Recycling method for waste acid generated during preparation of graphite oxide through liquid-phase chemical method
A chemical method and resource-based technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, graphene, manganese oxide/manganese hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of no resource-based comprehensive treatment technology, waste of resources, high acid content, etc., and achieve operating costs Low cost, saving production cost, simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
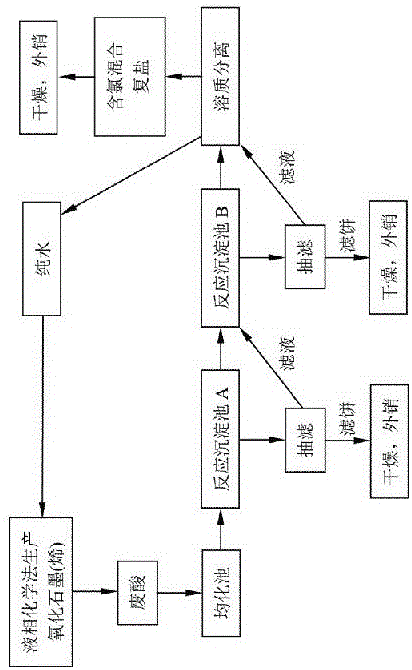
[0031] Use an acid-resistant pump to inject the waste acid into the homogenization tank for homogenization. The homogenized waste acid is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank A, and the amount of precipitant CaO and Ca(OH)2 is added according to the molar amount of sulfate ions in the waste acid. The mixture is stirred and reacted to form raw gypsum (CaSO4 2H2O). After precipitation, the supernatant is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the sediment is pumped to the filtration equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is discharged into the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the filter cake is raw gypsum. Add KOH to the reaction sedimentation tank B, adjust the pH value to 9, stir to form Mn(OH)4, then add potassium permanganate, react to form Mn3O4, after precipitation, the supernatant is pumped to the next process, and the sediment Pump to filtration equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is sent to the next process, and the filter cake i...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Use an acid-resistant pump to inject the waste acid into the homogenization tank for homogenization. The homogenized waste acid is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank A, and the precipitant CaO is added according to the molar amount of sulfate ions in the waste acid, and the reaction is stirred to form raw gypsum (CaSO4 2H2O), the supernatant after precipitation is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the sediment is pumped to the filtration equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is discharged into the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the filter cake is raw gypsum. Add NaOH to the reaction sedimentation tank B, adjust the pH value to 10, stir to form Mn(OH)2, then add potassium permanganate, and react to form MnO. After precipitation, the supernatant is pumped to the next process, and the sediment Pump to filtration equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is sent to the next process, and the filter cake is dried to obtain MnO. Th...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Use an acid-resistant pump to inject the waste acid into the homogenization tank for homogenization. The homogenized waste acid is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank A, and the amount of precipitant CaO and Ca(OH)2 is added according to the molar amount of sulfate ions in the waste acid. The mixture is stirred and reacted to form raw gypsum (CaSO4 2H2O). After precipitation, the supernatant is pumped to the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the sediment is pumped to the filtration equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is discharged into the reaction sedimentation tank B, and the filter cake is raw gypsum. Add KOH and NaOH to the reaction sedimentation tank B, adjust the pH value to 9.5, stir to form Mn(OH)2, then add sodium hypochlorite and potassium permanganate, react to form MnO2, and pump the supernatant to the next channel after precipitation In the process, the sediment is pumped to the filter equipment. Solid-liquid separation, the filtrate is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com