Patents
Literature
82results about How to "Avoid performance changes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
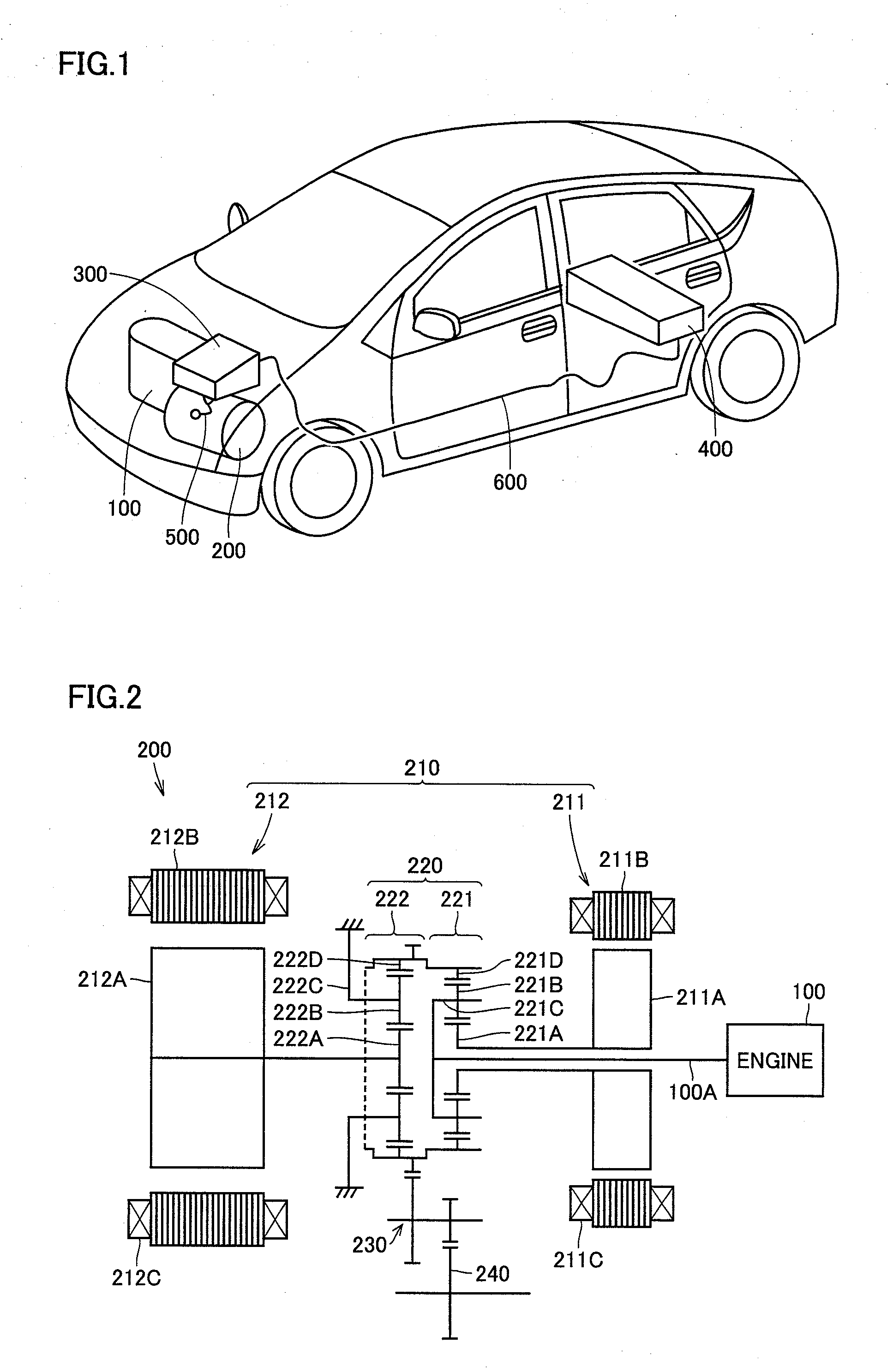
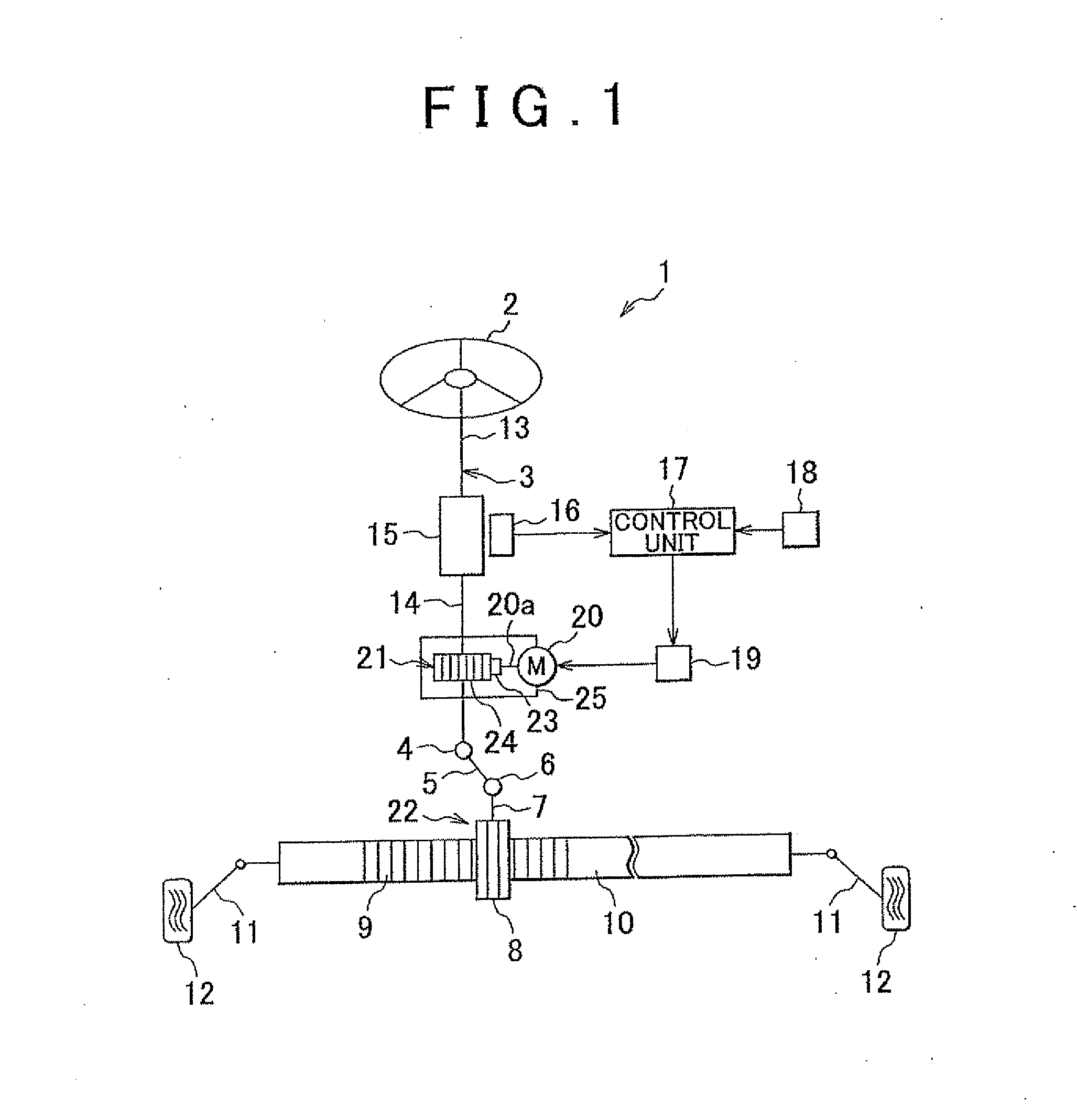
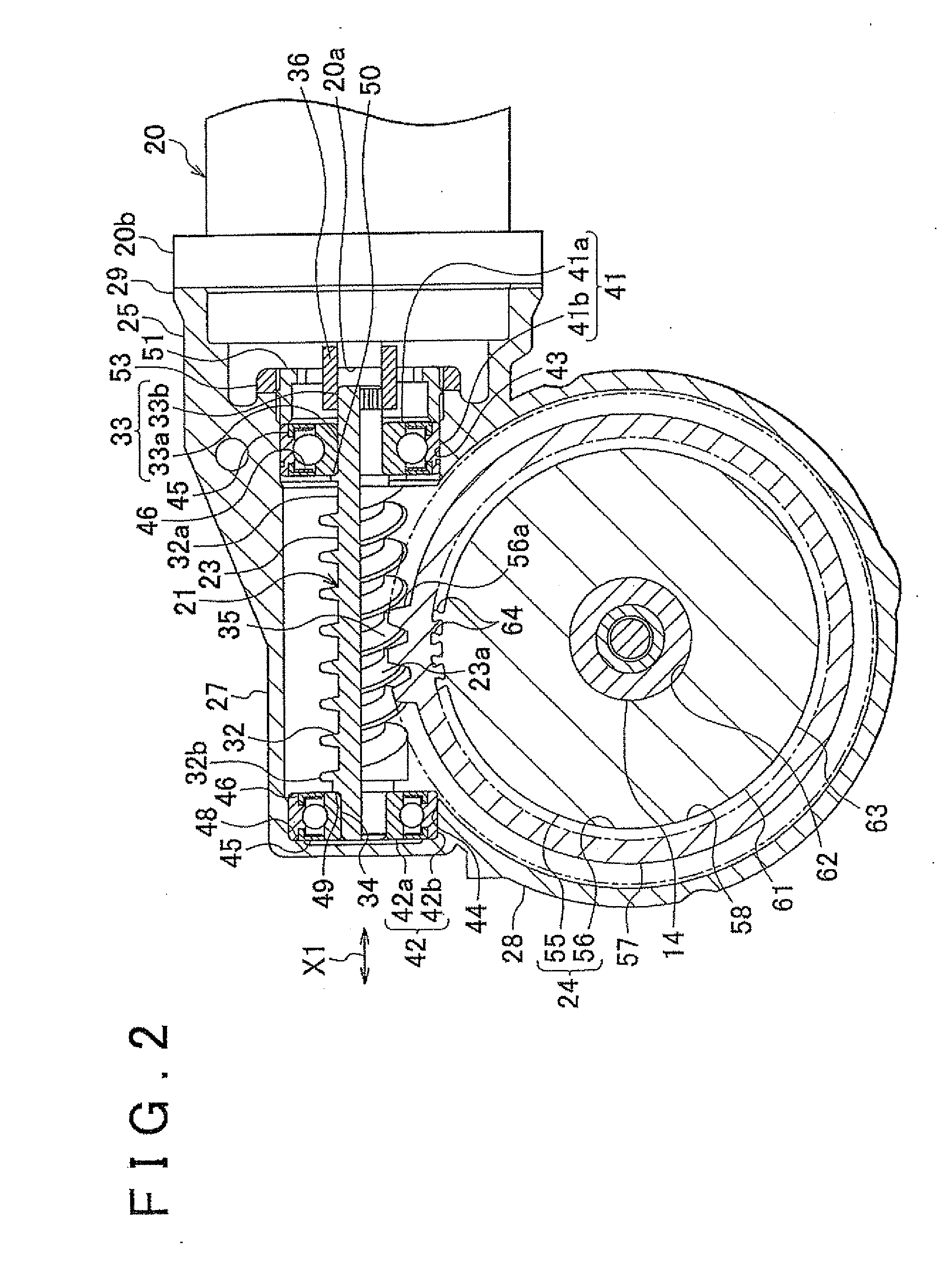
Control device for motor-driven vehicle
InactiveUS7610124B2Improve efficiencyHigh energyBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsMotor driveProcess engineering
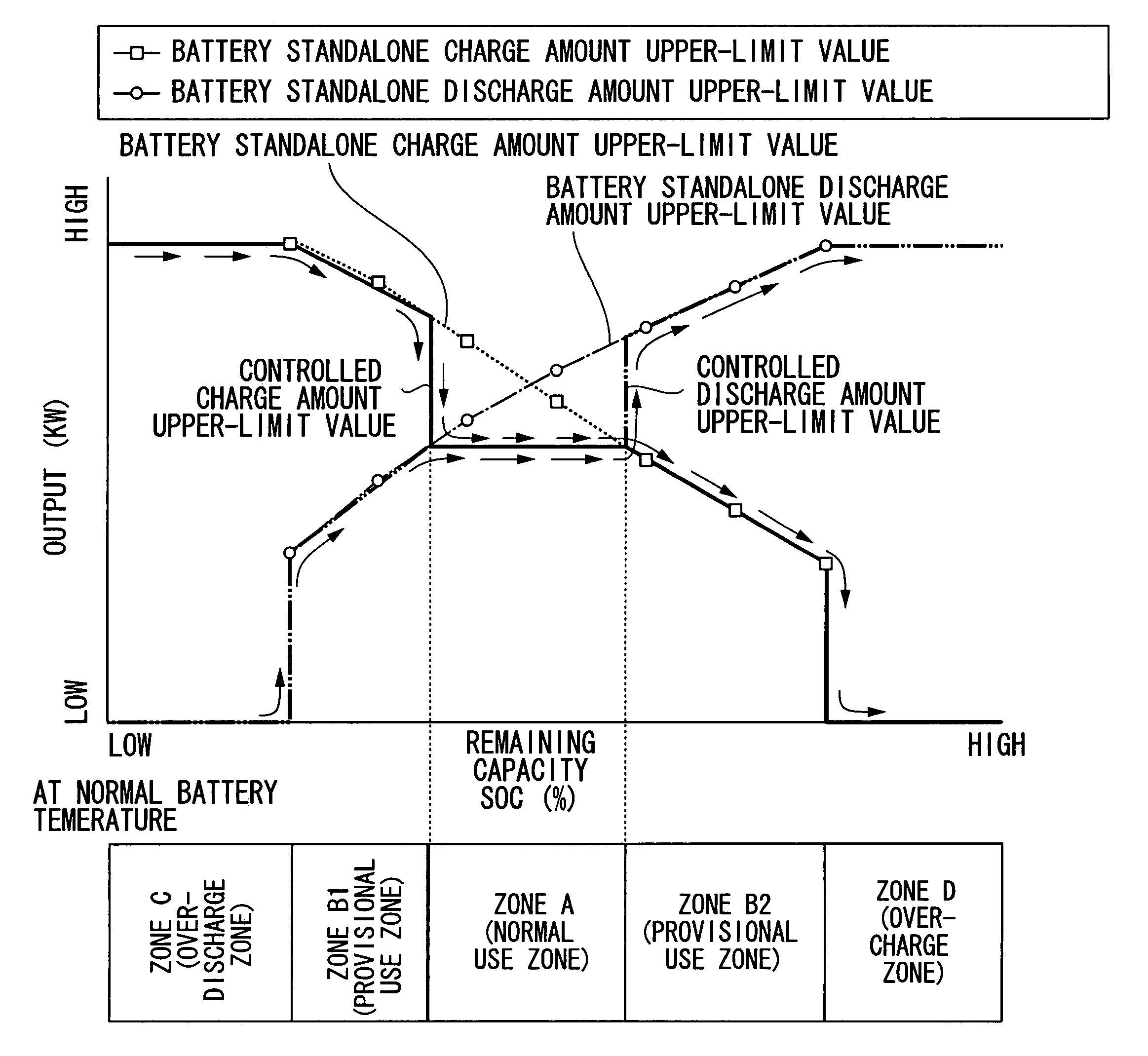
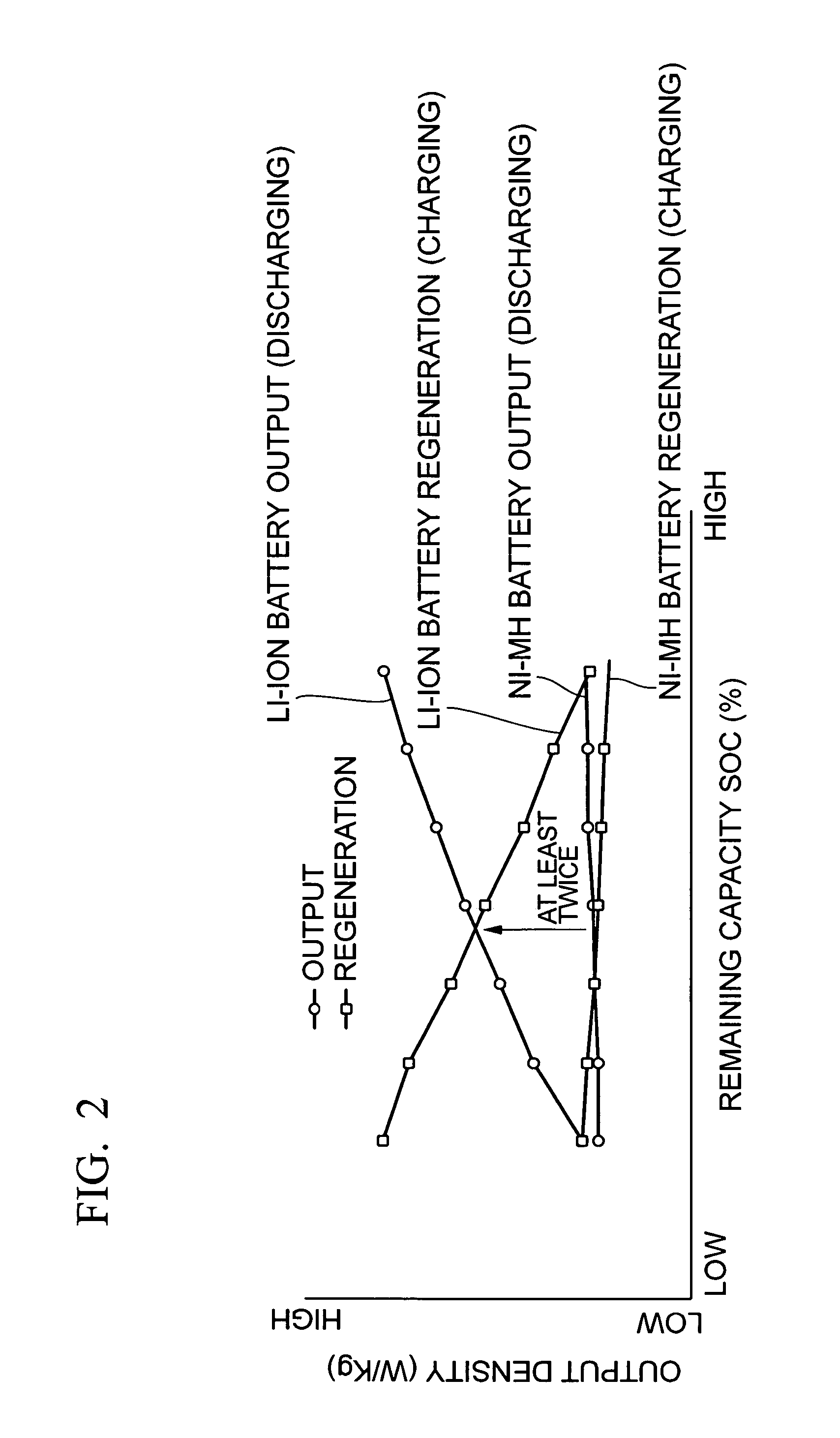
A control device for a motor-driven vehicle, the control device includes: a zone determining unit that determines at least a normal use zone, a discharge zone, an over-discharge zone, a charge zone, and an over-charge zone; and a control unit controlling the motor by stipulating the charge and discharge power of the storage unit for each zone that is determined by the zone determining unit, setting the normal use zone to be in a predetermined range that includes a remaining capacity at which the discharge output according to the remaining capacity of the storage unit and the charge input according to the remaining capacity of the storage unit are equivalent, and making the discharge output and the charge input in the normal use zone to be a predetermined value regardless of the remaining capacity of the storage unit in the zone.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
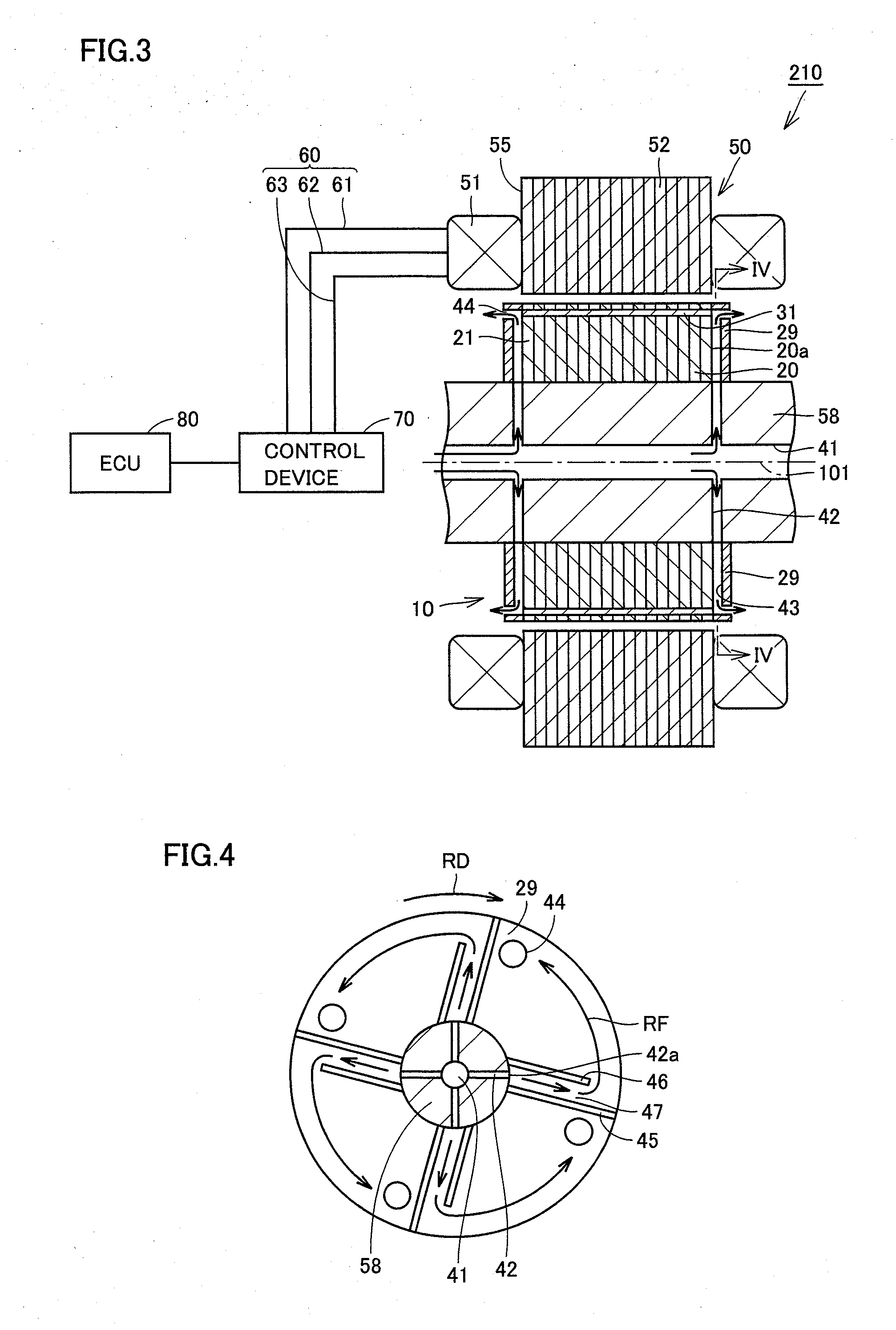
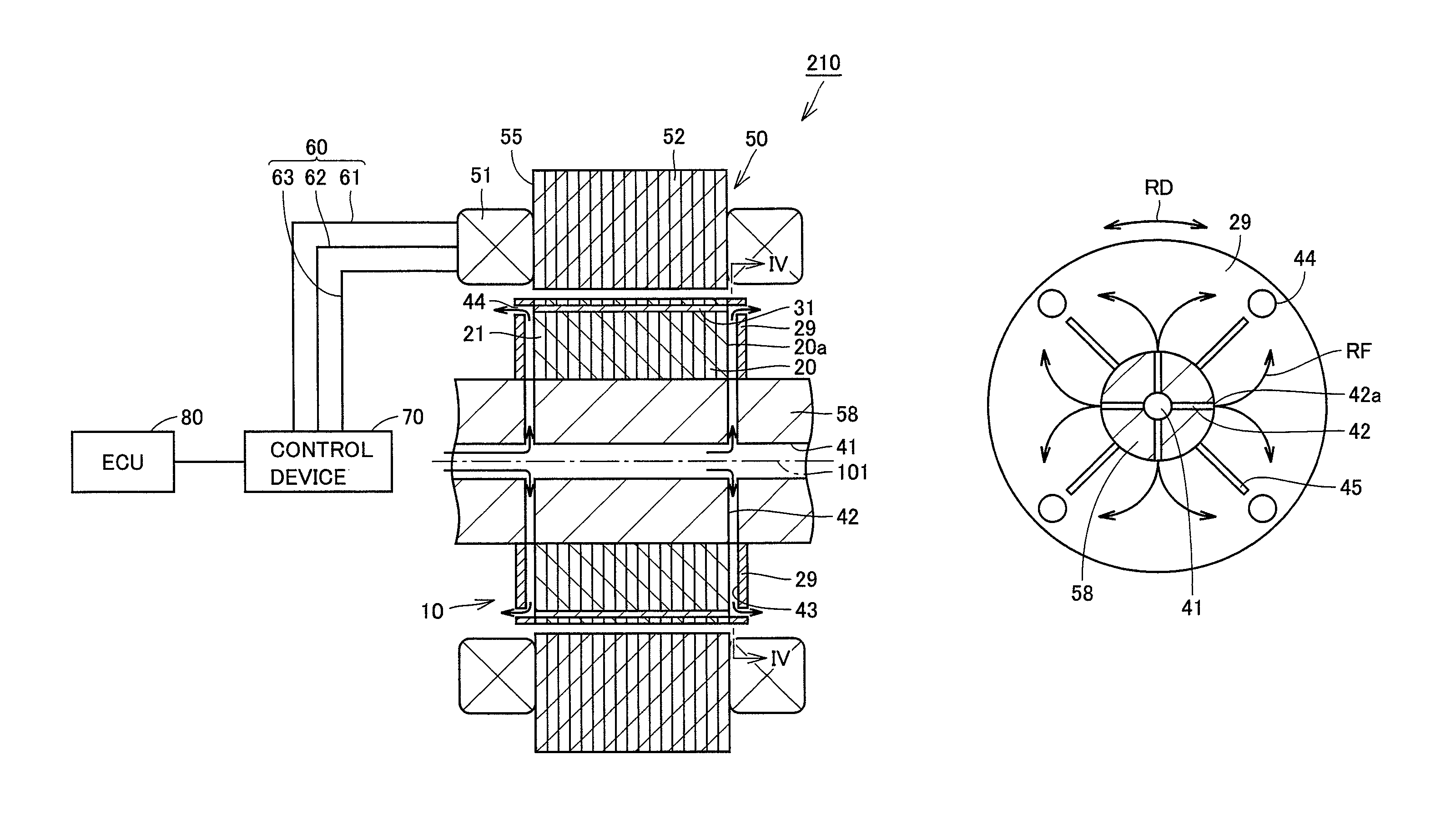
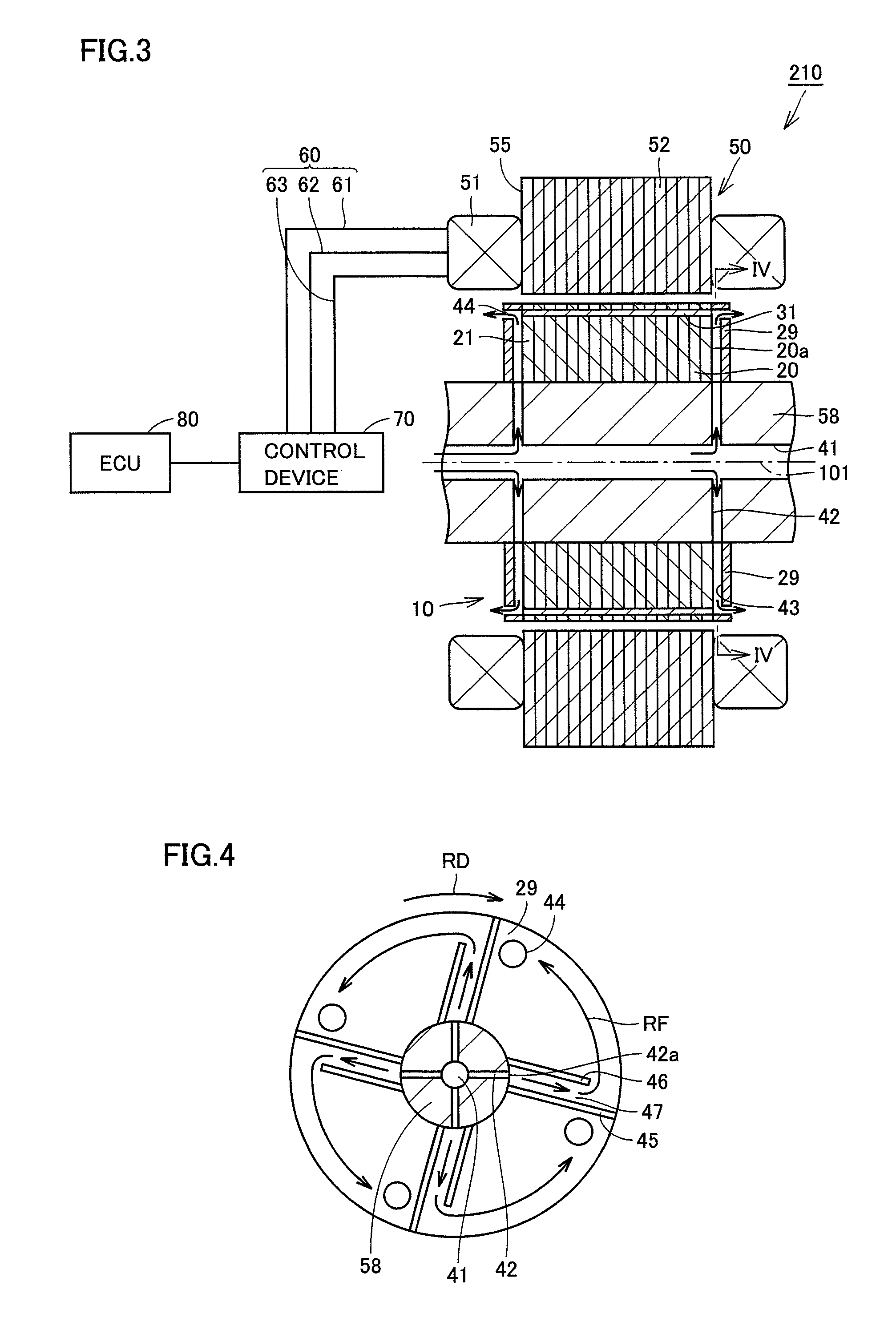
Rotating electric machine and drive device
InactiveUS20100237725A1Improve cooling effectAvoid performance changesHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric machineMagnet
There is provided a rotating electric machine capable of preventing a coolant from being retained at an outer surface of a rotor. This rotating electric machine includes a rotation shaft provided so as to be rotatable, a core body secured to the rotation shaft, a permanent magnet embedded in the core body, and an end plate provided so as to be opposed to an axial end surface of the core body. A first coolant channel is formed in the rotation shaft to allow a coolant to flow therethrough. A second coolant channel is formed between the end plate and the axial end surface of the core body to communicate with the first coolant channel. A partition wall that partitions the second coolant channel in a circumferential direction and a path wall that guides the coolant in the second coolant channel toward an outer peripheral edge region of the axial end surface where the permanent magnet is placed are formed inside the second coolant channel.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control device for motor-driven vehicle
InactiveUS20070118255A1Easy to useImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsMotor driveProcess engineering
A control device for a motor-driven vehicle, the control device includes: a zone determining unit that determines at least a normal use zone, a discharge zone, an over-discharge zone, a charge zone, and an over-charge zone; and a control unit controlling the motor by stipulating the charge and discharge power of the storage unit for each zone that is determined by the zone determining unit, setting the normal use zone to be in a predetermined range that includes a remaining capacity at which the discharge output according to the remaining capacity of the storage unit and the charge input according to the remaining capacity of the storage unit are equivalent, and making the discharge output and the charge input in the normal use zone to be a predetermined value regardless of the remaining capacity of the storage unit in the zone.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
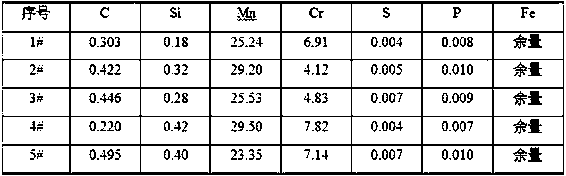
Full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire for high-manganese steel for preparing LNG storage tank
ActiveCN107052618AAvoid organizationAvoid performance changesArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsUltimate tensile strengthToughness
The invention discloses a full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire for high-manganese steel for preparing an LNG storage tank. According to the technical scheme, the full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire comprises 0.25-0.45wt% of C, 23-26wt% of Mn, 6-8wt% of Ni, 3-5wt% of W, 0.02-0.04wt% of N, less than or equal to 0.02wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.001wt% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire has the advantages that the price of adopted alloy elements is low, and an alloy component system is simple; and the low-temperature toughness of weld metal formed by the prepared full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire is excellent, the strength of the full-automatic submerged-arc welding solid-core welding wire is matched with the strength of the ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel for preparing the LNG storage tank, and the technical requirements for the strength and the ultralow-temperature toughness of the welded LNG storage tank can be met.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Pipe hoop stress tensility testing method
