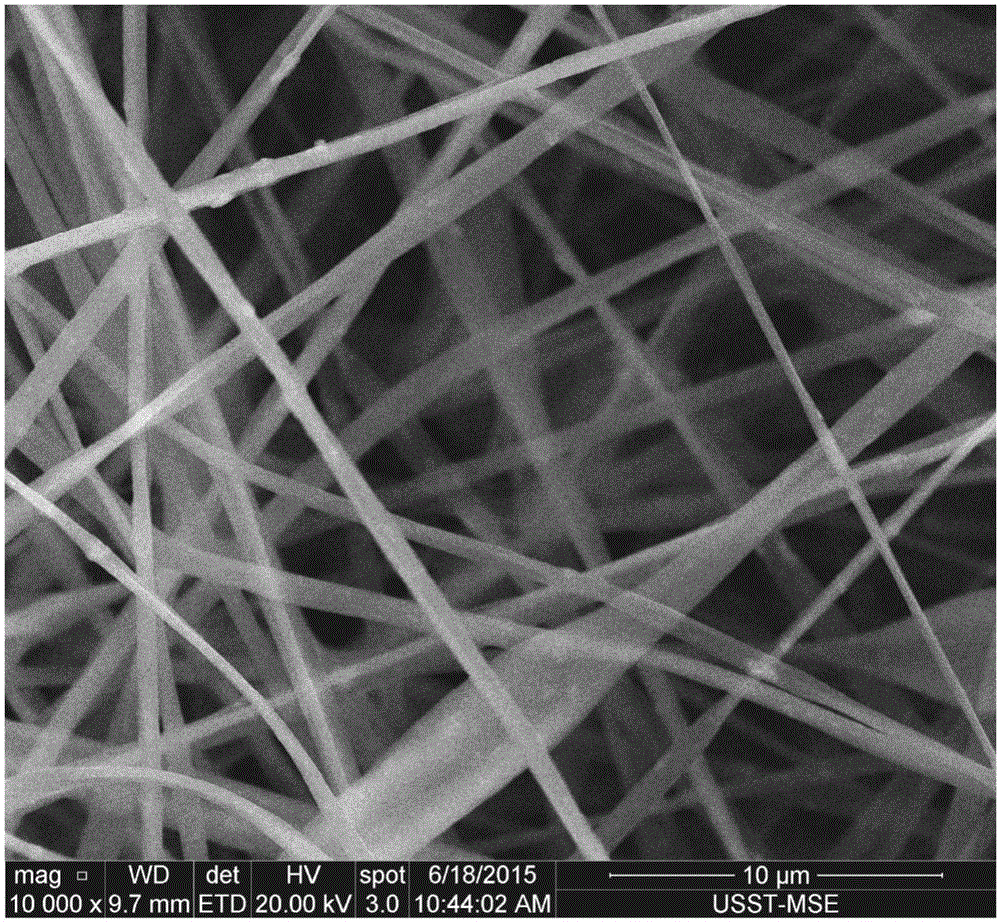
Bone tissue engineering timbering material and preparation method thereof
A technology for bone tissue engineering and scaffolding materials, applied in the field of materials science, can solve the problems of unfavorable cell growth, low mechanical strength, etc., and achieve the effects of firm bonding, little impact on human body pH, and improved strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
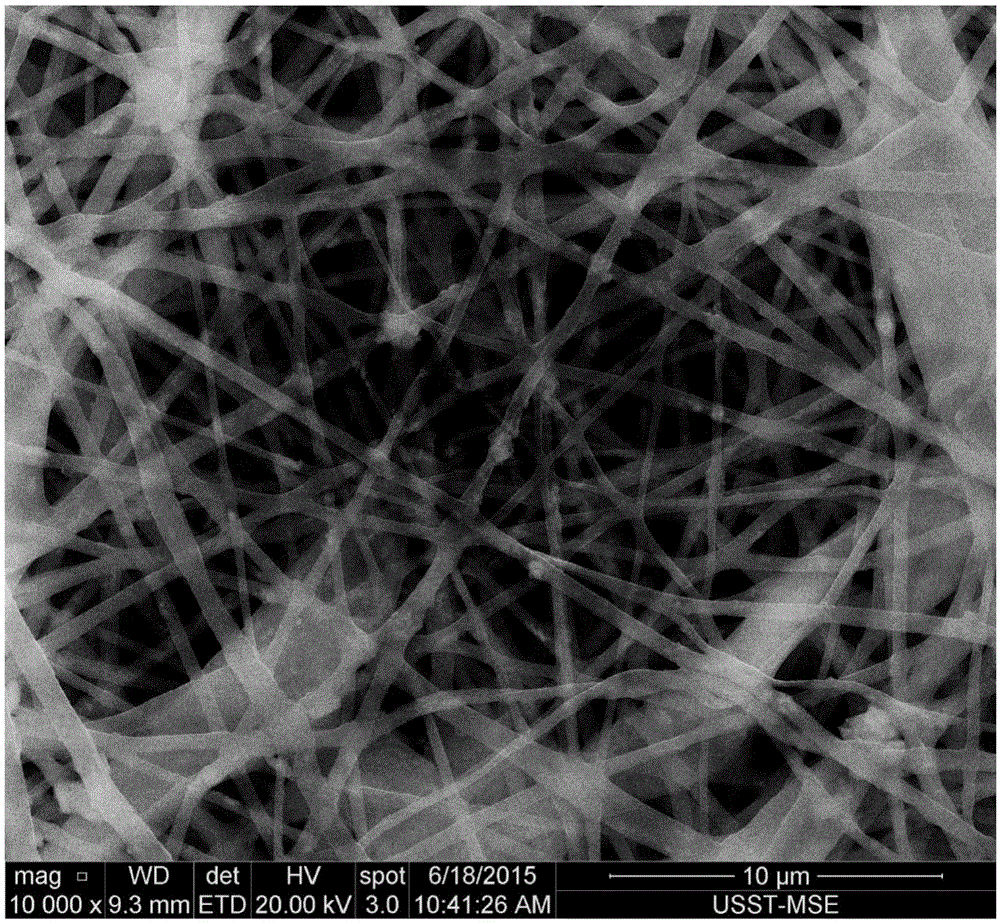
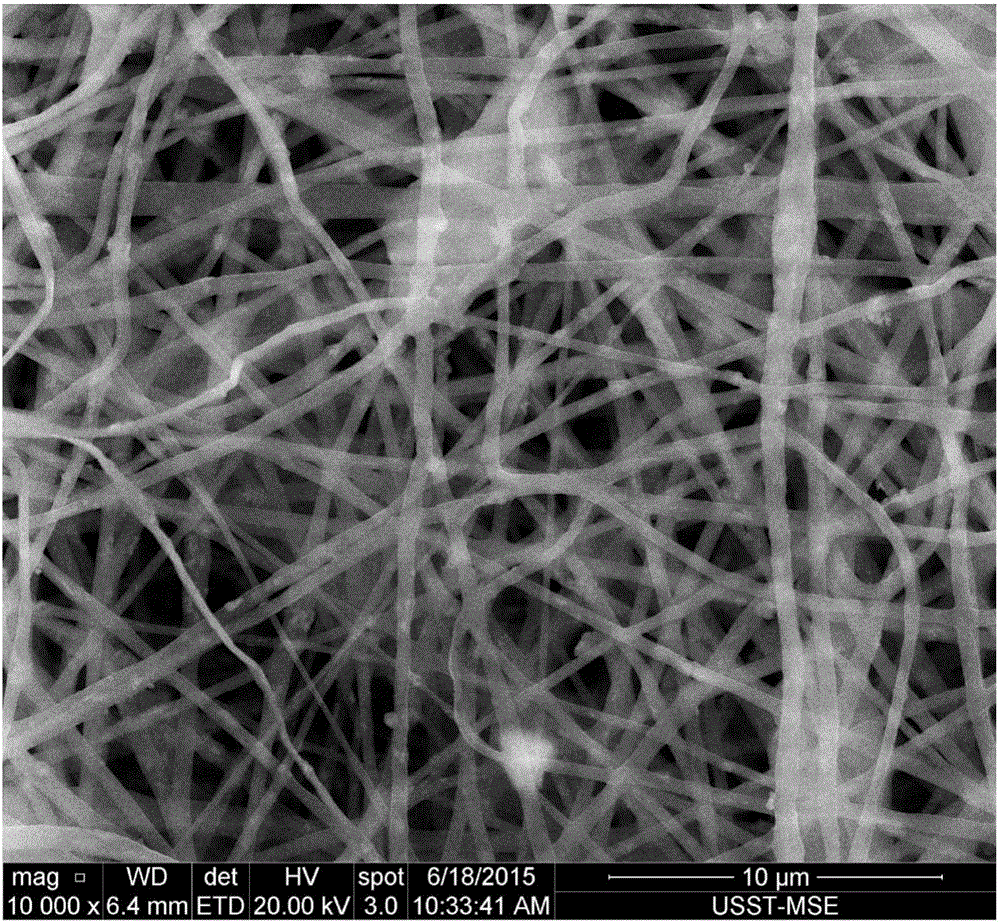
[0036] Add hydroxyapatite powder to absolute ethanol for 10 minutes of ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a suspension containing hydroxyapatite powder with a mass percentage concentration of 10%; dissolve stearic acid in 60°C absolute ethanol to prepare a mass percentage concentration 10% stearic acid solution. Then, according to the volume ratio of the hydroxyapatite suspension to the stearic acid solution of 1:1 to 3, the stearic acid solution was added to the 60°C hydroxyapatite powder suspension in the electromagnetic stirring state, and the heating and stirring were continued to make the modified The activating agent and the hydroxyapatite powder were fully reacted, the solvent was removed by suction filtration, and vacuum-dried at 60° C. for 24 hours to obtain the modified hydroxyapatite powder.
[0037] Mix dichloromethane and dimethylformamide at a volume ratio of 7:3 to form a mixed solvent. The poly-L-lactic acid is dissolved in a mixed solvent to prepare a solution w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com