Method used for producing high wet modulus cellulose fiber
A technology of cellulose fibers and a process method is applied in the field of producing high-wet modulus cellulose fibers, which can solve the problems of difficulty in controlling acid bath balance, affecting the quality of yellowing gum, and difficulty in environmental protection treatment, and achieves the solution of zinc sulfate. Balance and environmental issues, improve yellowing effect, improve fiber strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 A process for producing high wet modulus cellulose fibers
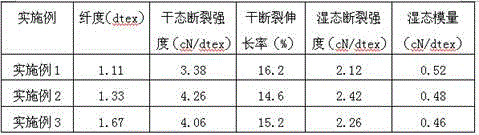
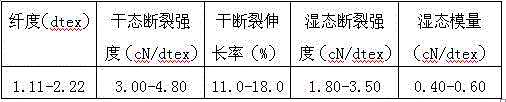
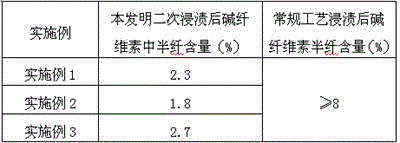
[0032]Use wood pulp with a degree of polymerization of 626 and a cellulose content of 91.2%, soak and alkalize for 20 minutes at a temperature of 40°C with a NaOH solution of a concentration of 236g / l, and the concentration of hemicellulose in the soaking solution is 32g / l to generate alkali cellulose, which is squeezed After crushing, it was aged at 36°C for 3 hours to obtain an alkali cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 432, 26.2% of cellulose A, and 17.1% of NaOH. Aged alkali cellulose is impregnated twice in NaOH solution with a concentration of 175g / l at a temperature of 28°C. The second impregnation time is 22min, and the concentration of hemicellulose in the impregnating solution is 8.2g / l, and then squeezed and pulverized to obtain Type A 29.6% cellulose, alkali cellulose containing 14.6% NaOH, of which the content of hemicellulose is 2.3%. The alkali cellulose after the secondary di...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 A process for producing high wet modulus cellulose fibers
[0034] Cotton pulp with a degree of polymerization of 960 and a cellulose content of 96.3% is used to soak and alkalize for 45 minutes at a temperature of 46°C and a NaOH solution with a concentration of 252g / l. After crushing, it was aged at 45°C for 9 hours to obtain alkali cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 463, 26.9% of cellulose A and 18.6% of NaOH. Aged alkali cellulose is impregnated twice in NaOH solution with a concentration of 196g / l at a temperature of 36°C. The hemicellulose concentration of the impregnated solution is 6.2g / l for a second impregnation time of 30 minutes, and then squeezed and pulverized to obtain Type A fiber Alkali cellulose with 28.6% plain and 15.2% NaOH, of which hemicellulose content is 1.8%. The alkali cellulose after the second dipping treatment is yellowed, and the addition of carbon disulfide is 48% of the weight of the first-class cellulose. After the ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 A process for producing high wet modulus cellulose fibers
[0036] Bamboo pulp with a degree of polymerization of 560 and a cellulose content of 90.3% is used for immersion and alkalization in NaOH solution with a concentration of 286g / l at a temperature of 36°C and a concentration of 286g / l for 50min. After crushing, it was aged at 40°C for 4 hours to obtain an alkali cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 438, 24.8% of cellulose A, and 18.3% of NaOH. Aged alkali cellulose is impregnated twice in NaOH solution with a concentration of 166g / l at a temperature of 30°C. The hemicellulose concentration of the impregnated solution is 10.8g / l for a second impregnation time of 36min, and then squeezed and pulverized to obtain Type A fiber Alkaline cellulose with 30.8% plain and 15.7% NaOH, of which hemicellulose content is 2.7%. The alkali cellulose after the second dipping treatment is yellowed, and the addition of carbon disulfide is 46% of the weight of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com