Pretreatment method of antibiotic production waste water
A technology for the production of wastewater and antibiotics, applied in multi-stage water treatment, water/sewage treatment, natural water treatment, etc., can solve problems such as ineffective treatment, secondary pollution, waste of water resources, etc., and reduce the pressure of subsequent biochemical treatment , low processing cost, high processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
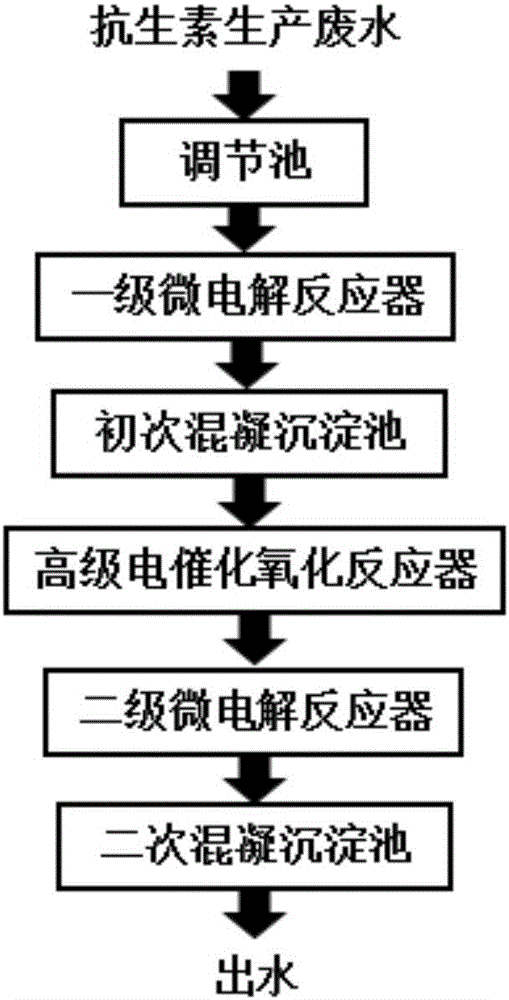
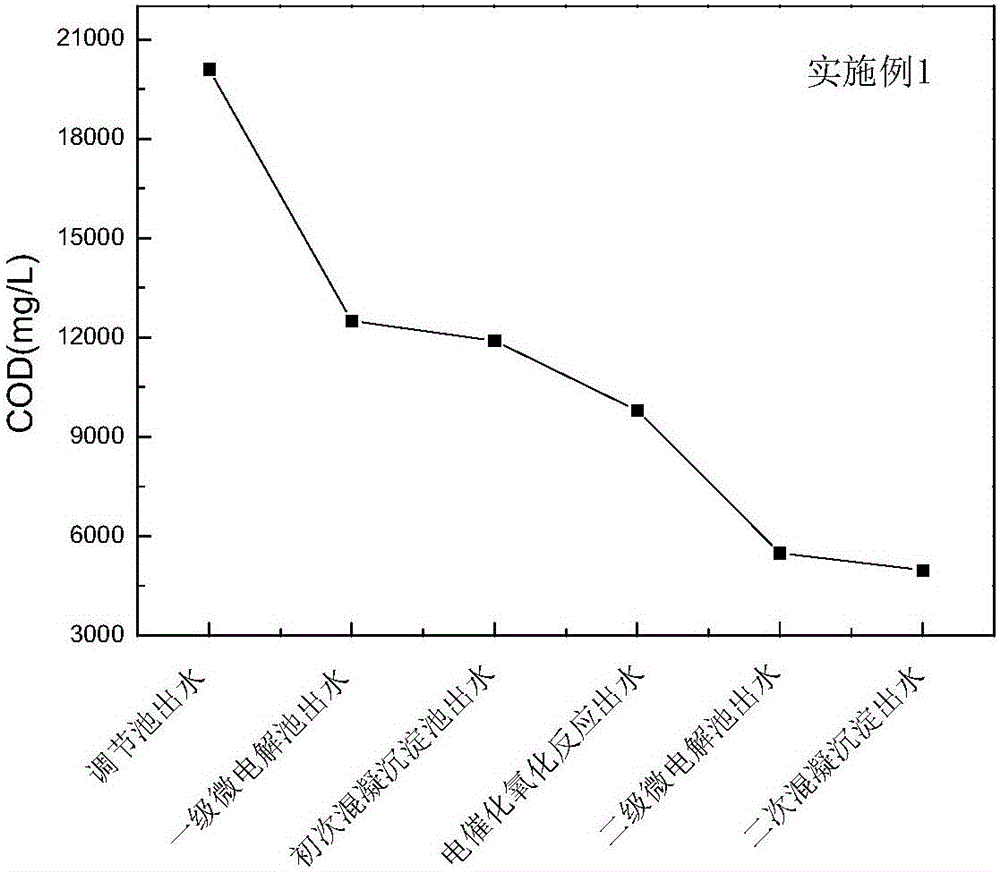
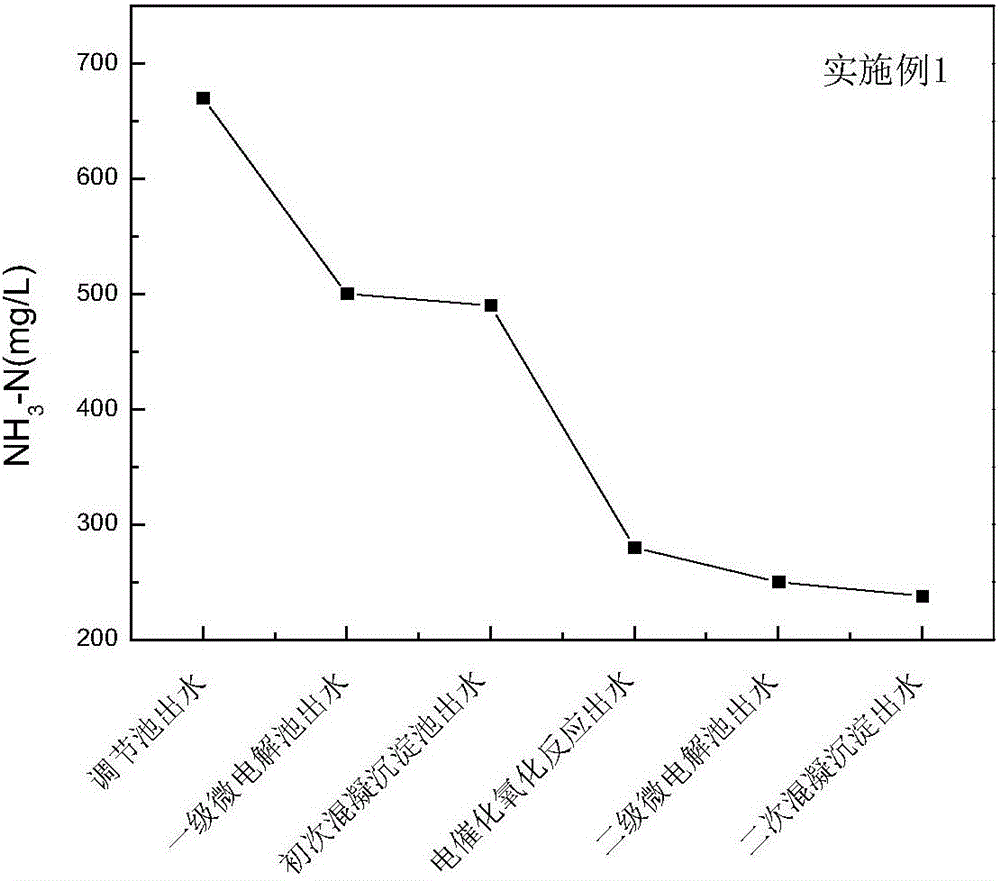
[0051] Embodiment 1: Azithromycin production wastewater pretreatment method:
[0052] Azithromycin production wastewater from a pharmaceutical company in Jiangsu was taken for a pilot test. The experimental process is as follows:
[0053] (1) First-level micro-electrolysis: Azithromycin production wastewater is discharged from the production workshop and enters the regulating pool. 2 SO 4 After adjusting the pH of the wastewater to 3.0-5.0, it enters the first-stage micro-electrolysis reactor. In the micro-electrolysis reactor, the wastewater rapidly undergoes galvanic reaction and redox reaction. Under the action of aeration, the wastewater and the structured packing are fully contacted and mixed to make the reaction continue. Proceed efficiently.
[0054] (2) Primary coagulation and sedimentation: After micro-electrolysis treatment, most of the small molecular organic matter in the wastewater is removed, and at the same time, the filler has a certain decolorization effect ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: solvent wastewater pretreatment method
