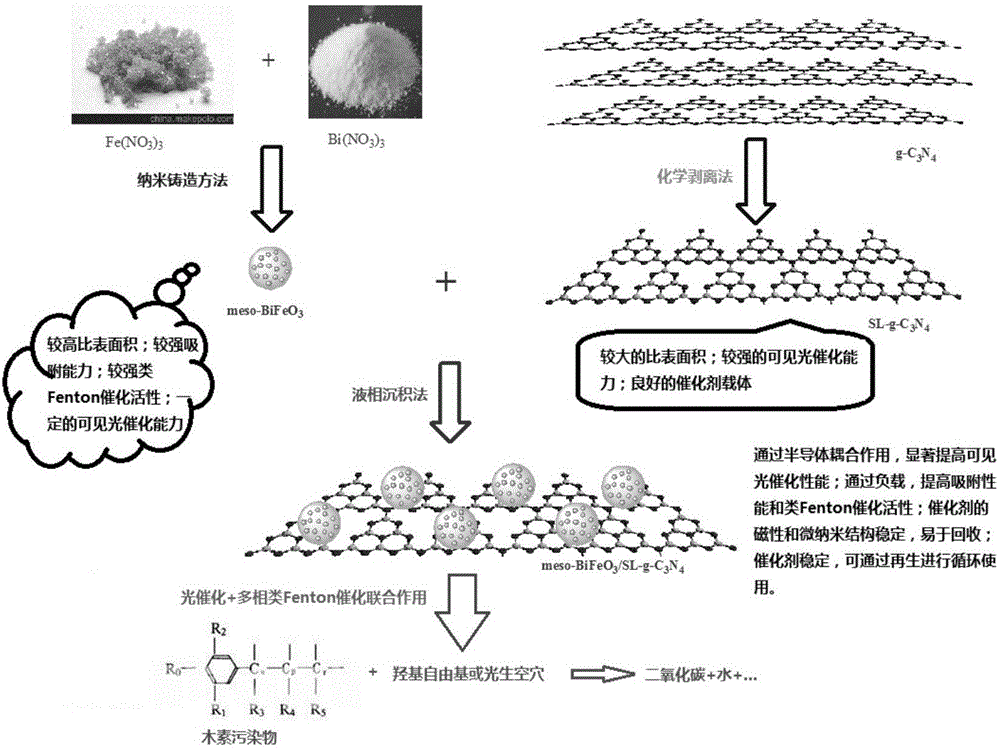
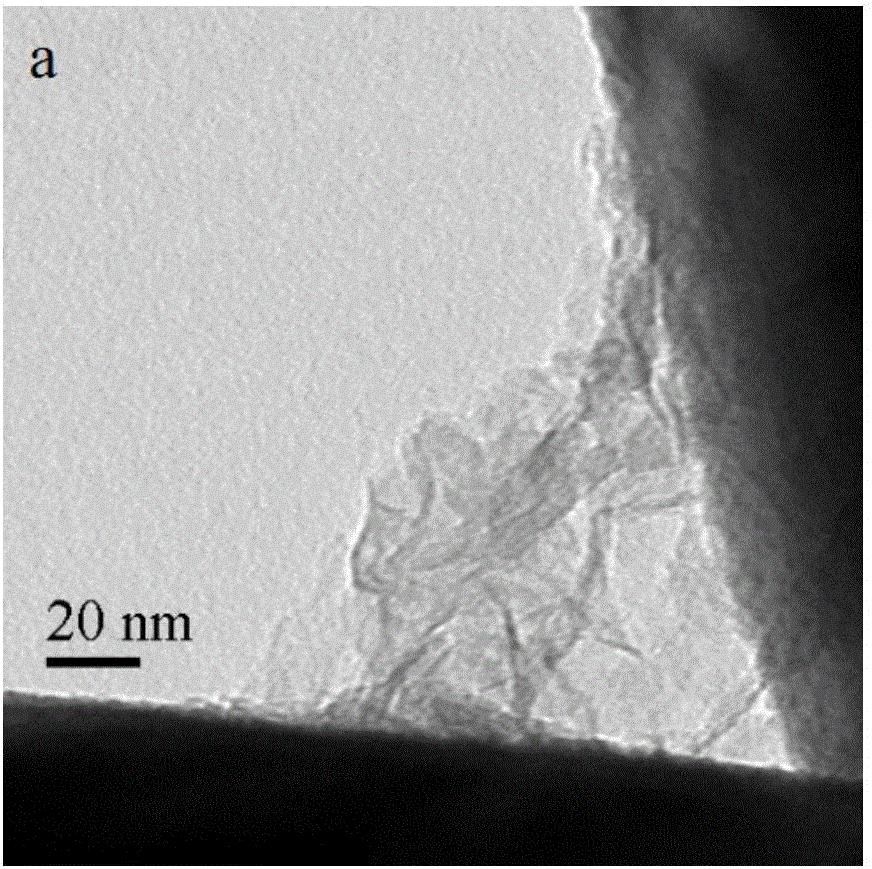
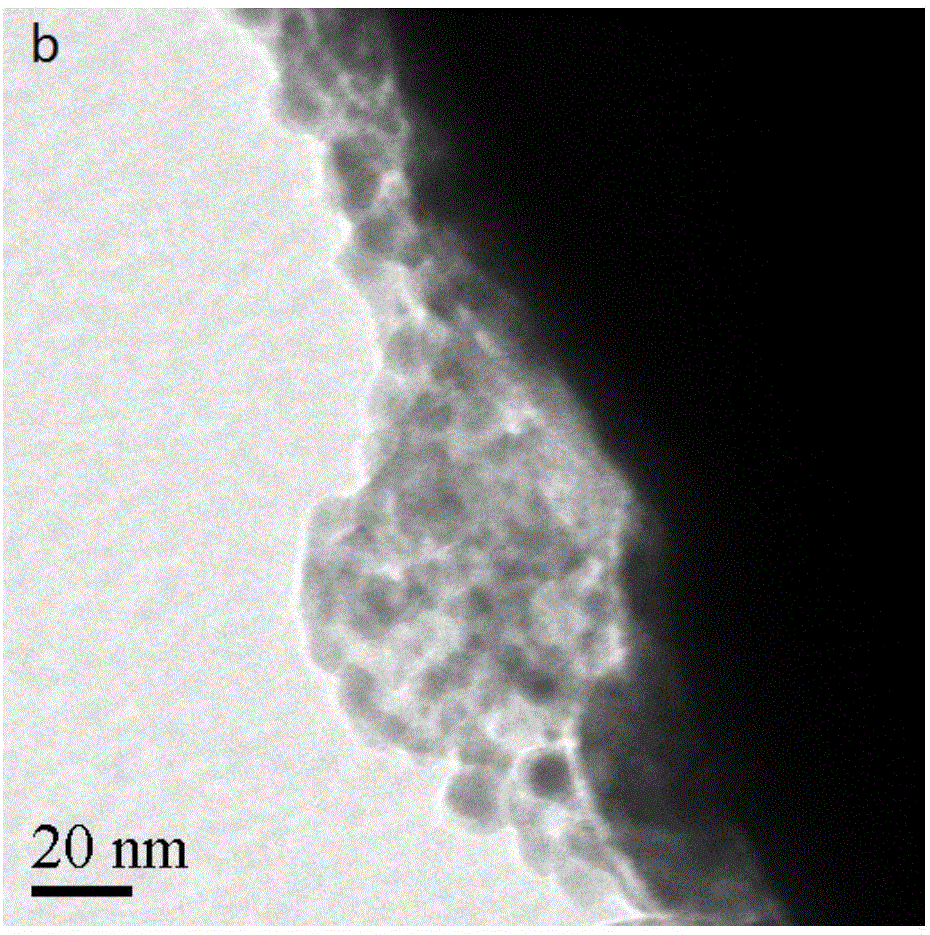
Bifunctional porous material efficient in adsorptively degrading lignin and preparation method thereof
A technology of adsorption and degradation, porous materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of limited adsorption capacity, negative impact of degradation, insufficient capacity, etc., to achieve good economic benefits and high efficiency Effect of degradation and strong adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Preparation of meso-BiFeO by liquid phase deposition method 3 / g -C 3 N 4 composite material
[0042] (1) meso-BiFeO 3 preparation of
[0043] Refer to literature (F. Kleitz, S.H. Choi, R. Ryoo, Chemical Communications 2003:2136–2137) to prepare large mesoporous cubic Ia3d Symmetrical silica (KIT-6) is the hard template. With Bi(NO 3 ) 3 and Fe(NO 3 ) 3 As raw material, meso-BiFeO was prepared by nanocasting method 3 catalyst. The details are as follows: First, a certain amount of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 , Bi(NO 3 ) 3 and KIT-6 were ground in a mortar and then dispersed in a volume of hexane to form a homogeneous mixture. Next, the above mixture was dispersed into a certain amount of hexane, refluxed and stirred at 70 °C for 12 h, then cooled, filtered, and then dried at 70 °C to obtain a solid product. The product was then heated to 600°C in an air-atmosphere tube furnace and held for 5 h. Finally, the solid was put into 2 M NaOH solution, vigorously s...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Preparation of porous BiFeO by hydrothermal method 3 / g -C 3 N 4 composite material
[0053] (1) g-C 3 N 4 Preparation of nanosheets
[0054] First put dicyandiamide into a muffle furnace, heat to 550°C, and keep it warm for 4 hours to obtain g-C 3 N 4 . Then, g-C 3 N 4 Mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid and stirred for 8 h, then poured into deionized water for ultrasonic treatment. After the mixture turned bright yellow, it was centrifuged to remove unstripped g-C 3 N 4 . Subsequently, the centrifuged suspension was washed with deionized water, and the above mixture was dried at 80°C to obtain the product.
[0055] (2) Porous meso-BiFeO 3 / g -C 3 N 4 Preparation of composite materials
[0056] ①Clean the 200mL beaker, 100mL measuring cylinder, glass rod, funnel, Buchner funnel, and 50mL volumetric flask used in the experiment, and dry them to prepare for the experiment;
[0057] ②Weigh 0.67g of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O with 0.808g Bi(NO 3 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com