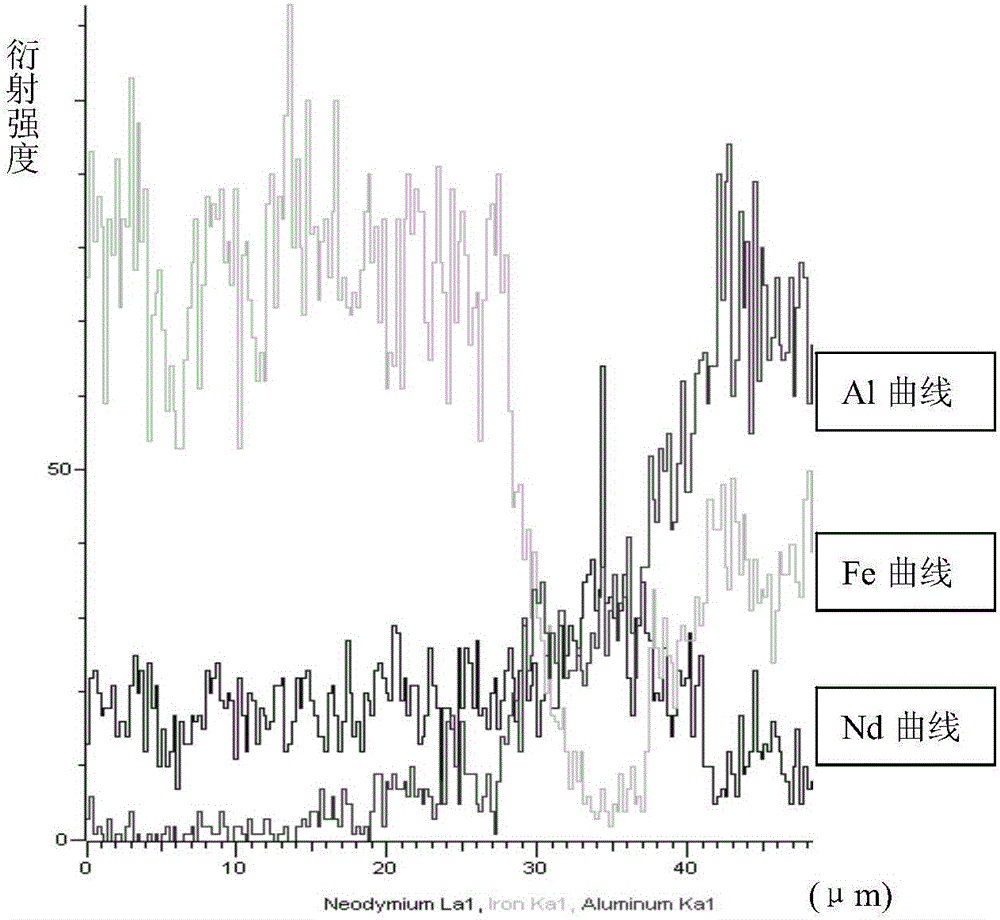
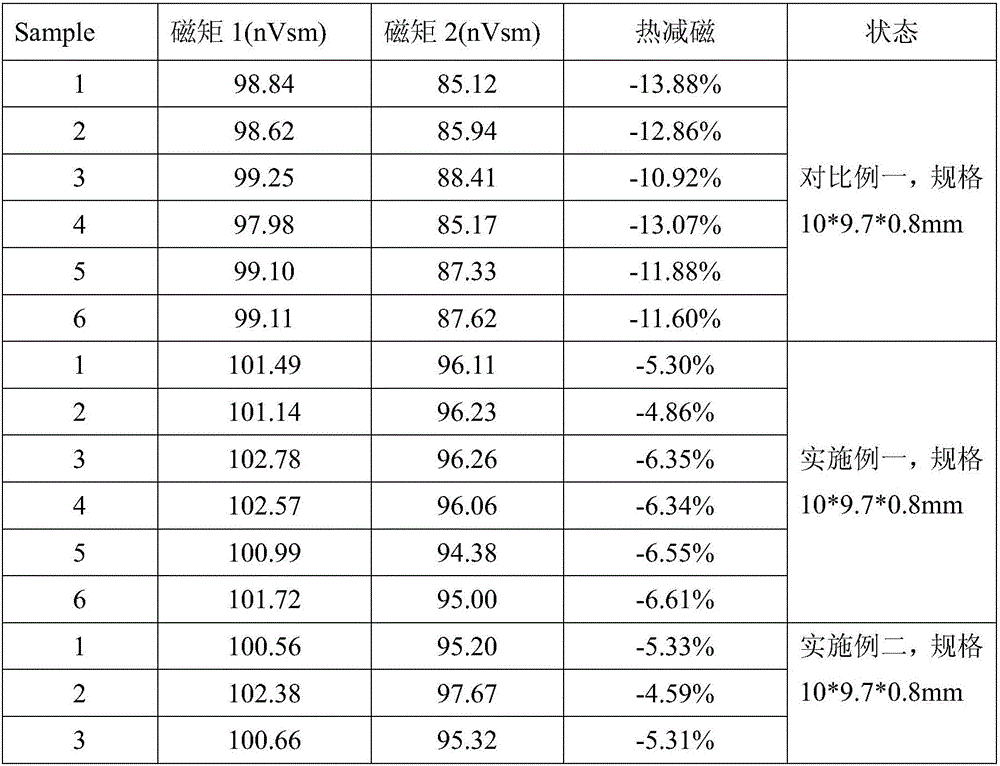
Preparation method of sintering neodymium iron boron sheet magnet
A technology of NdFeB and flakes, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient improvement ability, smaller grain size, and limited effect, so as to avoid fine grain size Minimize, reduce hard magnetic coupling, reduce the effect of direct contact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: A kind of preparation method of sintered NdFeB sheet magnet, comprises the following steps:
[0028]① Configure the raw materials of sintered NdFeB sheet magnets according to the design requirements, melt the raw materials in a vacuum electromagnetic induction furnace, cast them into quick-setting sheets with a thickness of 0.2-0.6mm at a temperature of 1450°C, and then speed them up in a hydrogen crushing furnace The condensed sheet is subjected to hydrogen crushing treatment to obtain a coarse powder with a particle size of 0.1-3mm, and then the coarse powder is accelerated by a high-pressure gas of 0.4-0.6Mpa in the airflow milling equipment to make it collide with each other to form a specific surface area and an average particle size 2.0 ~ 4.0μm powder;
[0029] ②Put the powder into the mold cavity of the forming press, and press the powder under the action of the orientation magnetic field to obtain a sintered NdFeB green body;
[0030] ③ Sintering ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment two: a kind of preparation method of sintered NdFeB sheet magnet, comprises the following steps:
