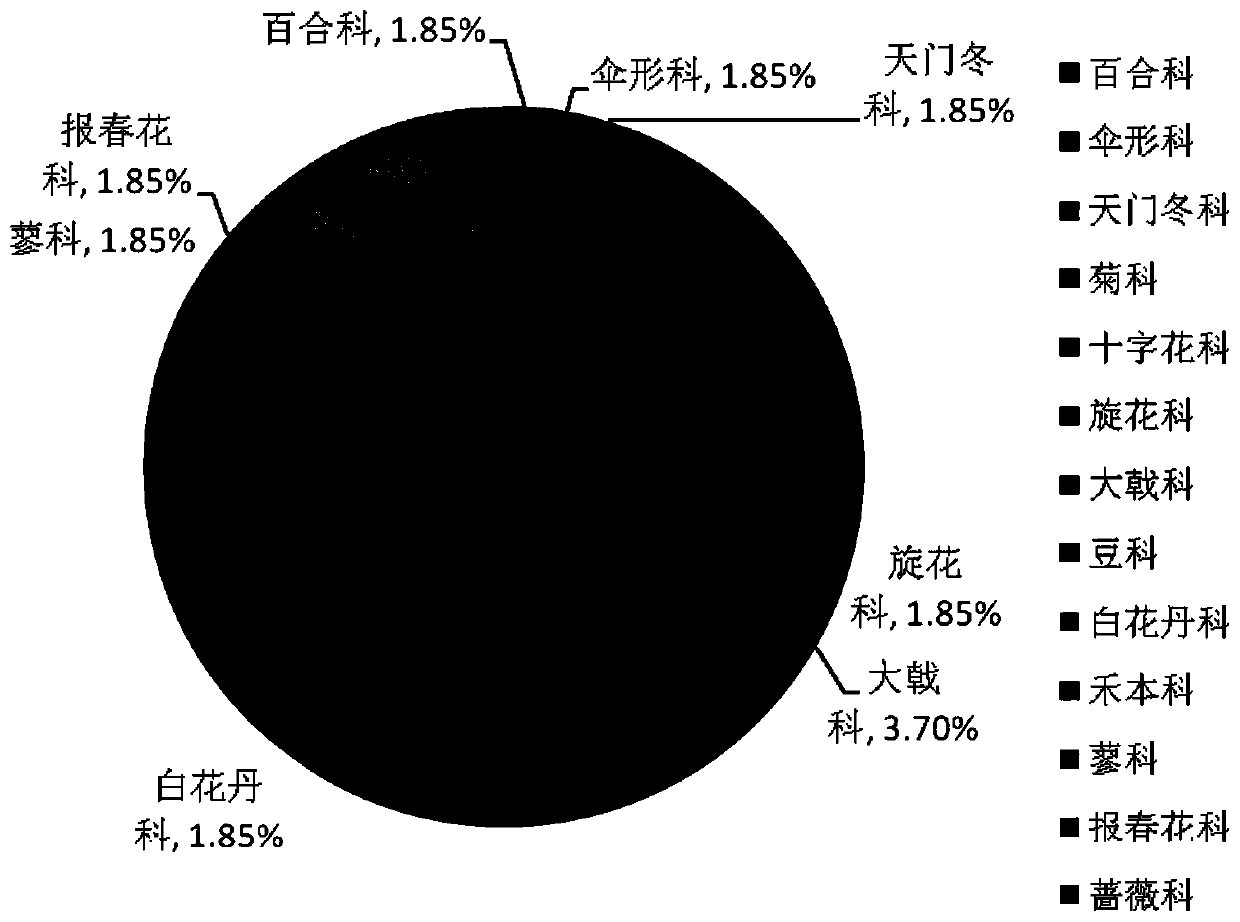
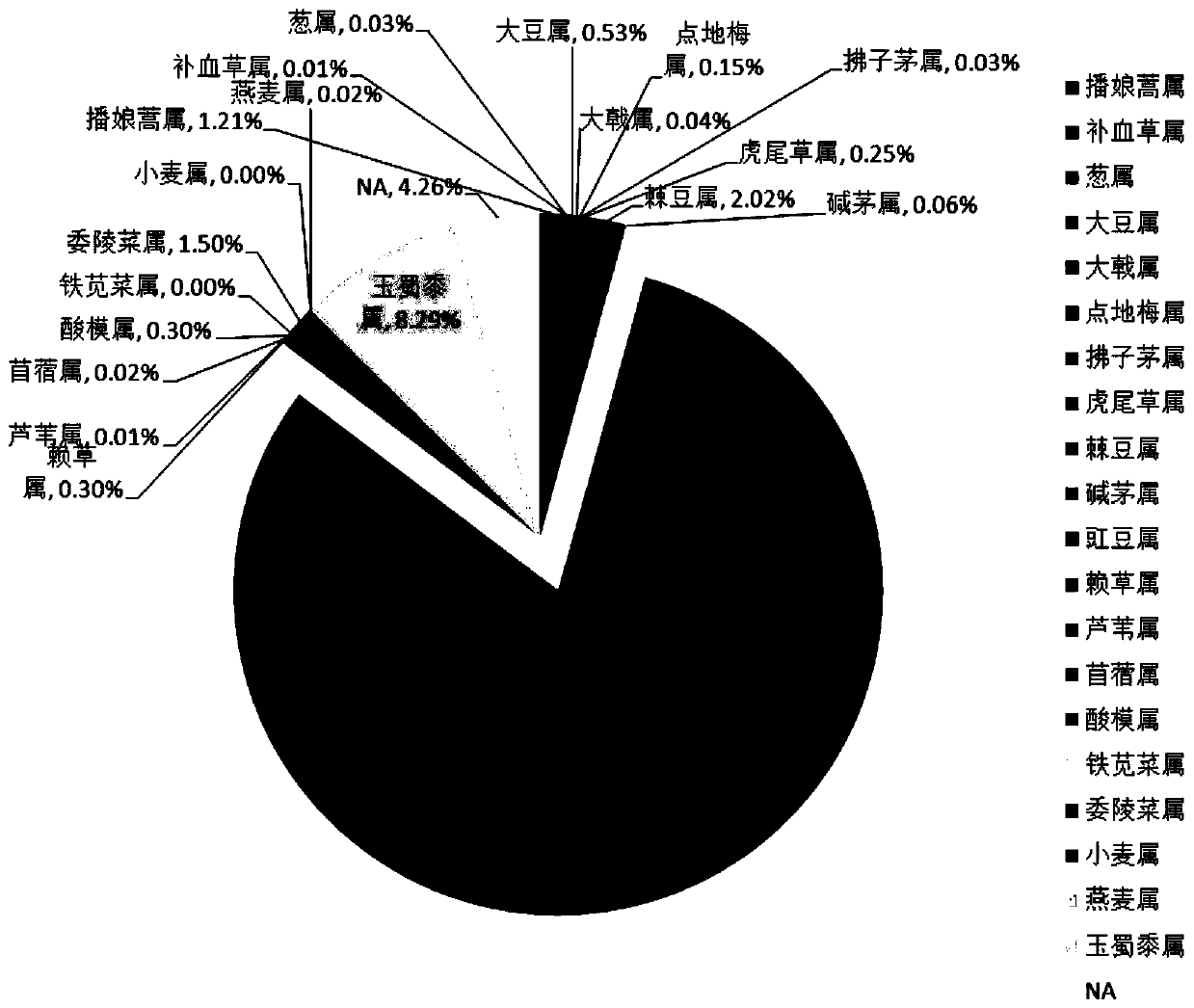
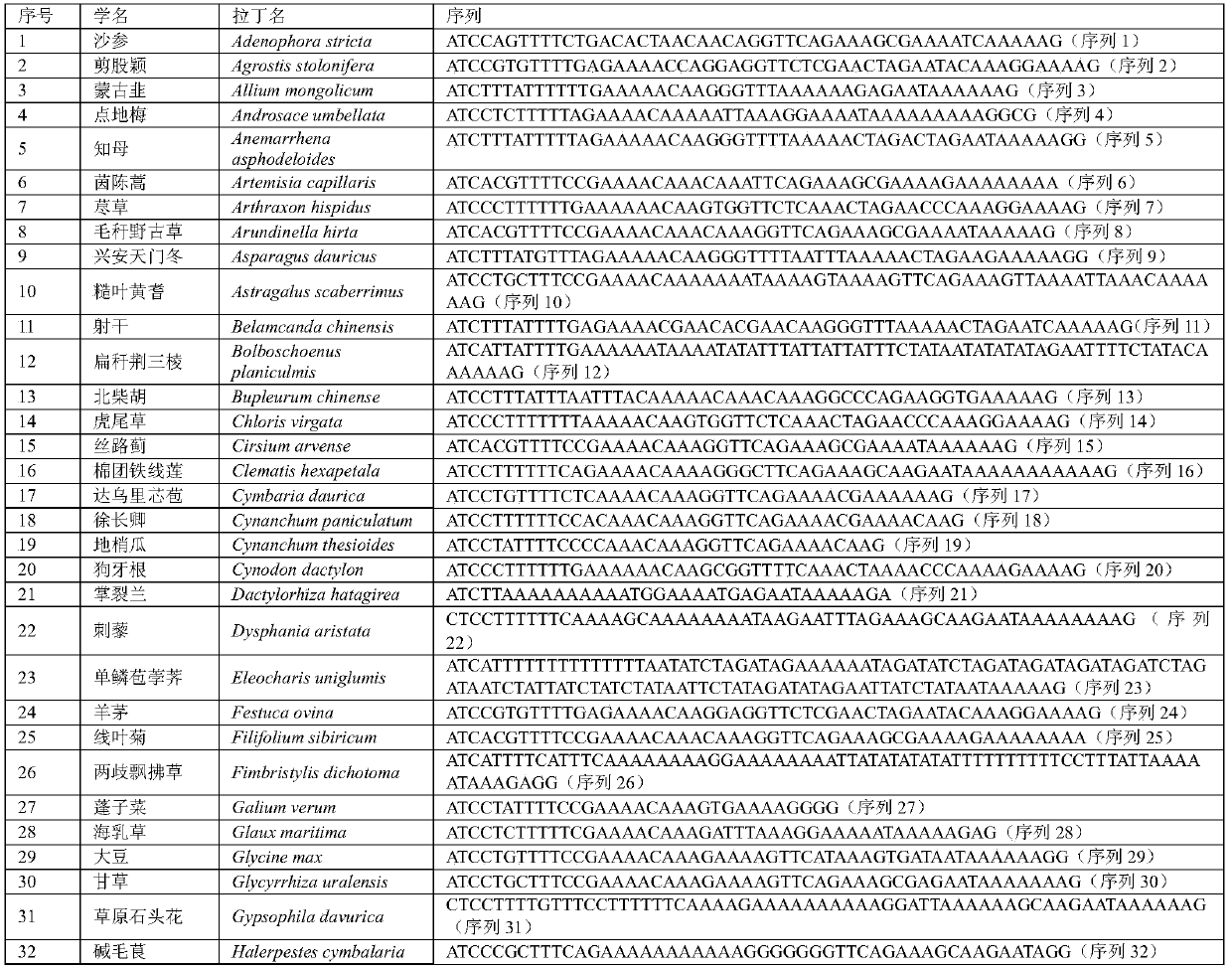
A method for analyzing great bustard food source plants by fecal dna
A technology of bustards and plants, which is applied in the field of analysis of bustard food source plants through feces DNA, and analysis of bustard food, can solve problems such as lack of scientific guidance, unclear food types and nutritional requirements of bustards, and unsuccessful artificial breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] Example 1. Analysis of bustard food source plants based on chloroplast DNA trnL barcodes
[0116] (1) Establish a complete sequence database of native plant chloroplast DNA trnL
[0117] 1. Collection of potential food source plants