[0061] The solvent wastewater from a pharmaceutical company in Jiangsu was taken for a pilot test. The experimental process is as follows: (1) First-level micro-electrolysis: the solvent wastewater is discharged from the production workshop and enters the regulating pool. 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the wastewater to 3.0-5.0 and then enter the primary micro-electrolysis reactor. Under the action of aeration, the waste water and the structured packing are fully contacted and mixed, so that the reaction can continue to proceed efficiently.
[0062] (2) Primary coagulation and sedimentation: By adding NaOH to adjust the pH of the wastewater to above 9.0, and adding PAC and PAM, the suspended particles in the wastewater are flocculated and removed by sedimentation, and finally achieve the effect of mud-water separation.
[0063] (3) Advanced electrocatalytic oxidation: After the initial coagulation and precipitation, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3: Azithromycin production wastewater pretreatment method
[0069] Azithromycin production wastewater from a pharmaceutical company in Liaoning was taken for a pilot test. The experimental process is as follows:
[0070] (1) First-level micro-electrolysis: Azithromycin production wastewater is discharged from the production workshop and enters the regulating pool. 2 SO 4 After adjusting the pH of the wastewater to 3, it enters the first-stage micro-electrolysis reactor. The wastewater undergoes galvanic reaction and redox reaction rapidly in the micro-electrolysis reactor. Under the action of aeration, the wastewater and the structured packing are fully contacted and mixed to make the reaction continue and efficiently proceed. .
[0071] (2) Primary coagulation and sedimentation: After micro-electrolysis treatment, most of the small molecular organic matter in the wastewater is removed, and at the same time, the filler has a certain decolorization effect on...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| chemical oxygen demand (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| loss rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com