Macromolecular temperature-sensitive driver and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of macromolecules and actuators, which is applied in the field of macromolecular temperature-sensitive actuators and its preparation, and can solve problems such as application limitations, complicated processes, and inability to realize receptor protein regulation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
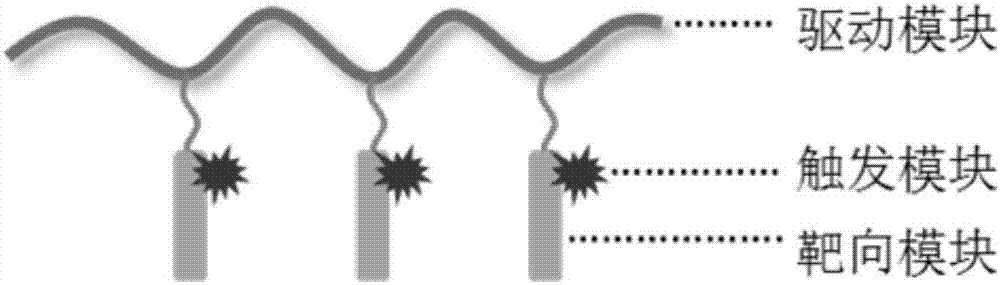
[0049] The structural schematic diagram of the macromolecular temperature-sensitive actuator prepared in this example is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it includes a targeting module composed of a polypeptide ligand, a driving module composed of a temperature-sensitive polymer, and a trigger module composed of a photothermal conversion molecule, the trigger module is connected to the targeting module, and the targeting module is The module is connected with the drive module. Among them, the photothermal conversion molecule is rhodopsin-18, and the polypeptide ligand is CKGGMSRTMS (in order to connect rhodopsin-18, amino acid K is added; in order to connect the polypeptide with the polymer, amino acid C is added. GG is a flexible spacer), connected with The molecular structure of the polypeptide ligand CK(P18)GGMSRTMS of rhodopsin-18 is shown below:
[0050]
[0051] In this embodiment, the synthesis method of the macromolecular temperature-sensitive actuator is as follows:...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The polypeptide ligand CK(P18)GYHWYGYTPQNVI was synthesized using the same polypeptide ligand synthesis method as in step (1) of Example 1, and its structure is as follows:
[0068]
[0069] Use the same method as step (2) of Example 1 to connect rhodopsin-18 to the polypeptide ligand, and then perform the same steps (3) and (4) as Example 1 to prepare a macromolecular thermosensitive actuator , whose structure is as follows:
[0070]
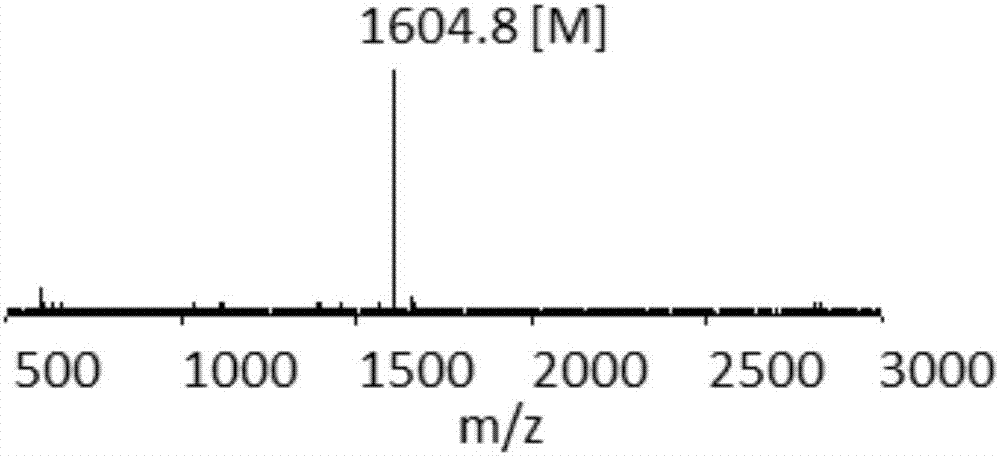
[0071] The MALDI-TOF spectrum of the polypeptide ligand CK(P18)GYHWYGYTPQNVI prepared in this example is as follows Figure 4 As can be seen from the figure, the molecular weight of the polypeptide is 2375.0, and the peak of the molecule plus sodium ion is 2397.0.
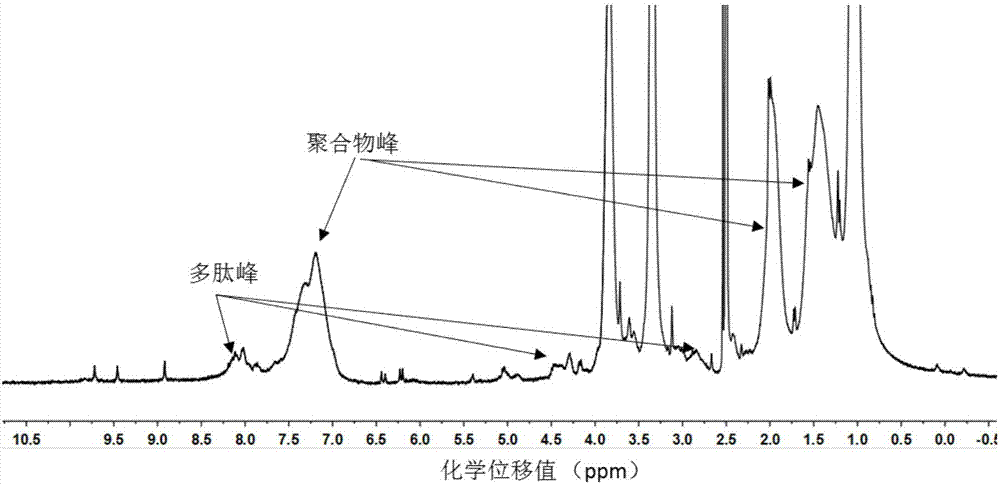
[0072] The structure of the obtained macromolecular thermosensitive actuator was characterized by hydrogen NMR spectroscopy, and the results are as follows Figure 5 As can be seen from the figure, the chemical shift values δ=3.43ppm and δ=3.18ppm correspond to -OCH...
Embodiment 3
[0074] The macromolecular temperature-sensitive actuator prepared in Example 1 is Image 6 The shown method regulates the oligomerization of the membrane receptor protein on the cell membrane surface, and the driver pulls the oligomerization of the receptor protein to verify that the method is as follows:
[0075] FITC-labeled thermosensitive driver molecules were incubated with adherent SKBR3 cells at a concentration of 3 μM in a confocal dish for half an hour to allow the molecules to bind to cell surface receptor proteins; the results of confocal laser microscopy imaging are as follows Figure 7As shown, picture A is the SEM picture without laser irradiation, and picture B is the SEM picture with and without laser irradiation. When the laser is not irradiated, the driver molecules are in a stretched state and spread on the cell surface, and almost There is no cell entry, and the cell surface fluorescence is weak; when the wavelength of 655nm is used, 4.77W cm -2 The sample...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com