Method using ultraviolet spectroscopy to detect p-coumaric acid in high-throughput manner
A technology of p-coumaric acid and ultraviolet light, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of low detection efficiency, difficulty in random mutation transformation of highly active TAL, low activity of tyrosine ammonia lyase and large-scale synthesis, etc., to achieve high detection efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Analysis of Spectroscopy Properties
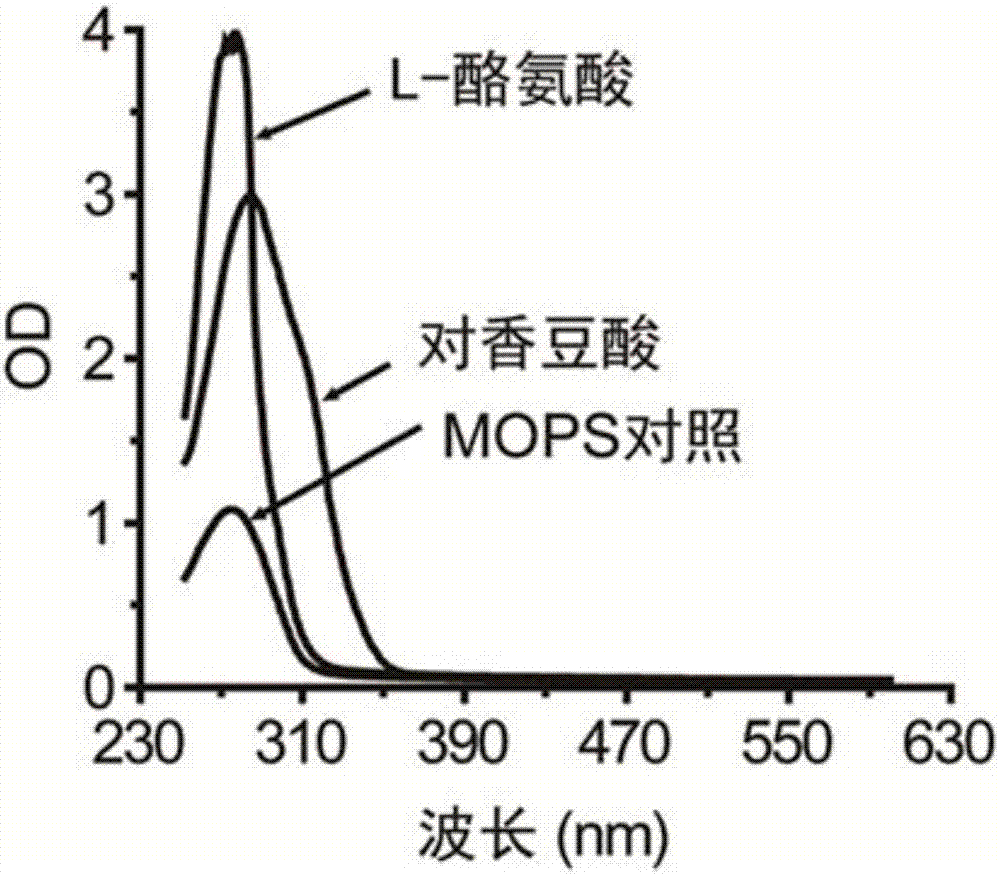
[0024] First, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as a solvent to prepare 200 mg / L p-coumaric acid and 50 mg / L L-tyrosine. Since L-tyrosine is the direct precursor of coumaric acid, in order to verify whether L-tyrosine and the UV absorption of coumaric acid will interfere with each other, the prepared sample was placed in the multifunctional microplate reader Cytation 3 The plate reader (BioTek) performs full-wavelength scanning from 230 to 999 nm. The results show that both substances have a maximum absorption peak at 290nm ( figure 1 ). That is, when the auxochrome group is not added, it is impossible to separate the maximum absorption peak of L-tyrosine and coumaric acid, so it is impossible to quantitatively analyze coumaric acid.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2 Effect of detection wavelength on detection results
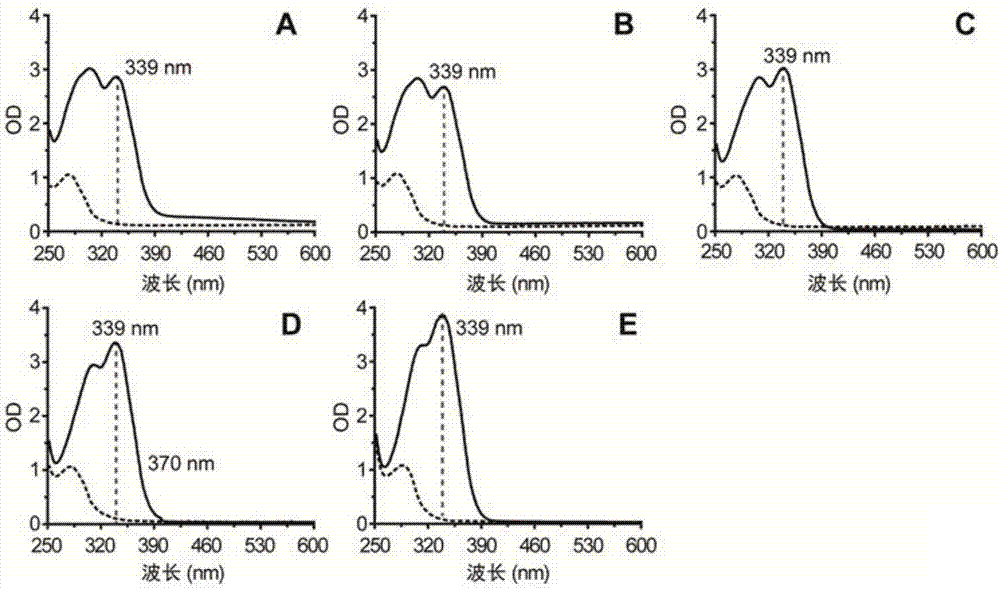
[0026] One of the important challenges in the detection of fermentation product yield is that the presence of complex components in the fermentation broth may interfere with the detection of target compounds. We use MOPS medium to cultivate wild-type E. coli BL21(DE3) for 