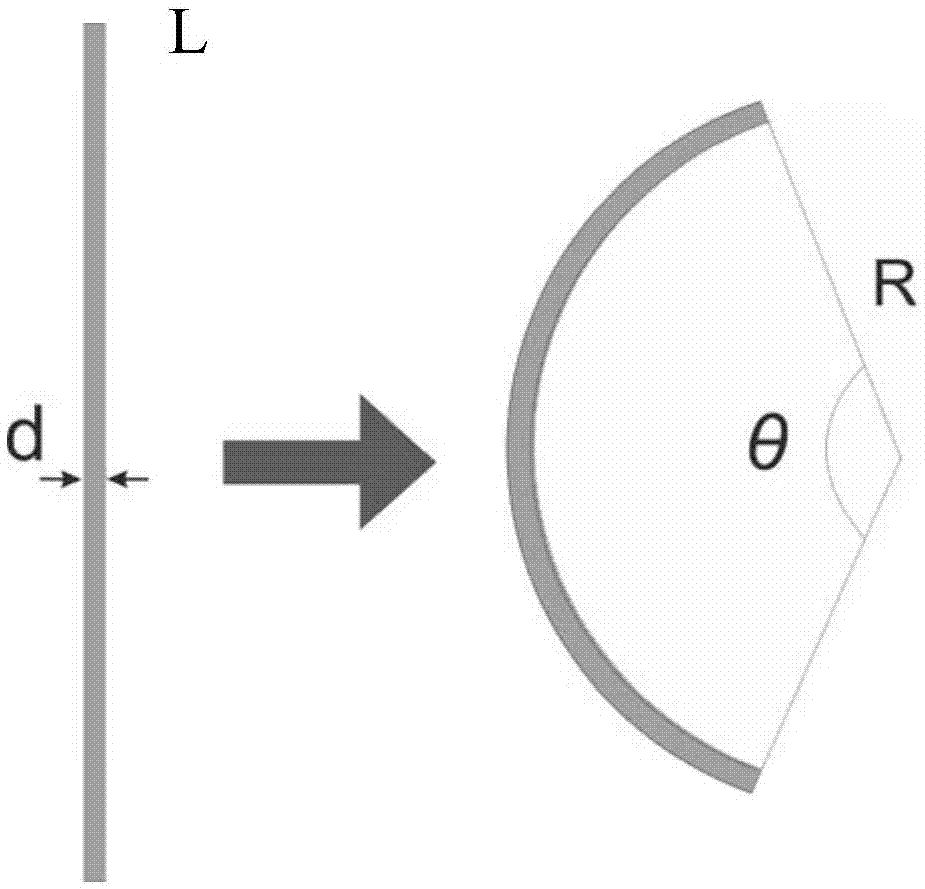
InactiveCN1865906AAvoid performance changesTest hoop tensile propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSEMI-CIRCLEEngineering
The disclosed tube circumferential tension performance test method comprises: using a semi-circle bar with same radius to cross the tube, starting up the testing machine to drive the upper and lower clamp, deforming the tube, and obtaining the test data. Compared to prior art, the benefit of this invention include: 1. changing no tube performance; 2. obtaining better testing result.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method of zeolite geopolymer cementing material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zeolite geopolymer cementing material. The method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing a silicon-aluminum mixture; (2), preparing an alkalineactivator; and (3), preparing a zeolite geopolymer cementing material. According to the geopolymer cementing material, metakaolin, zeolite, red mud, coal ash, magnesium oxide and other raw materialsare reasonably utilized, so that activation reaction of all the material components is improved; alkali metal ions are firmly combined in a reaction product, and the surface frosting problem can be slightly relieved. The prepared zeolite geopolymer cementing material is high in strength and high in hardening speed, and the 28-day strength can reach over 48 MPa. Magnesium oxide in the raw materialsplays a role of a filling and expanding agent and can effectively absorb carbon dioxide. By optimizing the proportion, the geopolymer is more excellent in corrosion resistance by being compared withordinary Portland cement, small in capillary pore number, good in impermeability, small in shrinkage, high in setting speed and high in applicability, and the sustainable development requirements of ecological environmental protection can be met.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Rotating electric machine and drive device
InactiveUS8242646B2Improve cooling effectAvoid performance changesHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric machineMagnet
There is provided a rotating electric machine capable of preventing a coolant from being retained at an outer surface of a rotor. This rotating electric machine includes a rotation shaft provided so as to be rotatable, a core body secured to the rotation shaft, a permanent magnet embedded in the core body, and an end plate provided so as to be opposed to an axial end surface of the core body. A first coolant channel is formed in the rotation shaft to allow a coolant to flow therethrough. A second coolant channel is formed between the end plate and the axial end surface of the core body to communicate with the first coolant channel. A partition wall that partitions the second coolant channel in a circumferential direction and a path wall that guides the coolant in the second coolant channel toward an outer peripheral edge region of the axial end surface where the permanent magnet is placed are formed inside the second coolant channel.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
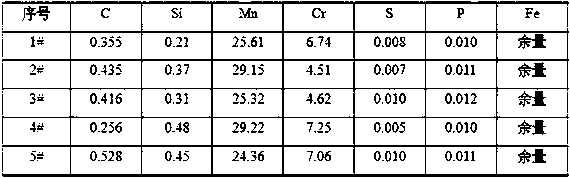
Tungsten electrode argon arc welding solid cored welding wire used for welding ultralow-temperature high manganese steel
ActiveCN107009046AAvoid performance changesReduce contentWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaUltimate tensile strengthToughness
The invention relates to a tungsten electrode argon arc welding solid cored welding wire used for welding ultralow-temperature high manganese steel. According to the technical scheme of the solid cored welding wire, the tungsten electrode argon arc welding solid cored welding wire used for welding the ultralow-temperature high manganese steel comprises the chemical components of 0.25-0.55 wt% of C, 23-26 wt% of Mn, 8-10 wt% of Ni, 3-5 wt% of W, less than or equal to 0.002 wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.001 wt% of S and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The solid cored welding wire is low in price of alloy element content and simple in alloy component system; and formed weld metal has good low-temperature toughness, and the strength of the weld metal is matched with the ultralow-temperature high manganese steel, and the technical requirements for the strength and ultralow-temperature toughness of LNG devices and other devices prepared through welding.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
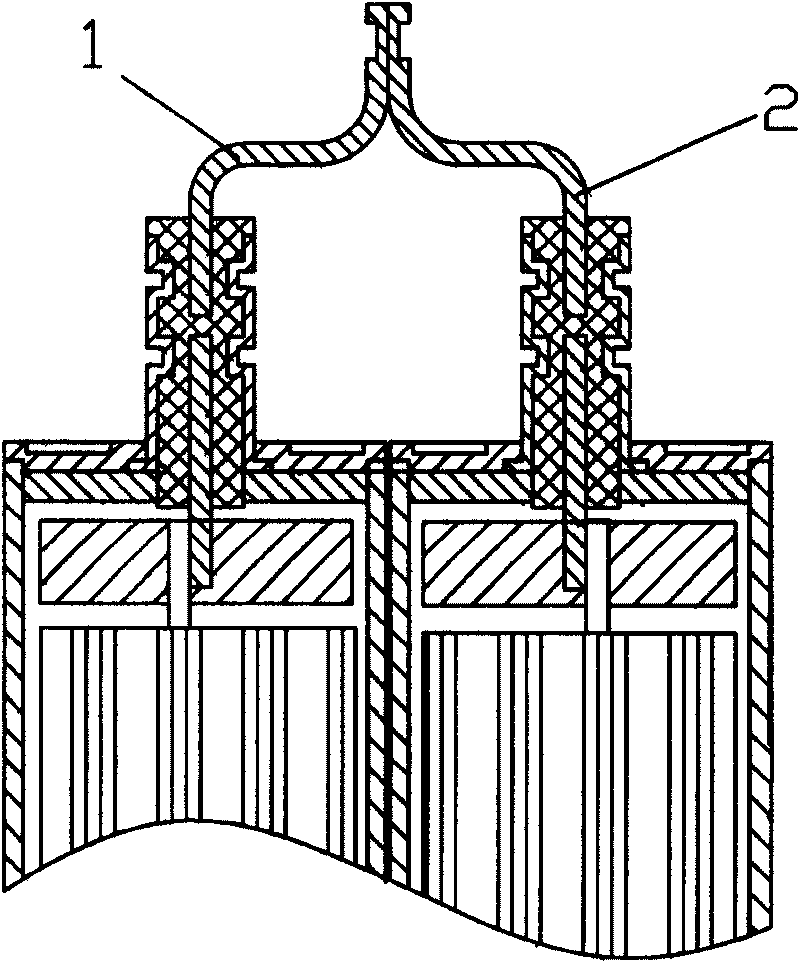
Power battery pack
ActiveCN101752600ALow reliabilityGuaranteed reliabilityFinal product manufactureSecondary cells manufacturePower batteryHybrid car
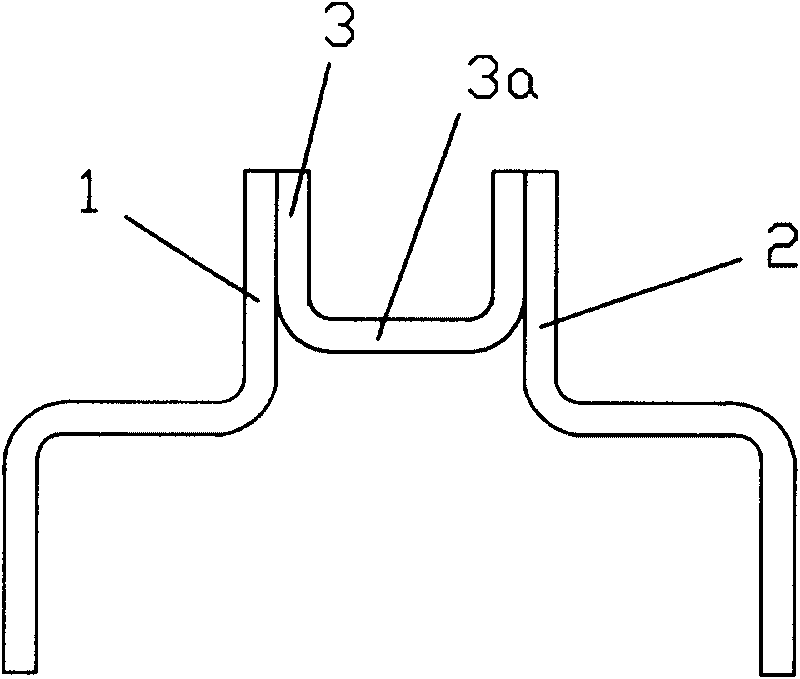
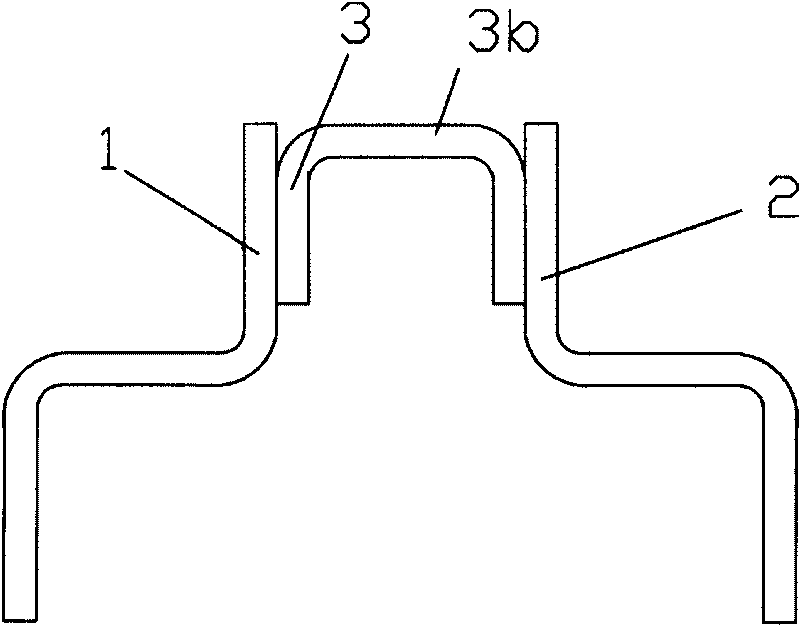
