Application of gene GmRAV1 related to photoperiod adjusting and controlling of soybean
A gene, soybean technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1: Cloning and sequence analysis of the GmRAV1 gene
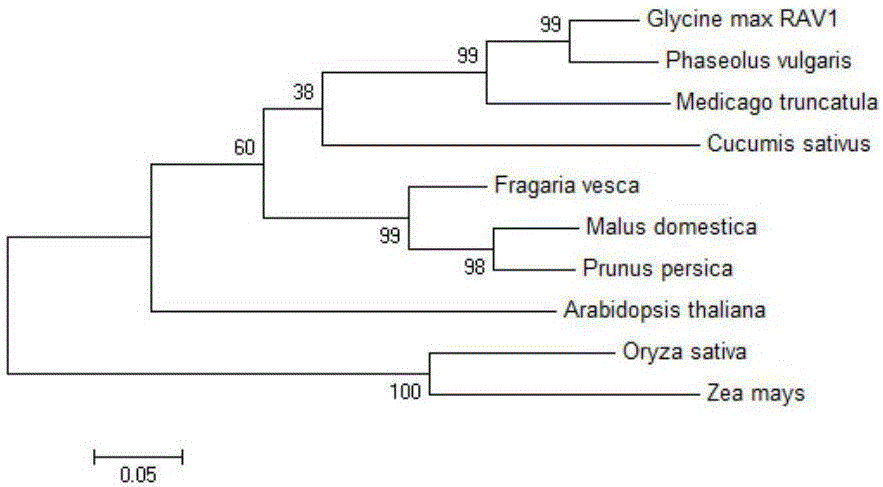
[0058] cDNA was obtained by reverse transcription using soybean leaf transcribed RNA as a template, and the cDNA was used as a PCR reaction template to obtain the gene DNA sequence of the full-length ORF region. The complete DNA sequence of the GmRAV1 transcription factor deduced from the soybean is 1757bp, the ORF is 1155bp, encoding 384 amino acids, containing the AP2 / B3 domain (see the 270th-1421st position in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1), and the sequence is in the plant genome database The accession number of phytozome (URL: https: / / phytozome.jgi.doe.gov / pz / portal.html) is Glyma01g22260.1. Homologous sequence comparison found ( figure 1 ), the sequence has 50.20% and 42.34% homology with phaseolus vulgaris (XM_007143739) and Medicago truncatula (XM_003591774) RAV1, and 47.07% homology with maize (Zea mays) (NM_001148270).
Embodiment 2
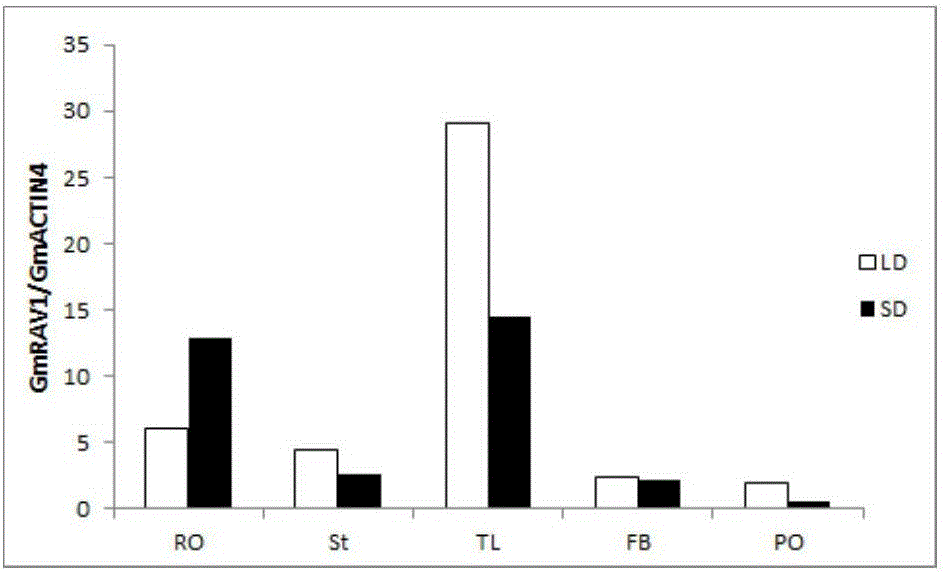
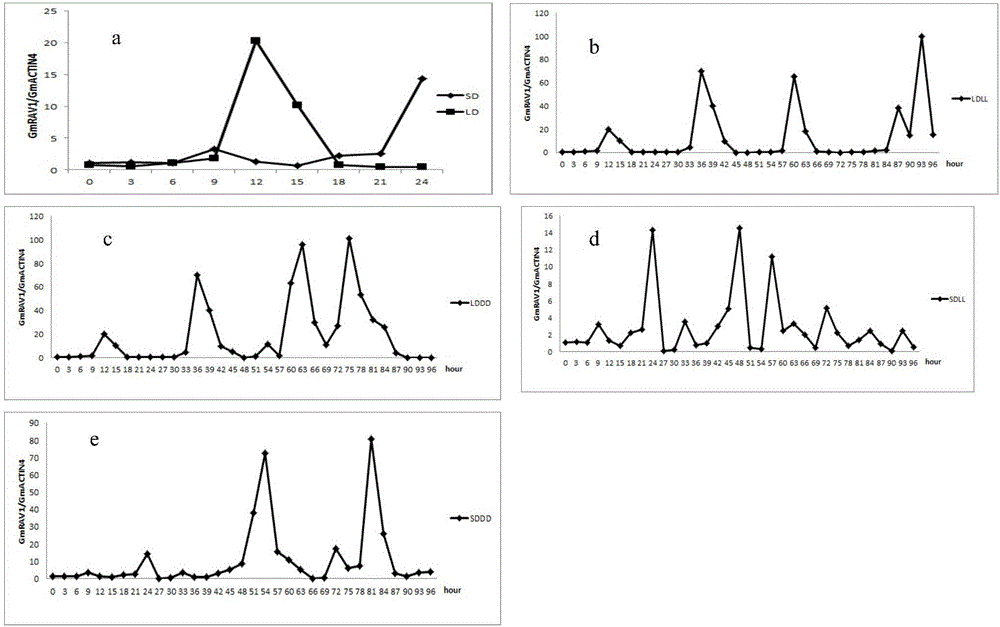
[0059] Example 2: Real-time RT-PCR analysis of the effects of day length and circadian rhythm on GmRAV1 gene expression
[0060] Soybean DN42 was cultivated in a light incubator at 25°C, 250mol m -2 sec -1 White light, grow under long-day (16h / 8h light / dark) (LD) conditions and grow on the 20th day after emergence (determined as 0d), part of it is transferred to short-day (SD) photoperiod (8h / 16h light / dark) growth, At 