A method for preparing three-dimensional mesoscopic device
A three-dimensional mesoscopic and device technology, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing microstructure devices, microstructure devices, and techniques for producing decorative surface effects, etc., can solve large-scale production obstacles, interrupt production processes, and increase time-consuming preparation of mesoscopic devices Problems such as production area, to achieve excellent mechanical properties, low internal friction, high strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1, utilize the Pd that diameter is 30 microns 40 Ni 10 Cu 30 P 20 Fabrication of microsprings with an outer diameter of 300 microns using metallic glass fibers
[0049] 1, prepare the palladium (Pd) base metal glass fiber of required diameter: adopt in supercooled liquid phase region, the palladium base metal (atomic percentage is Pd) that diameter is 1 millimeter 40 Ni 10 Cu 30 P 20 ) glass rods for thermoplastic stretching to produce Pd-based metal glass fibers with a diameter of about 30 microns.
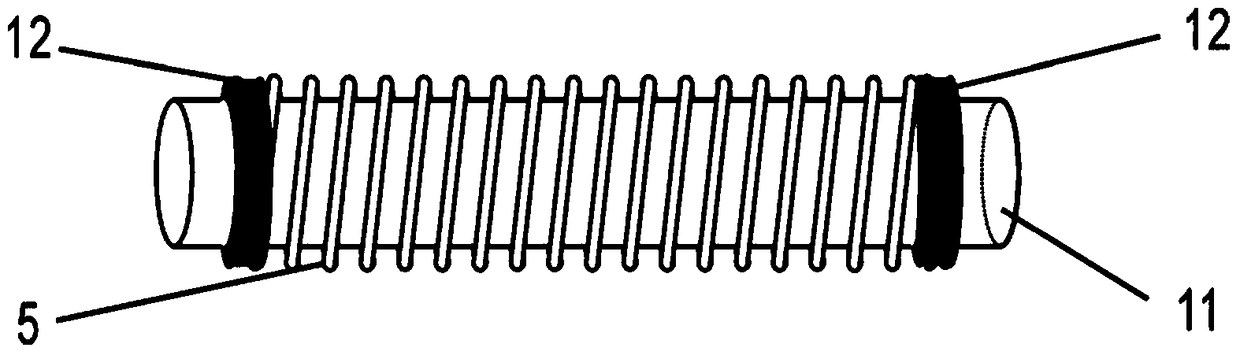
[0050] 2. Provide a cylindrical fixed shape mold, such as figure 1 As shown, the fixed shape mold 11 is a cylindrical stainless steel column with a diameter of 240 microns and a length of 30 mm, with matching mechanical fixtures 12 attached at both ends.
[0051] 3. The Pd-based metal glass fiber with a diameter of 30 microns prepared in step 1 is elastically wound by means of the cylindrical fixed shape mold 11 in step 2, and the required three-dimensio...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Embodiment 2, utilize the Mg that diameter is 10 microns 65 Cu 25 Gd 10 Fabrication of microscale springs with an outer diameter of 100 microns using metallic glass fibers
[0079] The method and steps of this example are basically the same as in Example 1.
[0080] When preparing magnesium-based metallic glass microscale springs, the power density of the irradiated nanosecond pulsed laser is 2.75×10 11 J / (m 2 s), the irradiation time is 20 minutes.
[0081] The size and shape parameters of the prepared Mg-based metallic glass microscale springs were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Such as Figure 10 As shown, the outer diameter of the micro-scale spring made of Mg-based metallic glass fibers with a diameter of 10 microns is about 100 microns, and the distance between nodes is about 46.5 microns. It can be seen from the figure that there is no obvious shear band on the surface of the metallic glass micro-scale spring, which shows that the method f...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Embodiment 3, utilize the Zr that diameter is 40 microns 52.5 Ti 5 Al 10 Cu 17.9 Ni 14.6 Fabrication of microscale springs with an outer diameter of 380 microns using metallic glass fibers
[0084] The method and steps of this example are basically the same as in Example 1.
[0085] When preparing zirconium-based metallic glass microscale springs, the power density of the irradiated nanosecond pulsed laser is 4.55×10 11 J / (m 2 s), the irradiation time is 20 minutes.
[0086] The size and shape parameters of the prepared zirconium-based metallic glass microscale springs were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Such as Figure 10 As shown, the outer diameter of the microscale spring made of Zr-based metallic glass fibers with a diameter of 40 microns is about 380 microns, and the distance between nodes is about 131.1 microns. It can be seen from the figure that there is no obvious shear band on the surface of the metallic glass micro-scale spring, whi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com