The invention provides a power battery pack with reliable connection and excellent electric power output performance, comprising: a plurality of single batteries (5), which are interconnected in serial or parallel via flaky electrode terminals (1, 2), wherein the electrode terminals (1, 2) are interconnected via an intermediate connector (3) with the function of buffer, and the connection relationship between the electrode terminals (1, 2) and the intermediate connector (3) is adherence connection. The intermediate connector (3) with the function of buffer can buffer stress when the electrode terminals (1, 2) receive load impact, thereby guaranteeing the reliable connection between the electrode terminals (1, 2). In addition, according to the invention, the power battery pack can include the function of automatic disconnection upon overheating by manufacturing the intermediate connector (3) with memory alloy material or in a structure of double metal sheets. The power battery pack is mainly applied to electric / hybrid cars.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Polyamide reverse osmosis membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111992049AIncrease water fluxIncrease water channelMembranesGeneral water supply conservationPolymer scienceActive agent
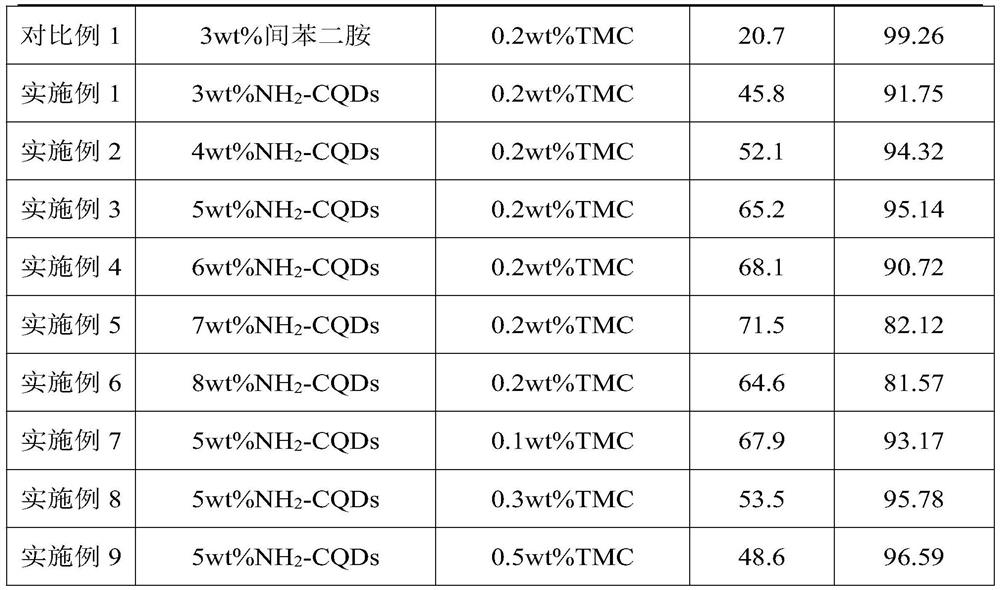
The invention provides a polyamide reverse osmosis membrane and a preparation method thereof. The membrane comprises a porous support membrane and a carbon quantum dot-containing polyamide layer growing on the surface of the porous support membrane, and the carbon quantum dot-containing polyamide layer comprises the following raw material components: aminated carbon quantum dots, an oil-phase reaction monomer, an oil-phase solvent, an acid acceptor, a pH regulator and a surfactant; the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing aminated carbon quantum dots; and 2, preparingthe polyamide reverse osmosis membrane. According to the polyamide reverse osmosis membrane disclosed by the invention, the aminated carbon quantum dots are used as a novel water-phase reaction monomer, and a polyamide layer structure containing the carbon quantum dots is formed on the polysulfone porous support membrane by directly carrying out a cross-linking reaction on amino groups on the aminated carbon quantum dots and trimesoyl chloride, so that the water flux can be improved from multiple aspects.
Owner:HUNAN OVAY TECH CO LTD
Electric welding rod for high-manganese austenite low-temperature steel
ActiveCN108971795AImprove matchReduce manufacturing costWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaWeight coefficientPotassium
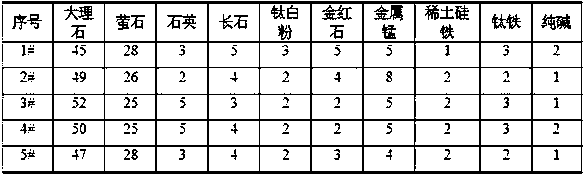
The invention discloses an electric welding rod for high-manganese austenite low-temperature steel. The electric welding rod is composed of a high-manganese welding core and a coating, wherein the surface of the welding core is coated with the coating. The total weight of the high-manganese welding core is adopted as the reference, and the high-manganese welding core comprises, by weight percentage, 0.20-0.50% of C, 0.15-0.45% of Si, 23.0-30.0% of Mn, 4.0-8.0% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.008% of S, less than or equal to 0.010% of P and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The total weight of the coating is adopted as the reference, and the coating comprises, by weight percentage, 45-52% of marble, 25-30% of fluorite, 2-7% of quartz, 3-5% of feldspar, 2-4% of titanium dioxide, 2-7%of rutile, 4-8% of manganese metal, 1-3% of rare earth and silicon iron, 2-5% of ferrotitanium and 1-2% of sodium carbonate. After all power materials are uniformly mixed according to the ratios, sodium-potassium water glass with the weight accounting for 23-29% the weight of the powder materials is added as a binding agent, and the powder materials are pressed onto the welding core; and the weight coefficient of the coating ranges from 0.35% to 0.45%. The electric welding rod meets the requirement for toughness in the environment with the low temperature being minus 196 DEG C so that the problems that existing high-manganese welding rods are poor in structure stability and insufficient in low-temperature toughness can be solved, and the domestic blank is filled up.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
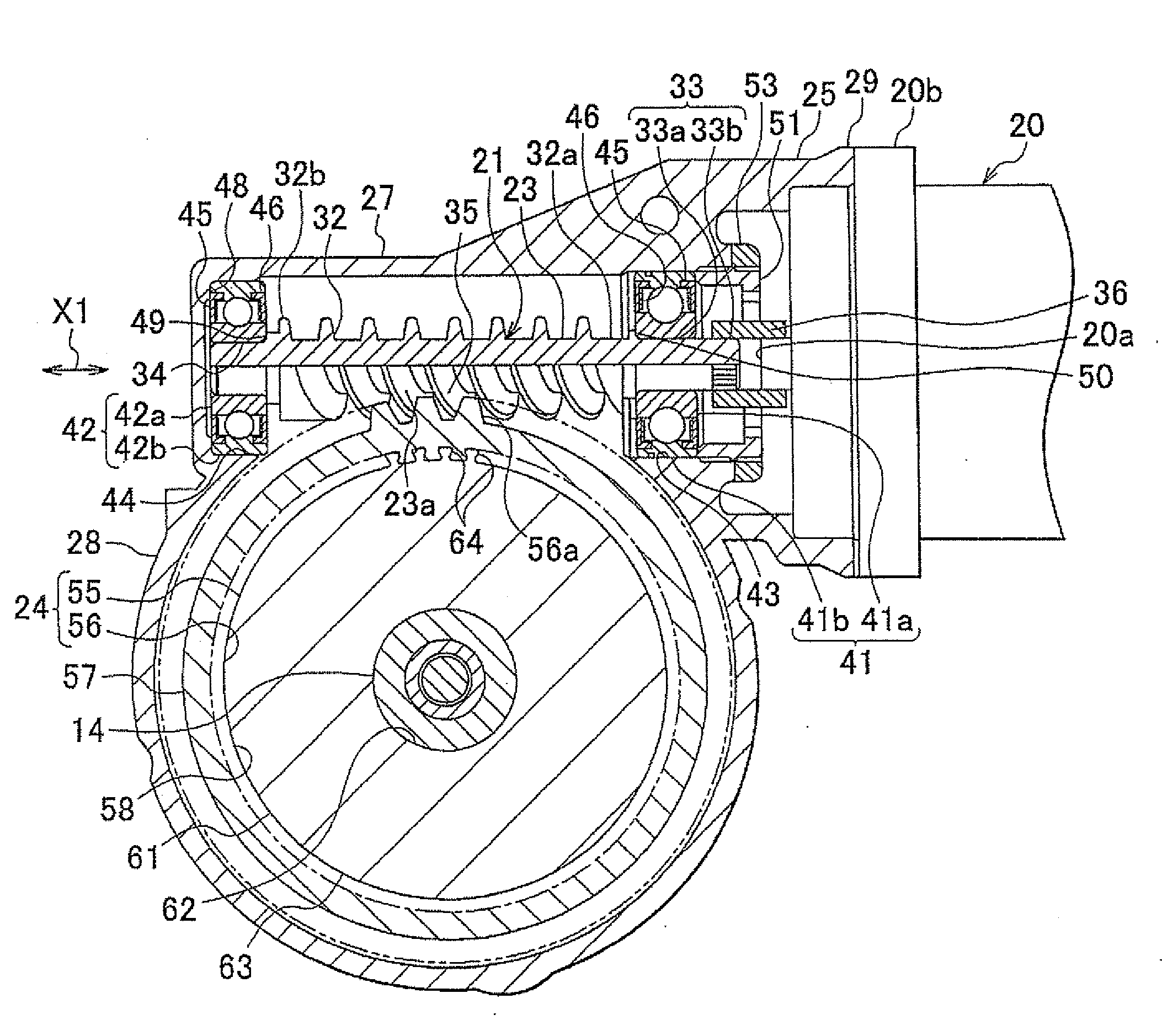
Worm drive
InactiveUS20120067151A1Increased durabilityReduced durabilityToothed gearingsPortable liftingEngineeringJoined teeth
A worm wheel of a worm drive includes an annular synthetic resin member having tooth portions meshing with a worm shaft and a core having an outside diameter portion joined to an inside diameter portion of the synthetic resin member. The outside diameter portion of the core has first joining tooth portions that protrude outward in a radial direction and are joined to the inside diameter portion of the synthetic resin member. Each of the first joining tooth portions includes a widening portion whose width in a circumferential direction increases toward the outside in the radial direction.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Limited current type oxygen sensor
InactiveCN102944600APerformance impactImprove long-term stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOxygen sensorDiffusion barrier
The invention relates to a limited current type oxygen sensor which comprises an electrolyte layer and a compact diffusion barrier layer. The electrolyte layer and the compact diffusion barrier layer are both made of La1-xSrxGal-yMgyO3-delta, wherein 0.1<=x<=0.2, 0.1<=y<=0.2, and 0.1<=delta<=0.2. The sensor has good long-term stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ultra-low frequency vibration isolator and design method thereof
