Soil improver prepared from waste materials of ecological fermentation bed and preparation method thereof
A soil conditioner and biological fermentation technology, applied in the fields of agricultural production and soil improvement, can solve the problems of breeding owners, low utilization efficiency of resources, and lack of use, and achieve a good working environment, rich soil microbial flora, The effect of improving soil structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
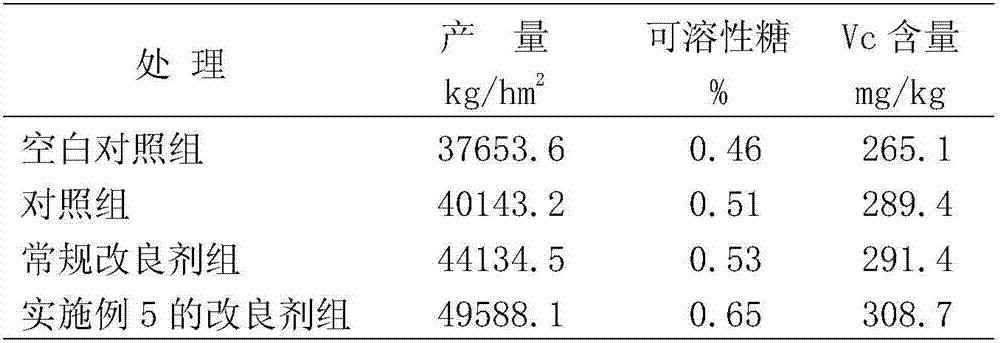
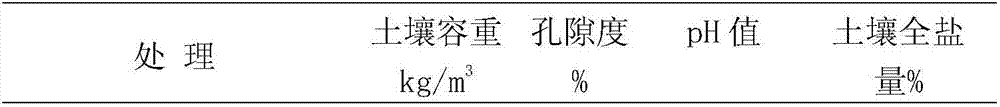
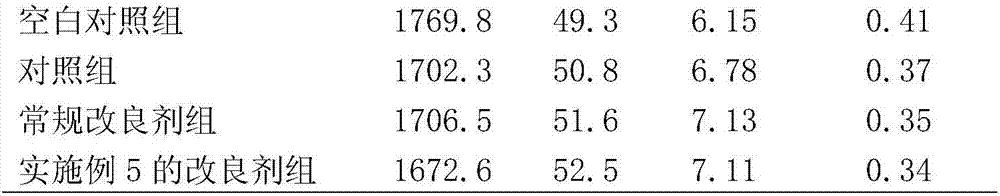
[0037] A soil conditioner prepared by utilizing the waste materials of the biological fermentation bed, which is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 90 parts of waste materials withdrawn from the biological fermentation bed, 25 parts of wheat straw, 20 parts of corncob powder, and 15 parts of sargassum 12 parts of chitin solution, 3 parts of plant ash, 1 part of shell powder, 4 parts of silkworm excrement, 5 parts of bentonite, 2 parts of seaweed, 3 parts of fulvic acid, 1 part of cellulase, and 1 part of protease.
[0038] The waste that exits from the biological fermentation bed is the waste that exits after the use of a common piggery biological fermentation bed for 1 year.
[0039] The preparation method of above-mentioned soil conditioner is as follows:
[0040] (1) Take the above-mentioned raw material components according to the proportioning ratio;
[0041] (2) drying the waste material that has been weighed and withdrawn from the biological ferme...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A soil conditioner prepared from waste materials of biological fermentation beds, prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 95 parts of waste materials exiting from biological fermentation beds, 30 parts of wheat straw, 25 parts of corncob powder, and 10 parts of sargassum 15 parts of chitin, 3 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of shell powder, 3 parts of silkworm excrement, 8 parts of bentonite, 1 part of seaweed, 4 parts of black humic acid, 0.2 parts of magnesium, 0.01 part of zinc, 0.01 part of manganese, iron 0.05 parts, 2 parts cellulase, 1 part protease.
[0048] The waste that exits from the biological fermentation bed is the waste that exits after the use of a common piggery biological fermentation bed for 1 year.
[0049] The preparation method of above-mentioned soil conditioner is as follows:
[0050] (1) Take the above-mentioned raw material components according to the proportioning ratio;
[0051] (2) drying the waste material that has been weig...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A soil conditioner prepared by utilizing the waste materials of biological fermentation bed, which is prepared from the following components in mass parts: 100 parts of waste materials withdrawn from biological fermentation bed, 20 parts of wheat straw, 30 parts of corncob powder, 15 parts of sargasso 10 parts of chitin, 4 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of shell powder, 4 parts of silkworm excrement, 10 parts of bentonite, 3 parts of seaweed, 5 parts of brown humic acid, 0.1 part of magnesium, 0.01 part of zinc, 0.01 part of manganese, iron 0.02 parts, 0.5 parts of grape oxidase.
[0058] The waste that exits from the biological fermentation bed is the waste that exits after the use of a common piggery biological fermentation bed for 1 year.
[0059] The preparation method of described chitin solution is: collect or buy the materials with higher chitin content such as shrimp shells and crab shells, dry it and pulverize it, then acidify it with concentrated nitric acid, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com