[0040] ① Configure the raw materials of sintered NdFeB sheet magnets according to the design requirements, melt the raw materials in a vacuum electromagnetic induction furnace, cast them into quick-setting sheets with a thickness of 0.2-0.6mm at a temperature of 1450°C, and then speed them up in a hydrogen crushing furnace The condensed sheet is subjected to hydrogen crushing treatment to obtain a coarse powder with a particle size of 0.1-3mm, and then the coarse powder is accelerated by a high-pressure gas of 0.4-0.6Mpa in the airflow milling equipment to make it collide with each other to form a specific surface area and an average particle size 2.0 ~ 4.0μm powder;
[0041] ②Put the powder into the mold cavity of the forming press, and press the powder under the action of the orientation magnetic field to obtain a sintered NdFeB green body;
[0042] ③ Sinteri...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment three: a kind of preparation method of sintered NdFeB sheet magnet, comprises the following steps:
[0052] ① Configure the raw materials of sintered NdFeB sheet magnets according to the design requirements, melt the raw materials in a vacuum electromagnetic induction furnace, cast them into quick-setting sheets with a thickness of 0.2-0.6mm at a temperature of 1450°C, and then speed them up in a hydrogen crushing furnace The condensed sheet is subjected to hydrogen crushing treatment to obtain a coarse powder with a particle size of 0.1-3mm, and then the coarse powder is accelerated by a high-pressure gas of 0.4-0.6Mpa in the airflow milling equipment to make it collide with each other to form a specific surface area and an average particle size 2.0 ~ 4.0μm powder;
[0053] ②Put the powder into the mold cavity of the forming press, and press the powder under the action of the orientation magnetic field to obtain a sintered NdFeB green body;
[0054] ③ Sinte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com