ActiveCN110259862AReduce the lower cutoff frequency of vibration isolationLower natural frequencyMagnetic springsShock absorbersVibration amplitudeControl theory
The invention discloses an ultra-low frequency vibration isolator and a design method thereof. The ultra-low frequency vibration isolator comprises a vibration isolation bearing platen, an upper shell, a lower shell, a bearing rod, a positive rigidity spring and a negative rigidity magnetic spring; and the bearing rod, the upper shell and the lower shell are coaxial, and the vibration isolation bearing platen is arranged on the top end of the bearing rod. The ultra-low frequency isolator and the design method can meet the requirements of the vibration isolator for the bearing capacity and the ultra-low inherent frequency; and meanwhile, the isolator can maintain the linear stiffness characteristic near a working point, so that the restriction to the vibration amplitude and the isolator performance is eliminated, and the excellent low-frequency vibration isolation performance is achieved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Pipe hoop stress tensility testing method
InactiveCN100487416CAvoid performance changesTest hoop tensile propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSEMI-CIRCLEEngineering
The disclosed tube circumferential tension performance test method comprises: using a semi-circle bar with same radius to cross the tube, starting up the testing machine to drive the upper and lower clamp, deforming the tube, and obtaining the test data. Compared to prior art, the benefit of this invention include: 1. changing no tube performance; 2. obtaining better testing result.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Seamless submerged arc flux-cored wire for welding high manganese steel LNG storage tank
ActiveCN110653515AExcellent solderabilityAvoid changes in the structure and properties of the fusion zoneWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaChromium carbideFerrosilicon
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Low-consumption thermal circulation type glass processing kiln furnace
InactiveCN109987822AQuality improvementAvoid performance changesGlass furnace apparatusWater circulationEngineering
The invention discloses a low-consumption thermal circulation type glass processing kiln furnace. The low-consumption thermal circulation type glass processing kiln furnace comprises a furnace body, wherein a feeding channel and a fuel gas pipe are arranged at upper parts of two sides of the furnace body respectively; a water tank and a working pool, which are parallel to the furnace body, are arranged at the outer side of the furnace body; the water tank and the working pool are located at two sides of the furnace body; a water outlet pipe is arranged at the top of the water tank; and a second heat exchanger is arranged on the water outlet pipe. According to the kiln furnace disclosed by the invention, three heat exchangers are arranged and pipelines are reasonably set and configured, sothat a fuel gas pre-heating function is realized, a combustion speed is improved and the processing time can be shortened; meanwhile, almost current feeding channels adopt metal channels so that performance changes, which are possibly caused by the fact that metal stays at high temperature state for long time, can be effectively avoided by cooling the metal channels, and the service life of the feeding channels is prolonged; surplus heat can be reasonably applied through water circulation and the energy-saving effect is realized; and air in glass liquid can be exhausted through a negative-pressure effect after glass is melted, and the quality of the glass liquid is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG GUANGPU SOLAR ENERGY PROJECT
Biodegradable spinning material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111733475AImprove spinning performanceHigh molecular weightBio-packagingMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentEmulsionAnti bacterial
The invention provides a biodegradable spinning material and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biodegradable materials. The biodegradable spinning material comprises the following preparation raw materials including, by mass, 80-93 parts of chemical-modified PBAT (Poly(butylene adipate terephthalate)), 1-8 parts of PCL (polycaprolactone), 0.5-2 parts of silver nanowire emulsion, 3-11 parts of functional master batch and 0.05-0.2 part of degradation balancing agent, wherein the weight-average molecular weight of the chemical-modified PBAT is 16000 to 38000, and the mass content of silver nanowires in the silver nanowire emulsion is 45% to 60%. The spinning material provided by the invention has the good spinnability and the good strength and is biodegradable, the degradation process can be effectively controlled according to the using requirements of people, a product obtained through spinning of the spinning material is good in breathability and anti-bacterial property, and a certain blocking effect is achieved in terms of clothing materials.
