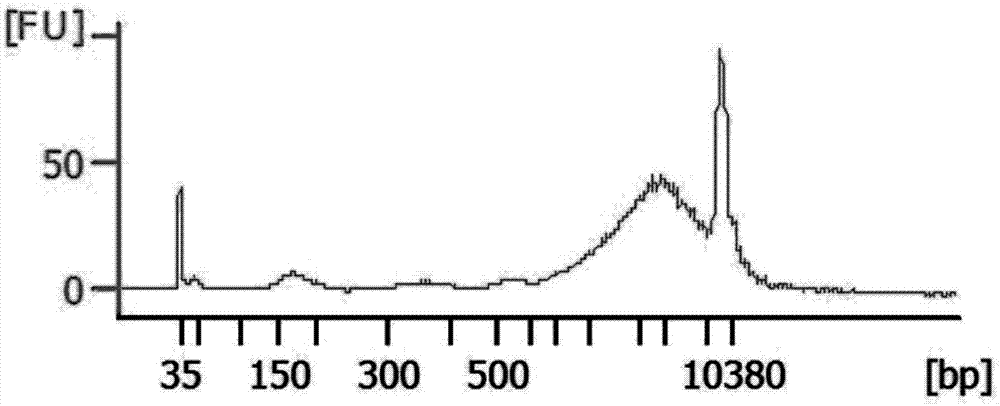
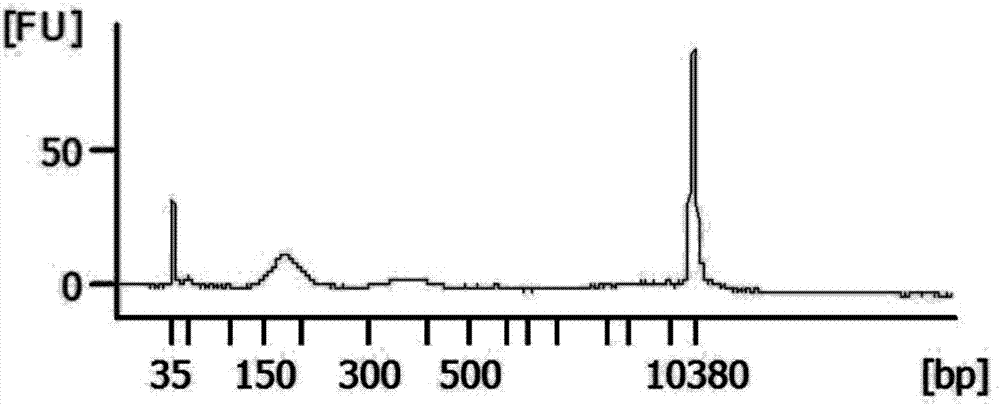
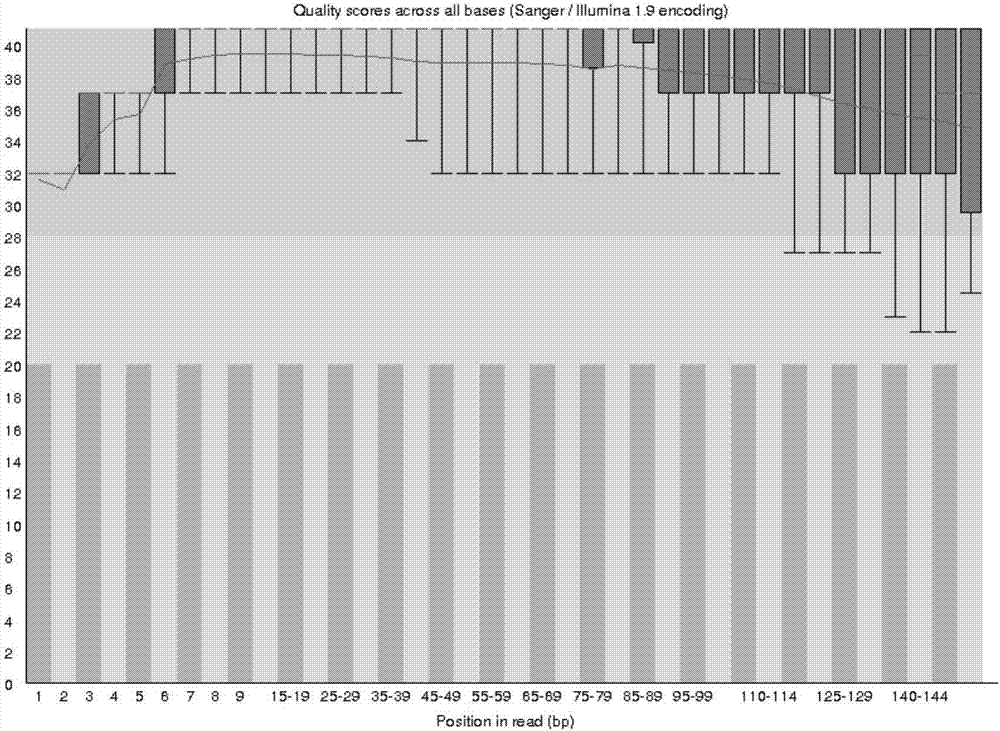
Method for extracting cfDNA (cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid) from hydrothorax, kit and constructed cfDNA library
A kit and pleural effusion technology, applied in the field of cfDNA library, can solve problems such as affecting detection, and achieve the effect of solving the problems of sample singleness and detection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1 Obtaining cfDNA in pleural effusion samples
[0077] 1 Separation of supernatant and sediment from pleural fluid samples
[0078] Take the freshly collected pleural effusion sample, centrifuge at 1800rpm for 10 min, absorb the pleural effusion supernatant into a new centrifuge tube, discard the pleural effusion sediment, and store the pleural effusion supernatant sample in a refrigerator at 4°C (-80°C).
[0079] 2 Column adsorption separation of cfDNA in pleural effusion supernatant
[0080] 2.1 Sampling: Take out the pleural fluid supernatant sample stored at 4°C (-80°C), and then process it at 16000rpm at 4°C for 10 min;
[0081] 2.2 Prepare the premix: prepare the lysate Buffer ACL Mix (QIAGEN), draw 2 times the total volume of pleural effusion of BufferACL Mix, invert and mix well;
[0082] 2.3 Add proteinase K: add 20 μl Carrier RNA to each ml of pleural fluid sample, then add 200 μl proteinase K to fully digest;
[0083] 2.4 Add ACL: Add 2 ml of lysis...
Embodiment 2
[0105] The construction of embodiment 2 DNA library
[0106] 3.1 Separation of cfDNA size fragments
[0107] a) Add enzyme-free water to the cfDNA sample extracted in Example 1 to make up to 50 μl, add 35 μl magnetic beads Axygen beads, and mix with a pipette;
[0108] b) Place the sample on the magnetic separation rack until the supernatant is clear, then pipette the supernatant into another 1.5ml low adsorption tube;
[0109] c) Add 65 μl magnetic beads Axygen beads to resuspend with a pipette and mix well, place on a magnetic separation rack until the supernatant is clear, discard the supernatant, add 50 μl of 75% ethanol to wash, remove the residual liquid with the pipette, and dry in the air;
[0110] d) Add 56 μL of enzyme-free water, mix well, pipette 51 μl of clarified liquid into a new 1.5ml centrifuge tube;
[0111] e) Take 1 μl to measure DNA concentration with Qubit. The resulting 50 μl ctDNA small fragments were directly used in the cfDNA KAPA library construct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com