48h. Subsequently, the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 5 minutes, and the supernatant was taken as the solvent (natural pH ≈ 4.5) to prepare 2% NaBH 4 The solution is used as an auxochrome group, and 10mg / L p-coumaric acid and 50mg / L L-tyrosine are added respectively. Subsequently, a multi-functional microplate reader was used to scan the full wavelength of 230-999nm. The scan results showed that when MOPS was used as a fermentation medium to culture E. coli BL21 (DE3) in the fermentation broth, NaBH 4 As a auxochrome group, a new absorption peak can be formed for coumaric acid at 339nm, and there is less overlap with the ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3 NBH 4 The influence of solution concentration and pH of fermentation broth on test results
[0029] (1) Use MOPS medium to cultivate wild-type E. coli BL21(DE3) for 48h, then centrifuge the fermentation broth at 12000rpm for 5min, take the supernatant as the solvent (natural pH≈4.5), and prepare the mass fractions of 1% and 2% respectively , 4% and 6% NaBH 4 The solution is used as a solvent to detect p-coumaric acid.
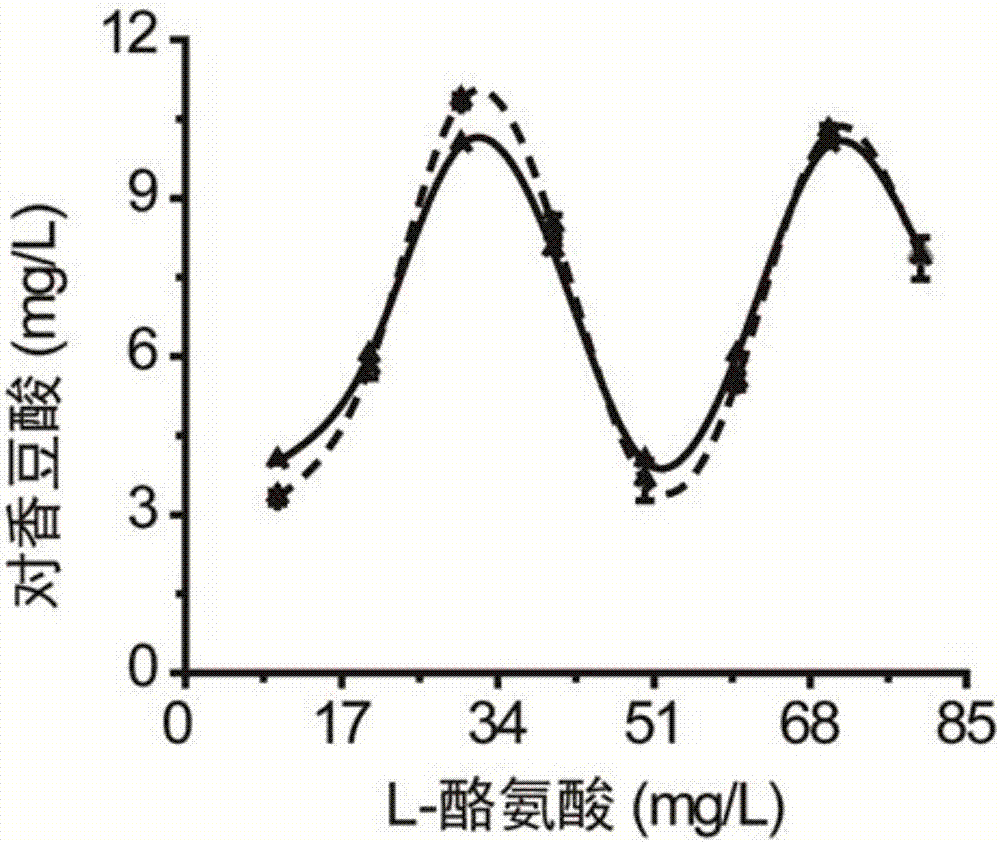
[0030] (2) Prepare standard solutions of p-coumaric acid with concentrations of 4, 8, 12, 16 and 20 mg / L with DMSO as the solvent. The standard solution of p-coumaric acid was compared with the NaBH of 1%, 2%, 4% and 6% obtained in step (1). 4 The solution is mixed in equal volume, and then the UV absorption intensity is detected in a multifunctional microplate reader to make a standard curve. Take the standard curve R 2 For the evaluation criteria, the results are shown in Table 1:
[0031] Table 1 NaBH 4 Concentration optimization
[0032]
[0033]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com