Owner:BEIJING CO FOUND HIGH TECH INCUBATOR
Liquid RFID antenna and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN108511874AFeatures SoftMaintain soft propertiesAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsElectricityInner loop
The invention provides a liquid RFID antenna comprising at least a loop antenna portion and a liquid metal antenna portion. The loop antenna portion is disposed on a first dielectric substrate. The loop antenna portion includes an inner loop antenna portion and an outer loop antenna portion. The liquid metal antenna portion is disposed in a second dielectric substrate. An interface between the inner loop antenna portion and the outer loop antenna portion on the first dielectric substrate is electrically connected to an electronic chip. The application provides a new mode for cyclic wire arrange in combination with the liquid metal antenna, expands the compatibility of RFID in multiple occasions, satisfies the electrical performance of the antenna while ensuring the soft characteristics, and provides an ingenious backup improvement scheme to greatly improve the satisfaction of the RFID in different scenarios.
Owner:苏州德索文信息科技有限公司
Composite semipermeable membrane and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20200353426A1Easy to separateSimple methodMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPolymer scienceHydrolysis
A method for manufacturing a composite semipermeable membrane is capable of forming, on a surface of a porous support in a highly reproducible manner, a separation layer that is extremely thin and that exhibits superior separability. It provides, on a surface of a porous support, a composite semipermeable membrane that has an organic / inorganic hybrid separation layer that is extremely thin and that exhibits superior separability. A method for manufacturing a composite semipermeable membrane includes forming, on a surface of a porous support, a separation layer containing a cross-linked condensate having a siloxane bond by bringing an organic solution that contains an organic silicon compound containing three or more reactive functional groups, each of which is at least one type selected from a hydrolyzable group and a hydroxyl group, into contact with water or an aqueous solution on the porous support, and by performing interfacial polycondensation of the organic silicon compound.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP +1
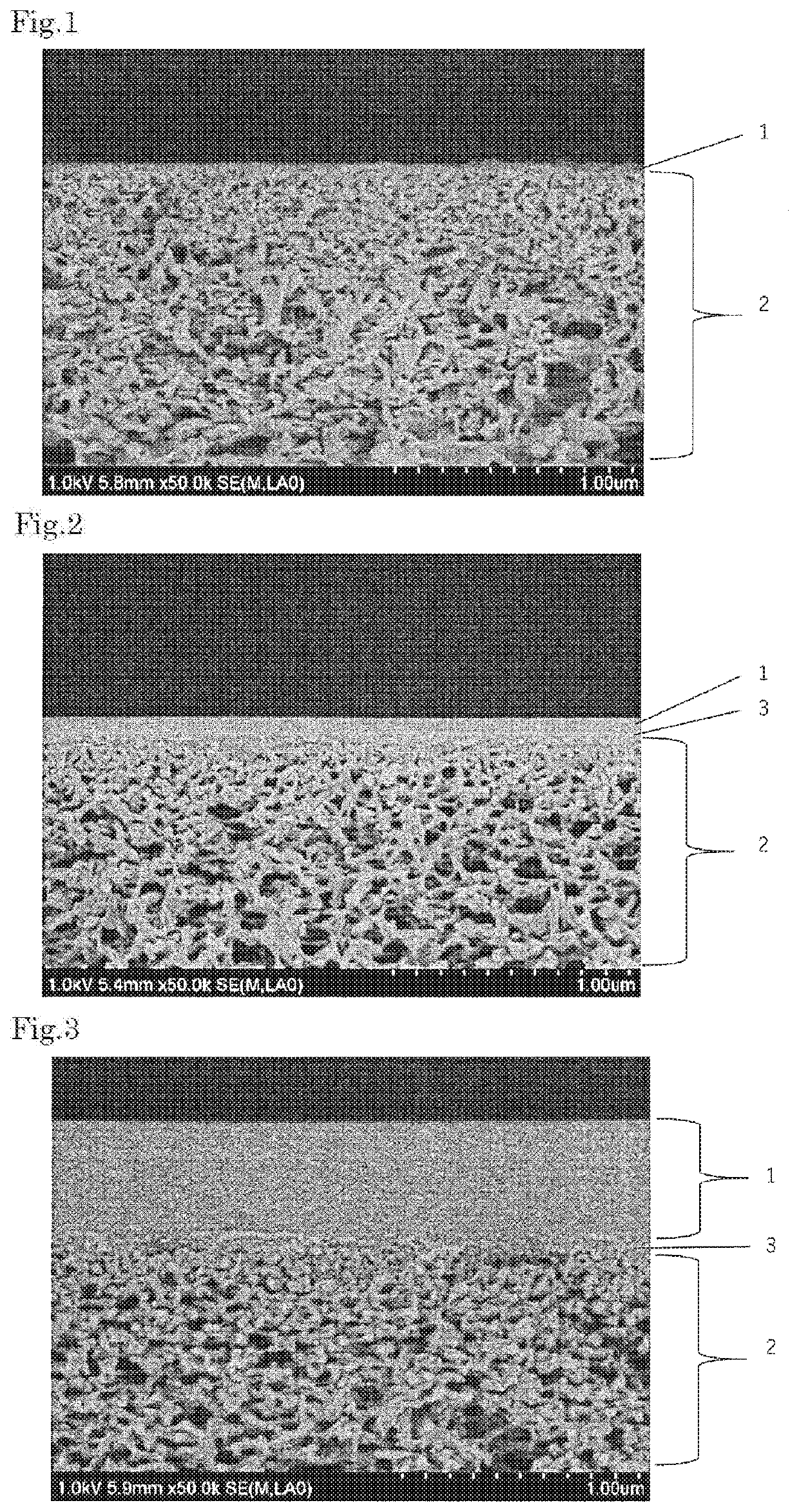
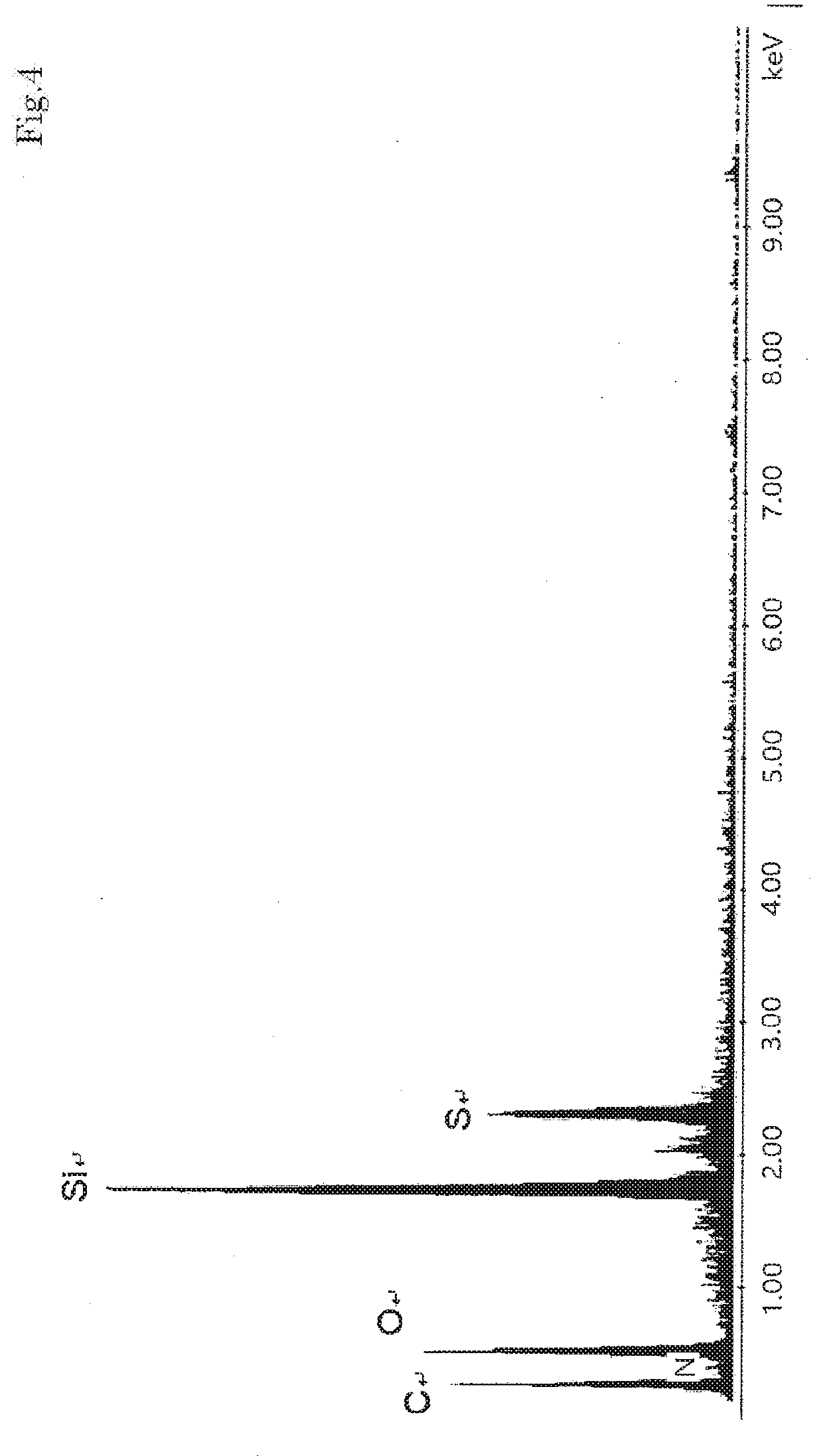
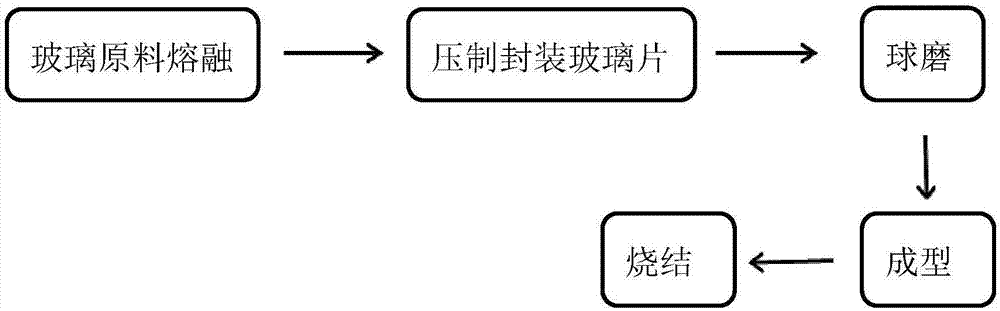
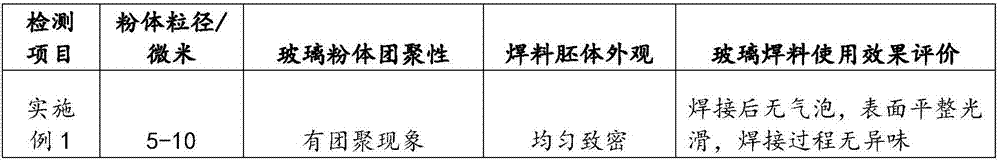
Glass welding material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a glass welding material and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of welding materials. The preparation method of the glass welding material comprises the following steps of (1) ball milling: performing ball milling on a packaged glass sheet to prepare glass powder; (b) forming: pressing the glass powder to form a welding material blank; (c) sintering: sintering the welding material blank, so as to obtain the glass welding material. The glass welding material has the advantages that no adhesive is contained, the technical problems of change of original characteristic of the glass powder due to adding of adhesive into the glass welding material and easiness in pollution to environment and harm to body health in the use process in the prior art are relieved, the original characteristic of the glass powder is guaranteed, and the pollution to the environment and harm to the body health due to volatilizing of the adhesive in the use process are avoided.