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, and 24 days after transfer, LD and SD leaves were collected simultaneously, quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80°C, and RNA was extracted. According to SYBR(R)ExScriptTM RT- The program of PCR Kit is used to carry out the fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction. The amplified fragment of GmRAV1 is 144bp, and the amplified fragment of the soybean housekeeping gene Actin4 (AF049106) is 214bp. The primers are as follows: GmRAV1 sense primer: GGTGTAGTGGCATAGTGGC, antisense primer:
[0061] TAAGAAGGGGAGAAGCTAGA; Actin4 sense pr...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: Construction of plant expression vector pCAMBIA3301-GmRAV1, transformation of soybean cotyledon nodes by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana by tidbit infection method
[0063] cDNA was obtained by reverse transcription using soybean leaf transcribed RNA as a template, and the cDNA was used as a PCR reaction template to obtain the gene DNA sequence of the full-length ORF region. The complete DNA sequence of GmRAV1 transcription factor inferred from the soybean is 1757bp, and the ORF is 1155bp. Using Bgl II and BstE II as restriction sites, design cloning primers, and perform PCR reaction at 94°C for 5min; 38 cycles: 94°C for 30s , 58°C for 30s, 72°C for 1min; 72°C for 10min; PCR products were subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments were recovered according to the instructions of the OMEGA GelExtraction Kit, and TaKaRa’s pMD18-T vector was used for ligation. The molar ratio of the gene and the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com