Bionic enzyme linked immunosorbent assay method capable of rapidly determining sulfonamide antibiotic residues
An immunoassay method and rapid assay technology, applied in the field of biomimetic enzyme-linked immunoassay for rapid determination of sulfonamide antibiotic residues, can solve the problems of unsuitability for large-scale screening assays, cumbersome preparation of biological antibodies, low sensitivity of color reaction, etc. Overcome the effects of long preparation period, good fluorescence response performance and high fluorescence response performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0025] 1. Specific examples
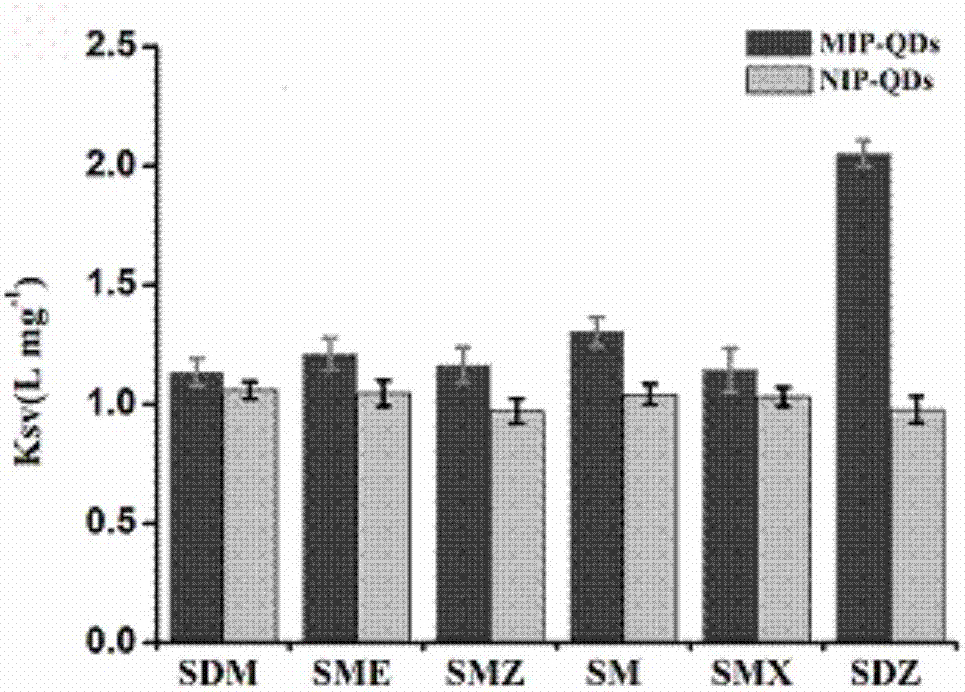
[0026] The present invention uses sulfonamide antibiotic molecular imprinting-quantum dot nanostructure artificial antibody as biomimetic antibody and signal response substance, and establishes a rapid detection method with high sensitivity and selectivity for sulfonamide antibiotics based on the principle of enzyme-linked immunosorbent technology. The specific process as follows:
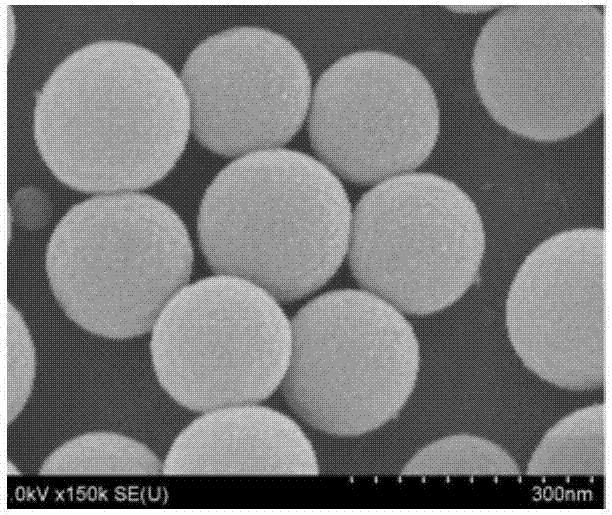
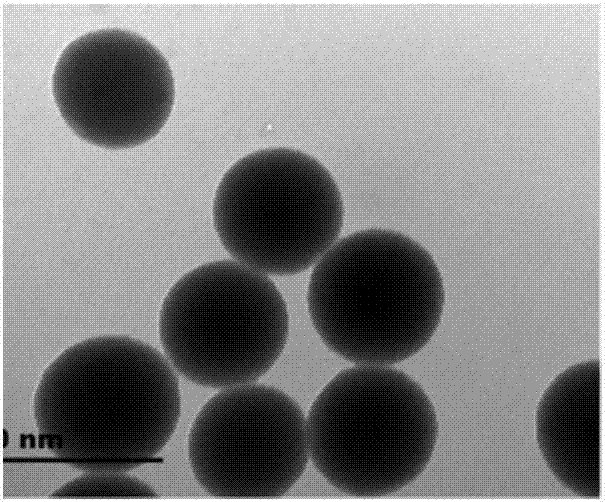
[0027] 1. Preparation of artificial antibody with molecular imprinting-quantum dot nanostructure
[0028] Add 7.5 mL cyclohexane and 1.8 mL Triton X-100 into a two-necked flask, stir magnetically at 150 rpm for 15 min, then add 400 μL of quantum dot solution with a concentration of 2.5 nmol / mL (quantum dots are CdS / ZnS), 50 μL tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and 100 μL ammonia water were stirred magnetically for 2 h; then 200 μL temp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com