Owner:南京广兆测控技术有限公司
Adhesive flow testing device and testing method
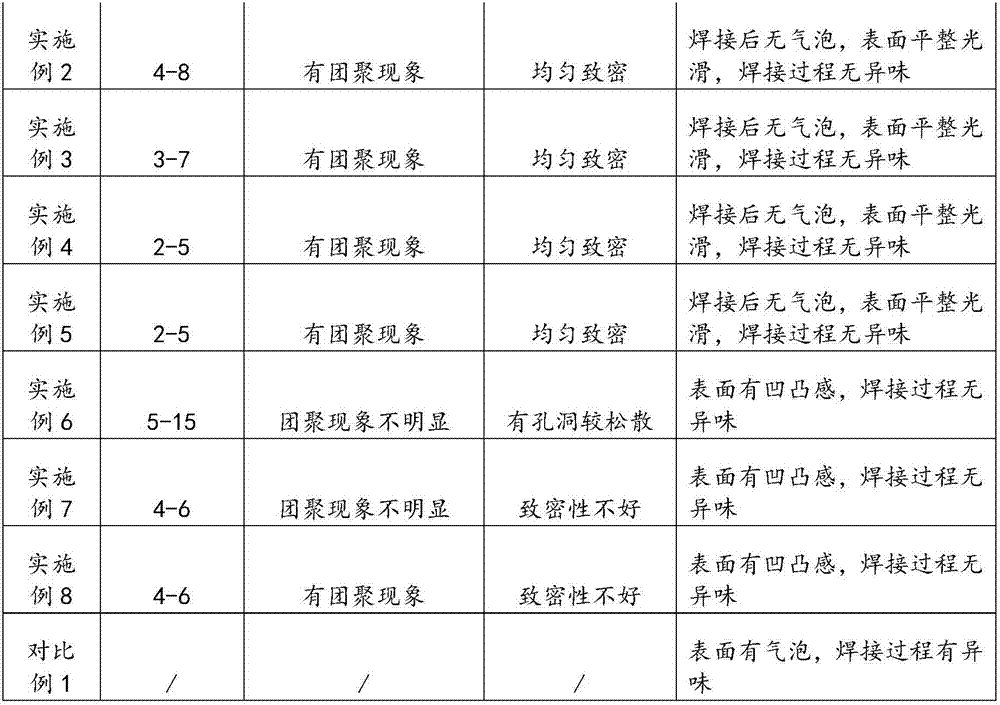
The invention discloses an adhesive flow testing device. The device comprises a base, a protection cover, a detection chamber, a display panel, a humidifying device, a drying device, a detection device and a control device, wherein the detection chamber is defined by toughened glass plates and a base; operation holes and rubber gloves are arranged on one toughened glass plate; the control device controls the humidifying device and the drying device to work; the detection device is placed in the detection chamber; the humidifying device, the drying device and the control device are placed in achamber defined by the base and the protection cover. The invention further discloses a testing method adopting the adhesive flow testing device. As a movable miniature detection chamber, the cost forproviding the required detection environment is much lower than that for controlling the laboratory environment, and materials can be drawn from the production line at any time for detection at any time; the provided detection device can detect fluidity of the adhesive on line; operators can be protected from harm caused by volatile substances of adhesives.
Owner:深圳市德顺通科技有限公司
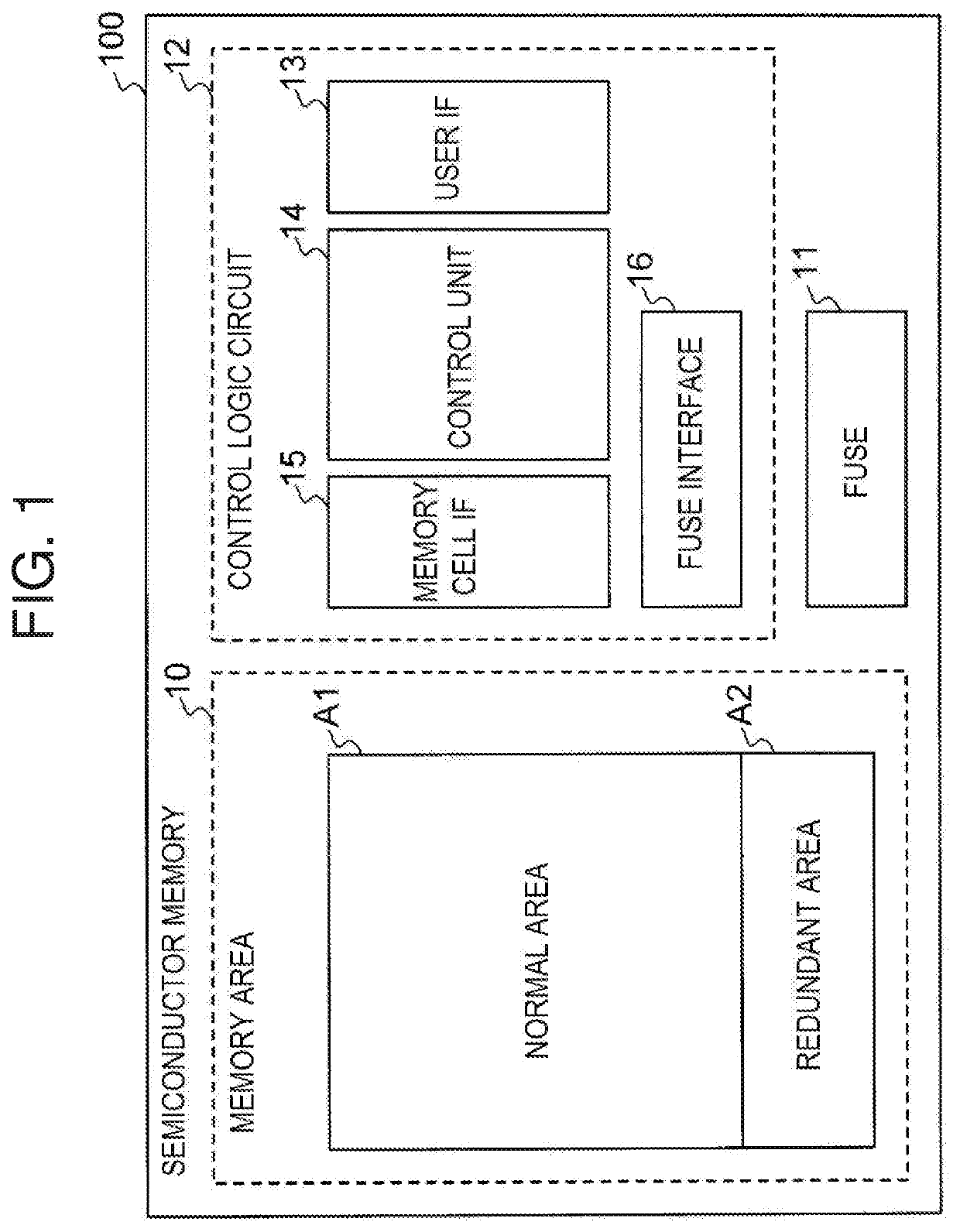
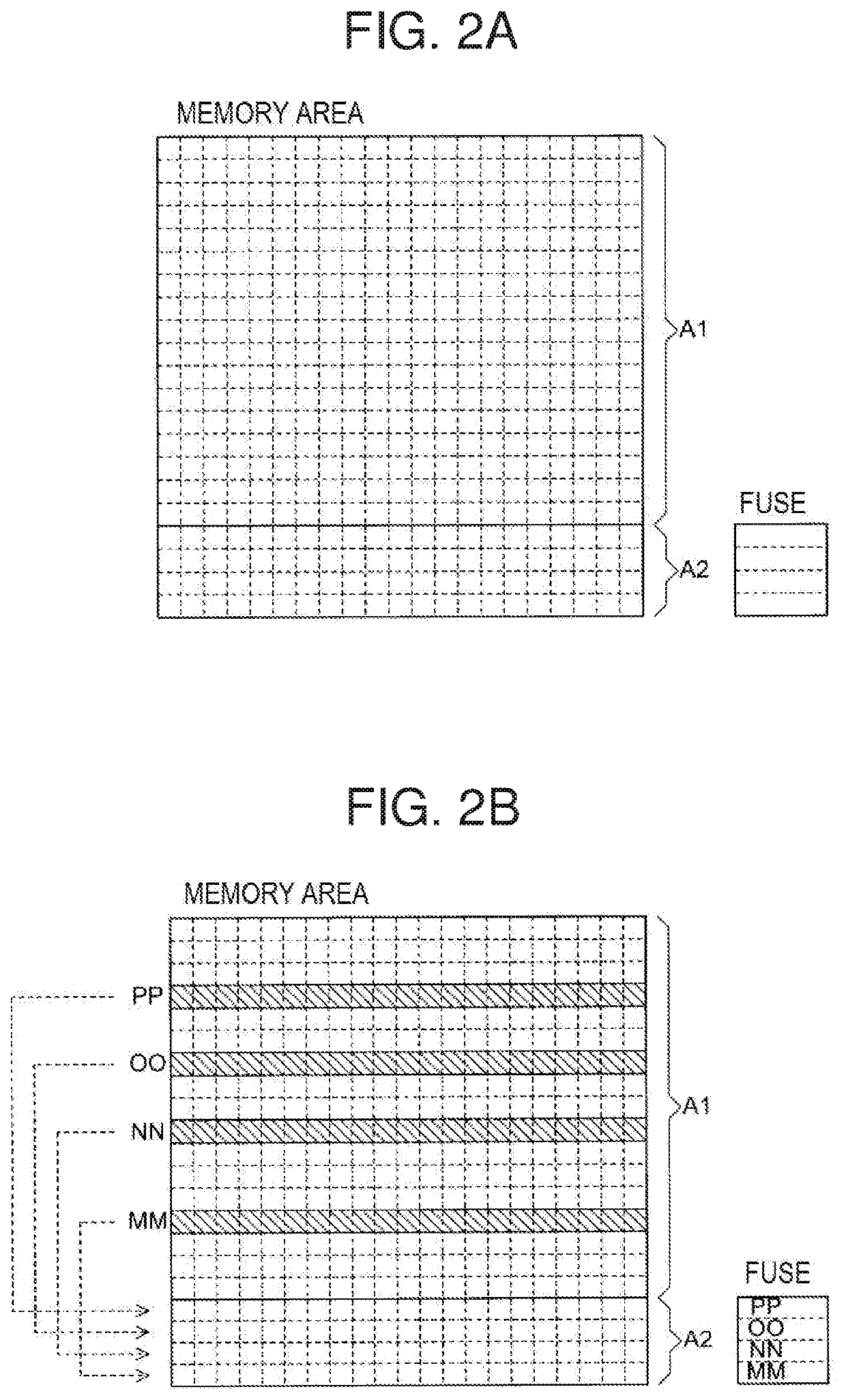
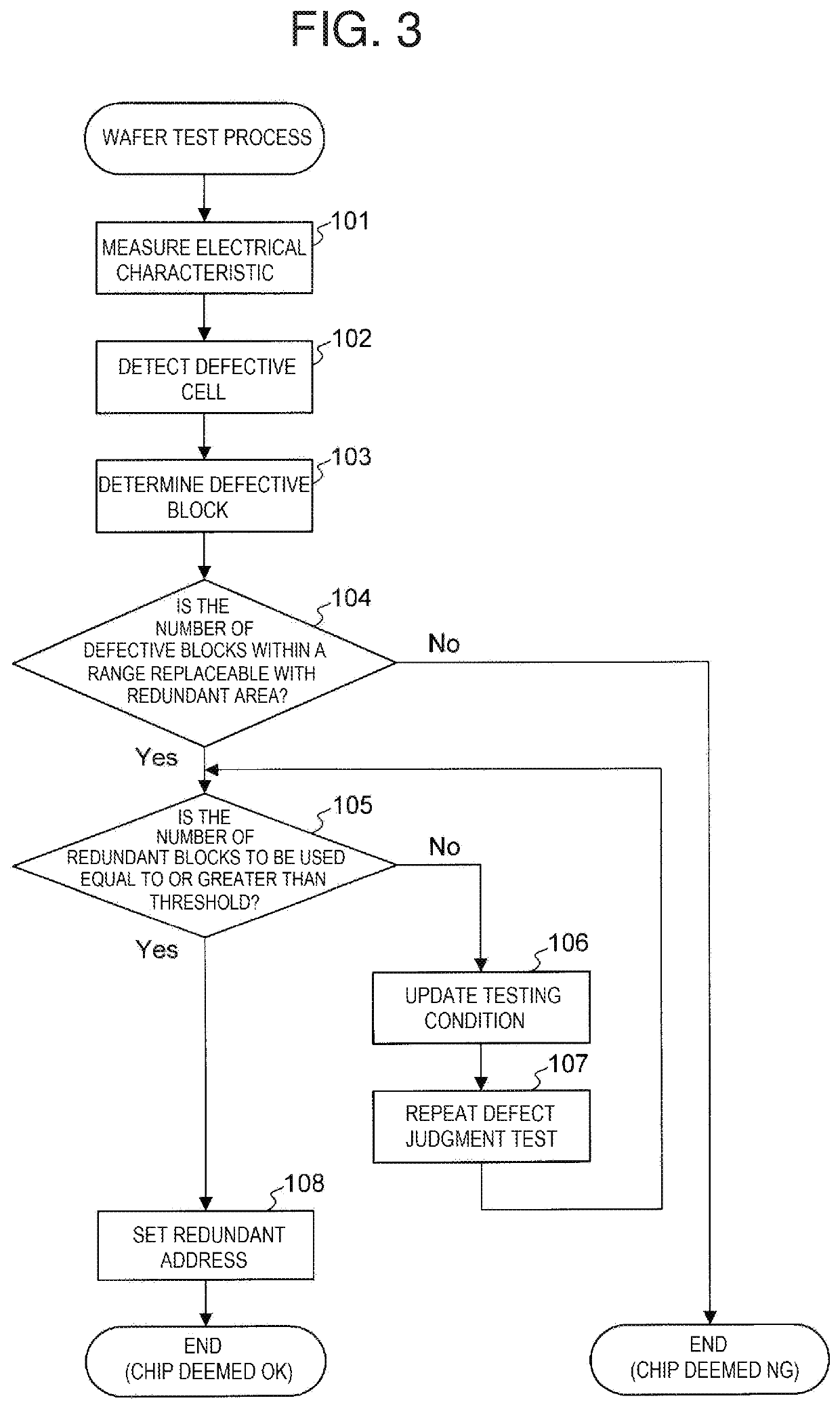
Testing method for semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20200027523A1Avoid performance changesLittle variationDigital storageMemory cellParallel computing
A testing method for a semiconductor memory includes determining which memory blocks are defective based on the number of defective cells in the block. The method includes determining whether the number of defective blocks exceeds a first threshold value and judging the semiconductor memory to be defective if the number of defective blocks is equal to or greater than the first threshold value. The method also includes comparing the number of defective blocks with a second threshold value equal to or less than the first threshold value and repeating the process of measuring and judging of the memory cells and memory blocks until the number of defective blocks is at least equal to the second threshold value, and then managing access to the defective blocks in a different manner from accesses to other blocks.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Gas metal arc welding flux-cored wire used for ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel
InactiveCN112894199AAchieve strength requirementsExcellent ultra-low temperature toughnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaIron powderManganese
The invention relates to a gas metal arc welding flux-cored wire used for ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel. According to the technical scheme, the gas metal arc welding flux-cored wire used for the ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel is composed of 65-70 wt% of a steel strip and 30-35 wt% of flux core powder; the steel strip comprises the following chemical components: 0.10-0.20 wt% of C, 0.01-0.05 wt% of Si, 3-7 wt% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.002 wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.001 wt% of S, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; and the flux core powder comprises the following chemical components: 28-34 wt% of rutile, 2-4 wt% of zircon sand, 2-4 wt% of potassium titanate, 20-25 wt% of electrolytic manganese, 8-15 wt% of nickel powder, 8-12 wt% of high-carbon ferro-chrome, and the balance iron powder. According to the gas metal arc welding flux-cored wire used for the ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel, all-position welding can be achieved, and the welding efficiency is high; and formed weld metal is good in forming, low in pore sensitivity and excellent in low-temperature toughness, and the strength matches that of the ultralow-temperature high-manganese steel.