[0118] In places where the bustard is active or where there are traces of bustard activity (feces, feathers, scratches, etc.), collect plant leaves, put fresh plant leaves in paper bags, add silica gel, and store them dry. Record the family, genus and species information of the collected plants.
[0119] 2. Plant DNA extraction
[0120] Take the leaves and put them in a mortar, grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen, and use a broad-spectrum plant genomic DNA rapid extraction kit (Item No.: DL116-01, Beijing Biomed Gene Technology Co., Ltd.) to extract plant genomic DNA.
[0121] Perform agarose electrophoresis on the extracted DNA, and use a UV spectrophotometer to determine the concentration and purity. For DNA with an OD260 / OD28...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Embodiment 2, the method verification based on fecal DNA analysis bustard eating habits
[0175] (1) Collect known plants to feed the great bustard in cages and collect feces
[0176]In places with great bustard activity or traces of bustard activity (feces, feathers, scratches, etc.) in the wild, 10 plants were collected from 8 species of plants. (Anemarrhenaasphodeloides), Bupleurum chinense, Leymus chinensis, Chloris virgata, Rhaponticum uniflorum, Scabiosa comosa, Potentilla discolor. In addition, it was fed with 2 plant staples, mung bean (Vigna radiata) and maize (Zea mays).
[0177] Before feeding the caged great bustards, old feces, leftover food and weeds on the ground were removed in advance to avoid interfering with subsequent analysis. Six adult great bustards with good daily feeding conditions were selected as experimental subjects, and they were given enough and clean water during the feeding period. The bustard was not fed on the first day, only water ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com