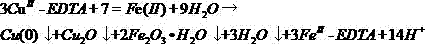Method for removing complex-state heavy metals from magnetic iron-based material through reduction decomplexing
A technology for iron-based materials and heavy metals, which is applied in the field of magnetic iron-based materials to reduce complexes and remove complexed heavy metals. It can solve the problems of high cost, large demand for chemicals, flammability and explosion of sodium dithionite, etc., and achieve short reaction process. , simple process, good separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Take 200 mL of simulated wastewater. The water sample mainly contains complexed copper, the molar ratio of heavy metals to complexing agents is Cu:EDTA=1:1, the concentration of EDTA-Cu is 0.2 mmol / L, and pH=5.0.
[0024] (1) Weigh a certain amount of ferrous salt and dissolve it in water without dissolved oxygen, add 2 g / L Fe 3 o 4 nanoparticles, and gradually add oxygen-free NaOH solution to the above solution to control Fe(II) and OH - The molar ratio of the mixture was 1:2, and the reaction was stirred for 10 min while adding, and a black-green suspension was obtained.
[0025] (2) Control the oxidation-reduction potential ORP3 2- Add 1.0 mL of 2 mol / L Na 2 CO 3 solution so that CO in wastewater 3 2- The concentration is 600 mg / L. According to the type and concentration of heavy metal ions in the wastewater, the suspension prepared in step (1) was added to make the concentration 0.4 g / L, and the reaction was stirred slowly for 30 min.
[0026] (3) The waste ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Take 200 mL of simulated wastewater. The water sample mainly contains complexed copper. The molar ratio of heavy metals to complexing agents is Cu:citric acid=1:1, the concentration of citric acid-Cu is 0.2 mmol / L, and pH=2.0.
[0029] (1) Weigh a certain amount of ferrous salt and dissolve it in water without dissolved oxygen, add 2 g / L Fe 3 o 4 nanoparticles, and gradually add oxygen-free NaOH solution to the above solution to control Fe(II) and OH - The molar ratio of the mixture was 1:5, and the reaction was stirred for 10 min while adding, and a black-green suspension was obtained.
[0030] (2) Adjust the pH of the wastewater containing heavy metals to above 5.0, and control the oxidation-reduction potential ORP of the wastewater by nitrogen exposure to 3 2- Add 1.0 mL of 2 mol / L Na 2 CO 3 solution so that CO in wastewater 3 2-The concentration is greater than 500 mg / L. According to the type and concentration of heavy metal ions in the wastewater, the suspen...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Take 200mL of simulated wastewater. The water sample mainly contains complexed copper, complexed cobalt, and complexed nickel. The molar ratios of heavy metals and complexing agents are Cd:Co:Ni:citric acid:NTA=1:1: 1:1:1, the concentration is 0.2 mmol / L, pH=8.0, CO in wastewater 3 2- The concentration is 745 mg / L.
[0034] (1) Weigh a certain amount of ferrous salt and dissolve it in water without dissolved oxygen, add 2 g / L Fe 3 o 4 nanoparticles, and gradually add oxygen-free NaOH solution to the above solution to control Fe(II) and OH - The molar ratio was 1:3, and the reaction was stirred for 10 min while adding, and a black-green suspension was obtained.
[0035] (2) Control the oxidation-reduction potential ORP<100 mV of wastewater by means of nitrogen aeration. According to the type and concentration of heavy metal ions in the wastewater, add the suspension prepared in step (1) to make the concentration 1.0 g / L, and stir slowly for 60 minutes.
[0036] (3)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com