Owner:浙江鸿途焊接科技有限公司 +2
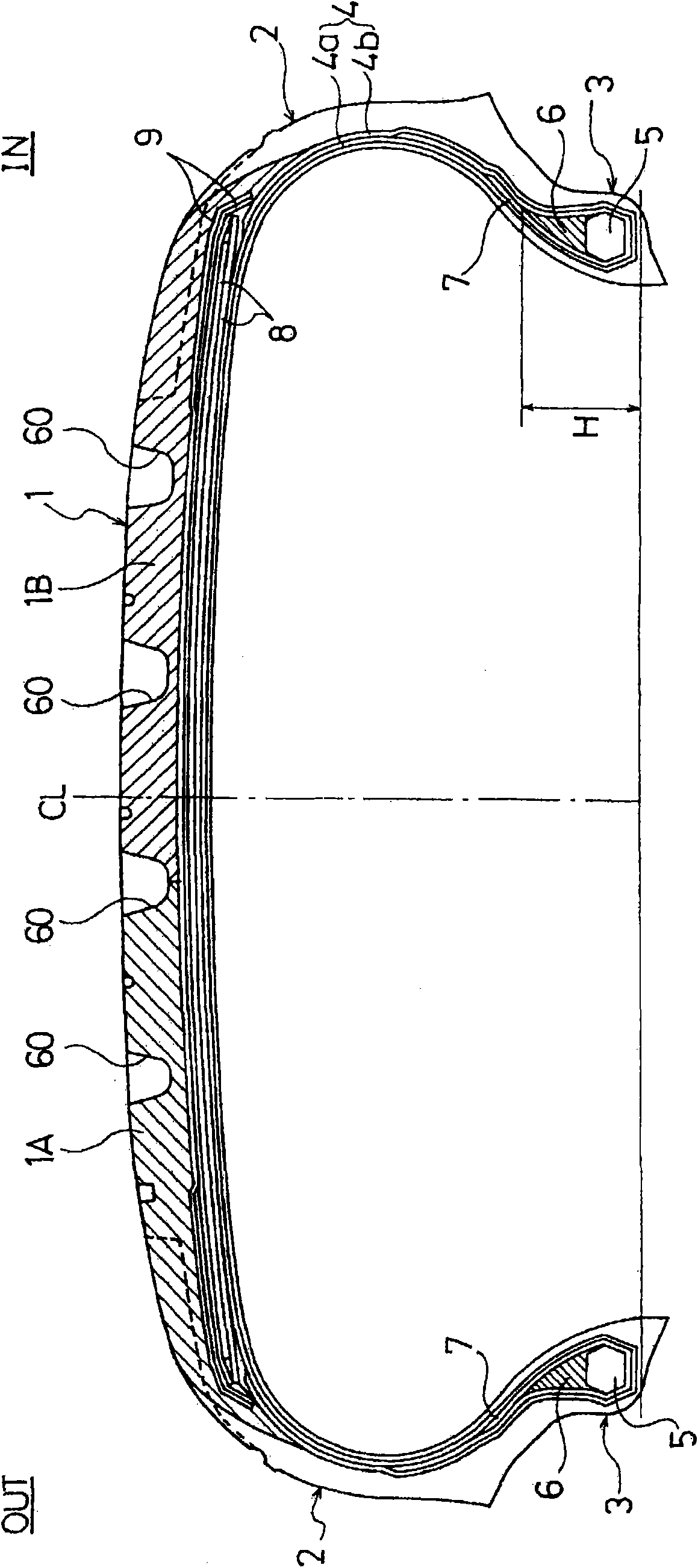
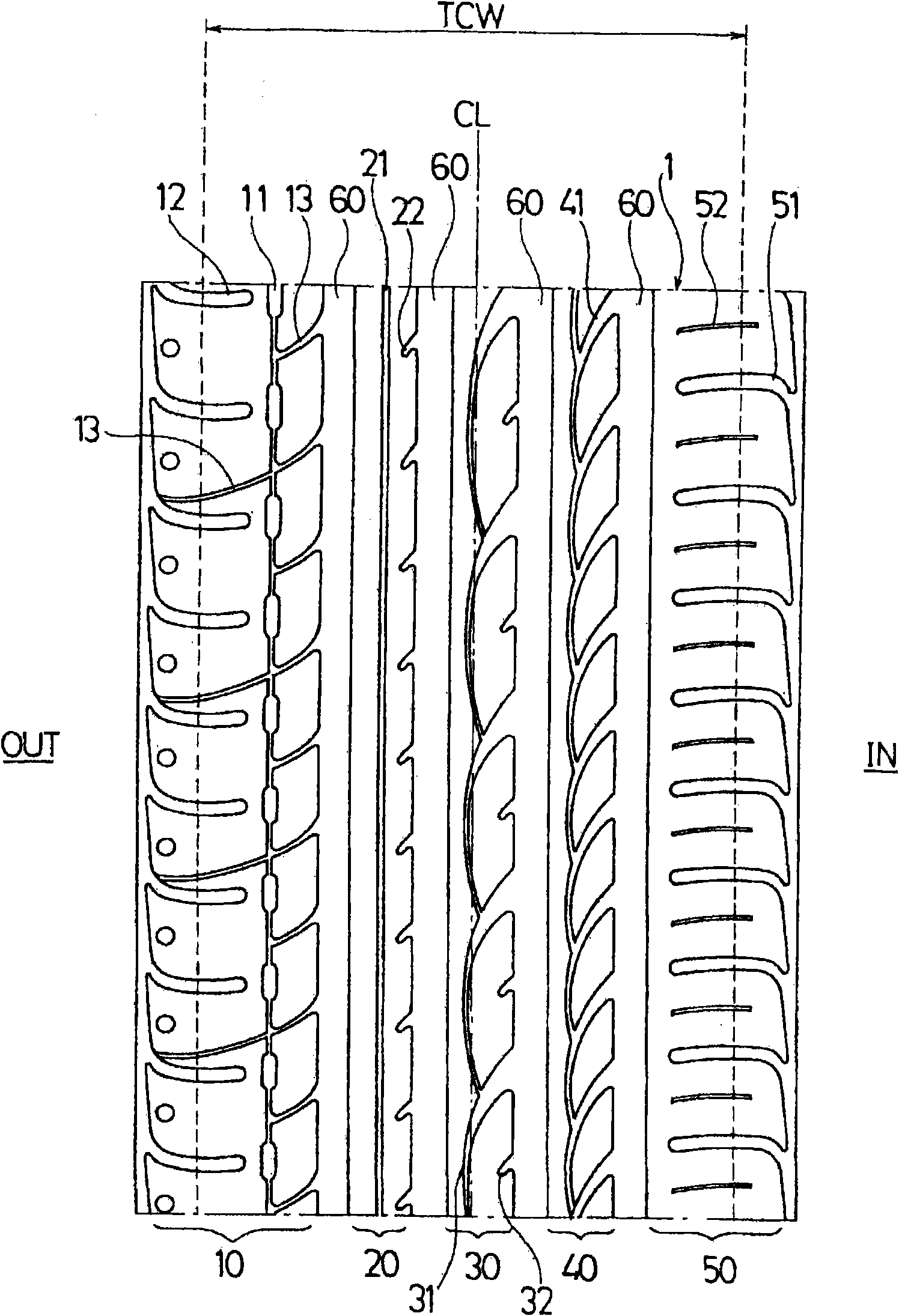
Pneumatic tire
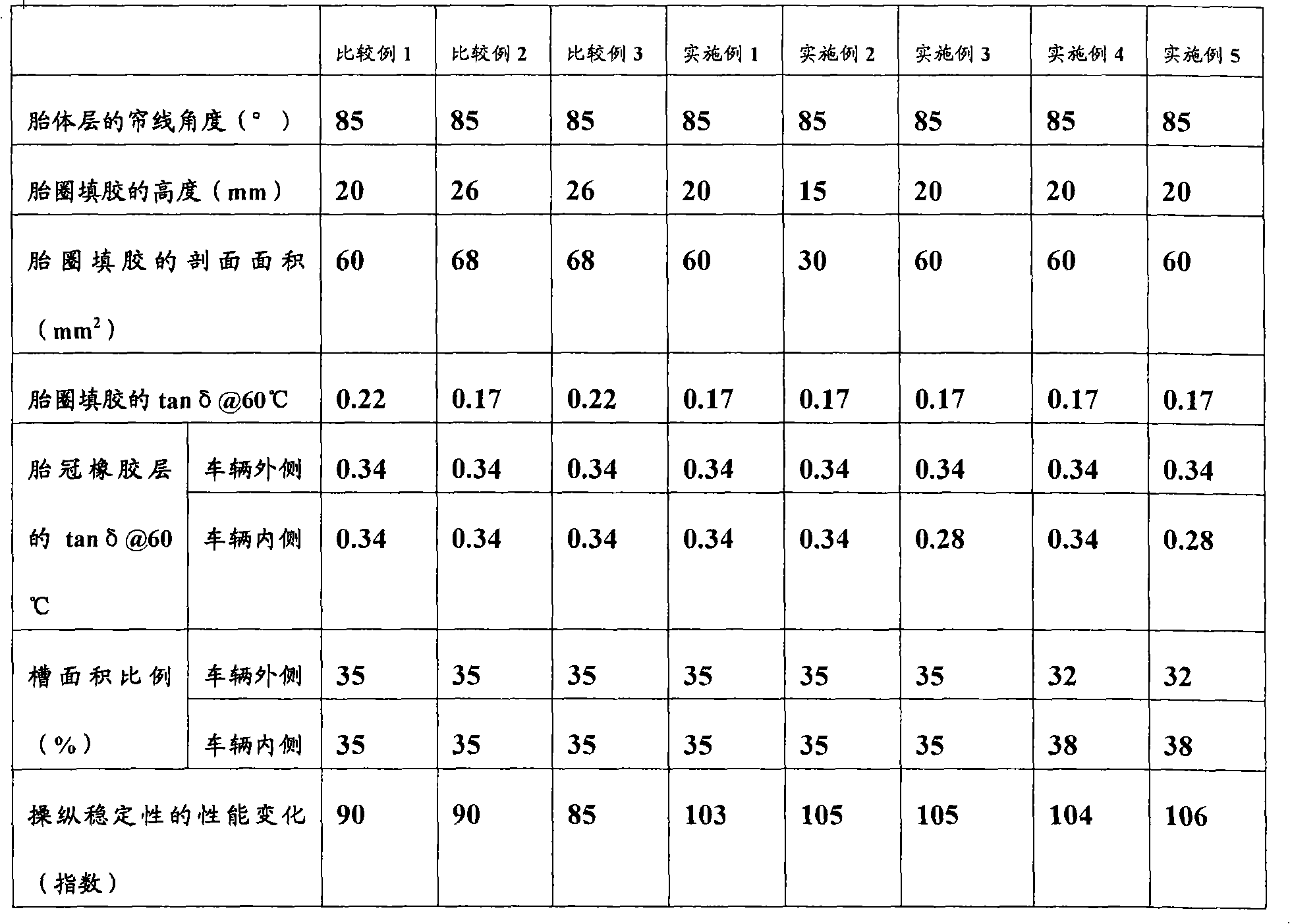
ActiveCN101541566AReduce repeated deformationSuppress feverPneumatic tyre reinforcementsInflatable tyresTan deltaMechanical engineering
A pneumatic tire that even when having a carcass layer of one-ply structure provided with its upward wound portion extending to an inferior area of belt layer so as to overlap an edge portion of the belt layer, inhibits any deterioration of driveability performance by continuous travel. The pneumatic tire has a carcass layer of one-ply structure, the cord angle of which with respect to the circumferential direction of the tire is in the range of 75 DEG to 90 DEG , provided between a pair of bead portions. At a tread portion, the carcass layer on its outer circumferential side is provided with a belt layer. The carcass layer is wound up around the bead core disposed in each of the bead portions from the tire inside to the outside so that the bead filler disposed on the bead core is pinched by the main body portion and upward wound portion of the carcass layer. The upward wound portion of the carcass layer extends to an inferior area of the belt layer so as to overlap an edge portion of the belt layer. The feature of the pneumatic tire resides in that the height of the bead filler from bead heel is 25 mm or less, and that the sectional area of the bead filler is 65 mm2 or less, and that the rubber composition constituting the bead filler exhibits a value of tan delta at 60 DEG C of 0.20 or less.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Thin film transferring device and using method thereof
ActiveCN107815662AImprove the efficiency of transfer productionSolve the problem of stress affecting device performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAdhesiveInternal stress
The invention discloses a thin film transferring device and a using method thereof. The thin film transferring device comprises a box and a vacuum pump; the table top of a first carrying table arranged inside the box and the table top of a second carrying table inside the box are oppositely arranged in the first direction, the table top of the first carrying table is used for bearing a first carrier and an adhesive layer, and the table top of the second carrying table is used for bearing a second carrier and a to-be-transferred thin film; the first carrying table and / or the second carrying table are / is lifted in the first direction; and the vacuum pump is used for providing a vacuum environment for the box. Through a covering and pressing manner, the to-be-transferred thin film is transferred to a to-be-transferred carrier, the vacuum pump is used for providing the vacuum environment for the box, gas in an adhesive is extracted, no air bubbles exist between the transferred thin film and the adhesive, the problem that the device performance is influenced by internal stress of the thin film due to the air bubbles of the adhesive is solved, the product yield is improved; and meanwhile, under the negative pressure environment, the adhesive layer can be in sufficient contact with elements on the two sides, the degree of density is large, the bonding speed is high, and the thin filmtransferring and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU JUZHEN PHOTOELECTRIC
Semiconductor pressure sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120152029A1Suppressing the variation in the performance of a semiconductor pressure sensorAvoid performance changesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationEngineering
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor pressure sensor, a multilayer structure including a polysilicon diaphragm, a polysilicon gauge resistor formed on a side of a space which is to serve as a vacuum chamber below the polysilicon diaphragm, and a group of insulating films containing the polysilicon diaphragm and the polysilicon gauge resistor and having an etching solution introduction hole in contact with a sacrificial layer is formed on the sacrificial layer. Then, an etching solution is supplied through the etching solution introduction hole and the sacrificial layer is etched with the etching solution, to thereby obtain a diaphragm body formed of the multilayer structure, which functions on the vacuum chamber, and a surface of a silicon substrate below a first opening of a first insulating film is etched to thereby form the space which is to serve as the vacuum chamber and a diaphragm stopper disposed in the space, protruding toward near the center of the diaphragm body. With this structure, it is possible to provide a technique for suppressing the variation in the performance of a semiconductor pressure sensor when the semiconductor pressure sensor is downsized.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Activating and starting method of fischer-tropsch synthetic catalyst
