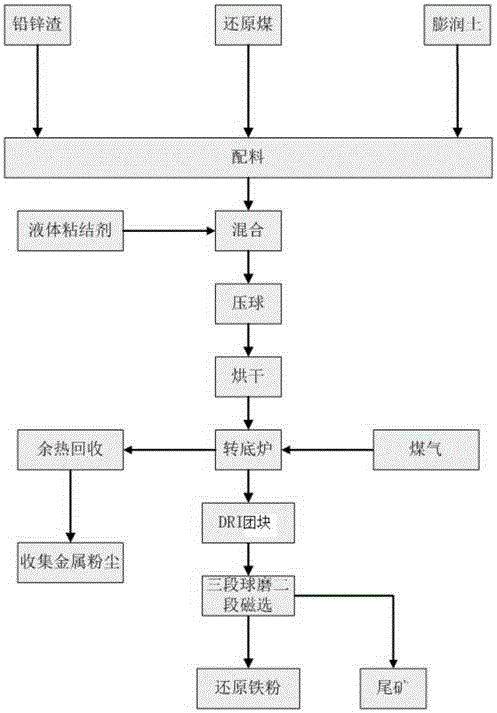
Iron extracting process of lead and zinc residues treated through rotary hearth furnace
A technology of lead-zinc slag and rotary hearth furnace, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of environmental pollution, resource waste, and large land occupation, and achieve the effects of short process flow, high recovery rate, and comprehensive utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1 Rotary hearth furnace treatment lead-zinc slag iron extraction process
[0025] The annual processing capacity of the project is 200,000 tons of lead-zinc slag (dry basis), with a moisture content of 10%. The main components of lead-zinc slag are shown in Table 1:
[0026] Table 1 Chemical multi-element analysis of lead-zinc slag
[0027] TF Fe 2 o 3
SiO 2
Al 2 o 3
CaO MgO S P Ag Pb Zn Cl 22.01 32.17 4.675 1.695 3.615 0.908 13.07 0.091 0.013 2.78 3.1 0.02
[0028] Rotary hearth furnace is used for direct reduction smelting, which requires 5,000 tons of bentonite, 7,000 tons of liquid binder and 50,000 tons of coal powder per year.
[0029] 1) Batching - compaction: take lead-zinc slag, reducing agent and additives according to the proportion for batching, fully mix, press into agglomerates, and dry at 200°C to obtain dry agglomerates; among them, the additives are bentonite and liquid binder ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 Rotary hearth furnace treatment of lead-zinc slag iron extraction process
[0037] The annual processing capacity of the project is 200,000 tons of lead-zinc slag (dry basis), with a moisture content of 10%. The main components of lead-zinc slag are shown in Table 4:
[0038] Table 4 Chemical multi-element analysis of lead-zinc slag
[0039] TF Fe 2 o 3
SiO 2
Al 2 o 3
CaO MgO S P Ag Pb Zn Cl 22.01 32.17 4.675 1.695 3.615 0.908 13.07 0.091 0.013 2.78 3.1 0.02
[0040] Rotary hearth furnace is used for direct reduction smelting, and 20,000 tons of bentonite, 4,000 tons of liquid binder are required to be added every year, and 30,000 tons of coal powder are consumed.
[0041] 1) Batching - compaction: take lead-zinc slag, reducing agent and additives according to the proportion for batching, mix thoroughly, press into agglomerates, and dry at 30°C to obtain dry agglomerates; among them, the addi...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3 rotary hearth furnace treatment lead-zinc slag iron extraction process
[0049] The annual processing capacity of the project is 200,000 tons of lead-zinc slag (dry basis), with a moisture content of 10%. The main components of lead-zinc slag are shown in Table 7:
[0050] Table 7 Chemical multi-element analysis of lead-zinc slag
[0051] TF Fe 2 o 3
SiO 2
al 2 o 3
CaO MgO S P Ag Pb Zn Cl 22.01 32.17 4.675 1.695 3.615 0.908 13.07 0.091 0.013 2.78 3.1 0.02
[0052] Rotary hearth furnace is used for direct reduction smelting, and 8,000 tons of bentonite, 10,000 tons of liquid binder and 70,000 tons of pulverized coal are required to be added every year.
[0053]1) Batching-pressing: Take lead-zinc slag, reducing agent and additives according to the proportion for batching, fully mix, press into agglomerates, and dry at 115°C to obtain dry agglomerates; among them, the additives are bentonite an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com