ActiveCN102863983AAvoid buyingReduce operating costsCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionParaffin waxPtru catalyst
An activating and starting method of a fischer-tropsch synthetic catalyst comprises the following steps of (1) adding the catalyst in an activation reactor to activate partial needed fischer-tropsch synthetic wax and preheating to 100-180 DEG C; (2) injecting mixed slurry of the pre-mixed fischer-tropsch synthetic wax and the catalyst in the activation reactor, supplementing the fischer-tropsch synthetic wax to enable the formed mixed slurry to achieve a preset liquid level in the activation reactor, and evenly mixing the fischer-tropsch synthetic wax and the catalyst to be activated; (3) conducting catalyst activation at needed activation conditions; and (4) transporting activated catalyst slurry to a fischer-tropsch synthetic reactor to be used for conducting a fischer-tropsch synthetic reaction. By means of the method, starting cost can be obviously reduced, and buying of a large quantity of paraffin wax and liquid wax is avoided.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
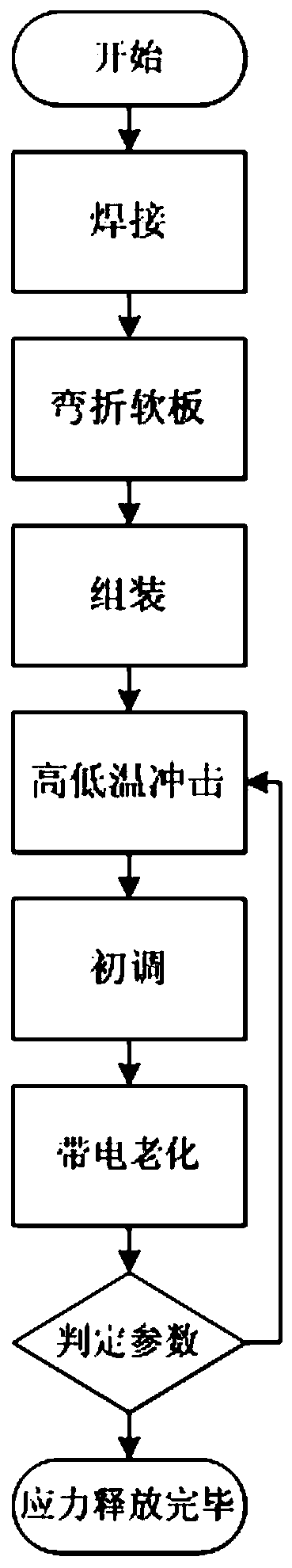
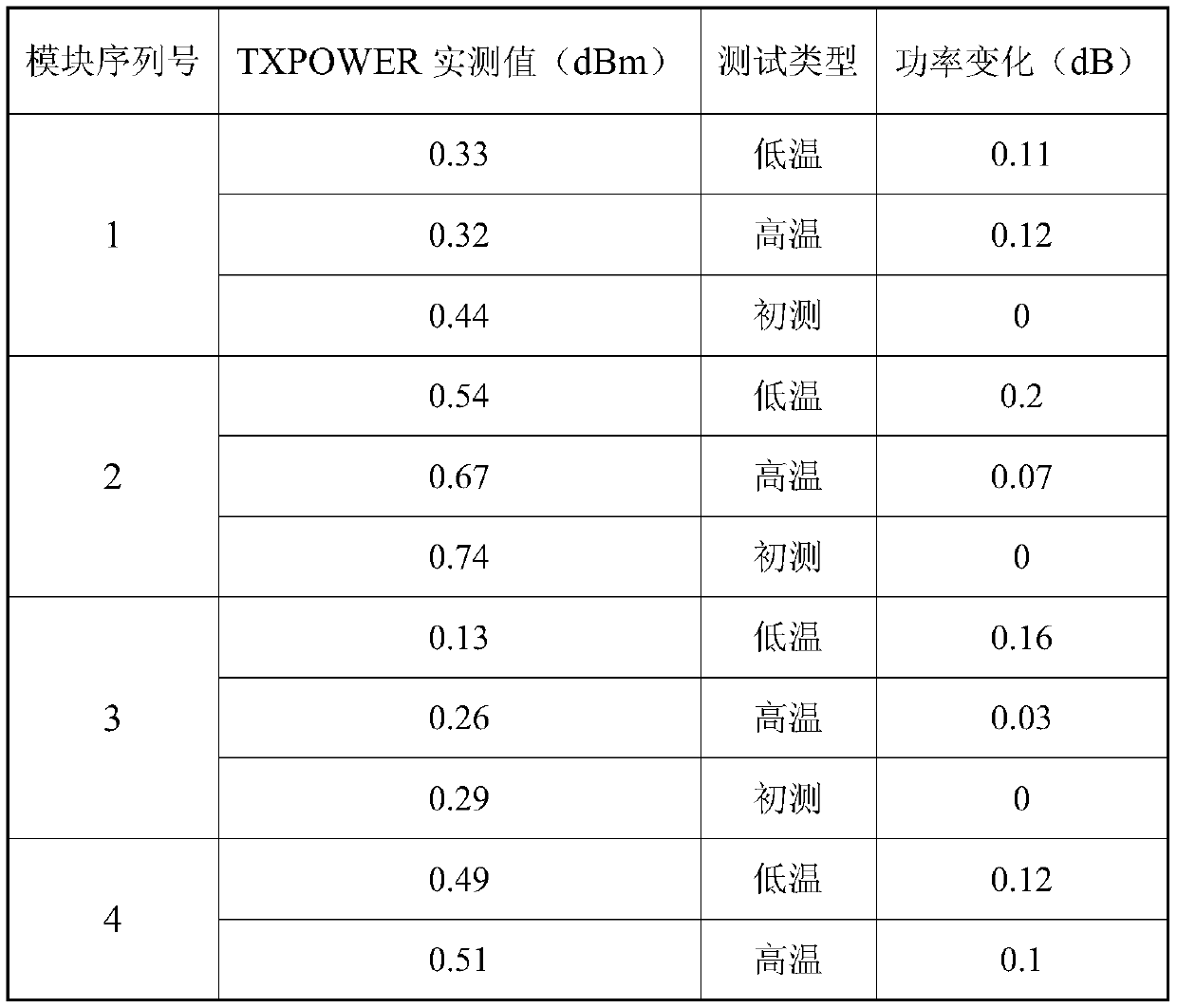
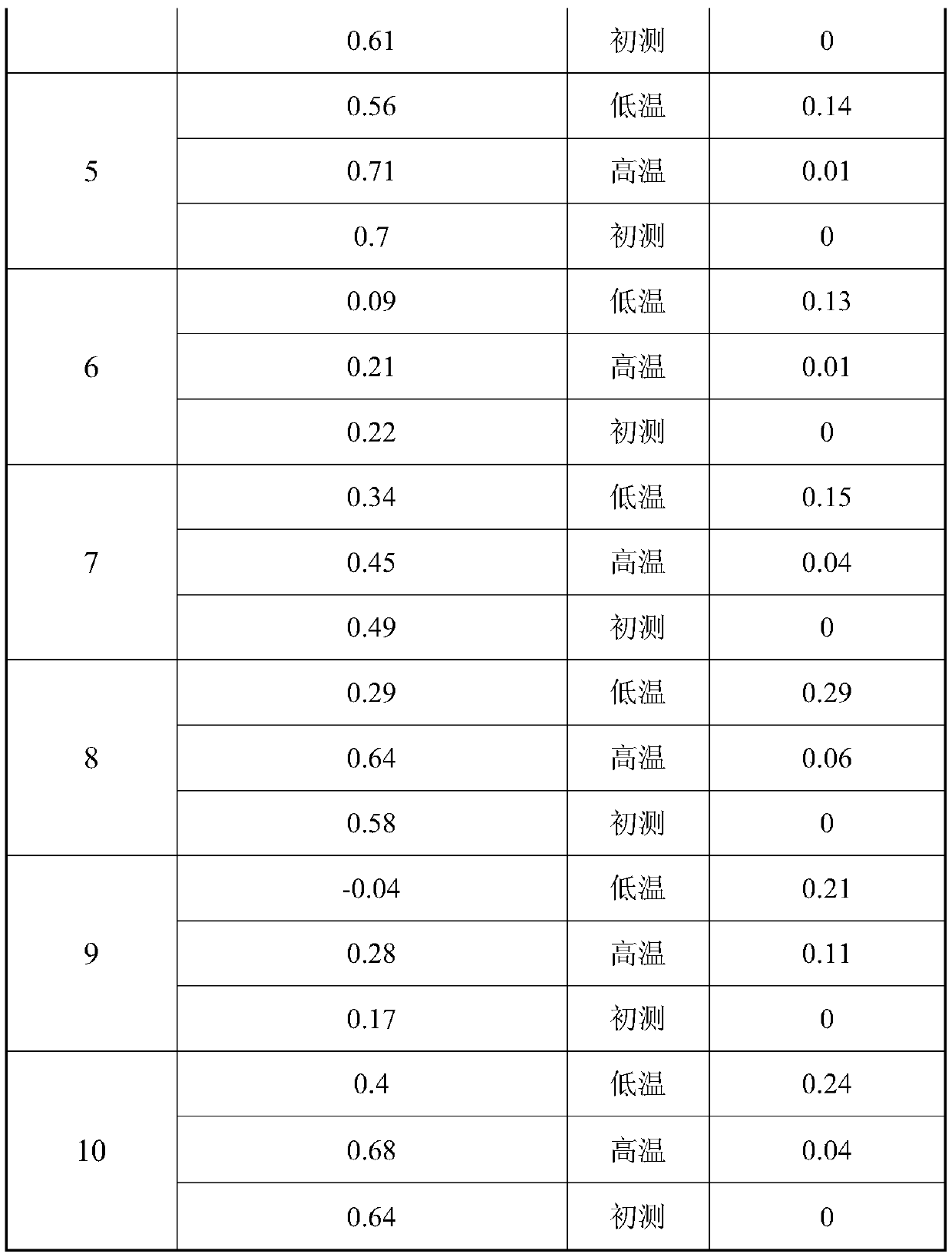
Optical module stress release method
ActiveCN110205472AAvoid powerAvoid performance changesFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesOptical ModuleEngineering
The invention relates to the field of optical communication, in particular to a production process of an optical module. An optical module stress release method comprises the following steps: (1) welding an optical device; (2) bending a soft plate; (3) assembling the optical module; (4) performing rapid high-low temperature impact on the optical module; (5) performing normal temperature initial adjustment on the performance of the optical module; (6) electrically aging the optical module; and (7) carrying out a final detection test on the optical module, and comparing parameters such as power,current and reported value of normal temperature initial adjustment to check whether the stress release is complete. With the method, the stress generated when the optical device is welded and the soft plate is bent and the stress generated when the optical device, the soft plate and a PCBA plate are assembled into a tube shell can be effectively released, and the variation of power deviation andperformance caused by the stress of the optical device in the tube shell of the optical module is avoided, so that the stability and reliability of the optical module are guaranteed. The process is simple and convenient, and the method is suitable for the optical modules in various packaging forms.
Owner:DALIAN CANGLONG OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Method for preparing three-dimensional mesoscopic device
ActiveCN106927420AImprove mechanical propertiesGood physical propertiesDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingGlass fiberThree dimensional shape
The invention relates to a method for preparing a three-dimensional mesoscopic device. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a micro-nano scale metallic glass strip or a metallic glass fiber, and performing elastic folding by means of a die of a fixed shape and forming the desired three-dimensional shape and then fixing; by controlling the energy density and irradiation time of lasers or plasmas and the rotation speed of a rotatable support frame, making the three-dimensional shape of the metallic glass strip or the metallic glass fiber formed by elastic folding generate structural relaxation quickly, so as to finish rapid shaping of the three-dimensional shape; and taking down the metallic glass strip or the metallic glass fiber, then the three-dimensional mesoscopic device of the desired shape is obtained. The preparation method of the invention is simple and easy and convenient for industrialization.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com