Method for recycling water sediment
A resource utilization and sediment technology, applied in the direction of botanical equipment and methods, applications, planting substrates, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient utilization of sediment, large investment in treatment facilities, unfavorable environmental governance, etc., and achieve less odor and better performance The effect of stabilizing and promoting growth and reproduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-10
[0045] Embodiment 1-10, adopt the method of the present invention to prepare humic substance product
[0046] In all the embodiments of this series, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics: the method is used for resource treatment of water body sediment, and the method includes the following steps: the weight ratio of the sediment to the culture substrate is 10:1 -3 After mixing and pulverizing the raw materials, inoculating high-temperature-resistant organic matter-degrading bacteria for high-temperature fermentation in an aerobic environment to obtain humus;
[0047] The inoculum amount of the organic matter-degrading bacteria is 1-10% of the weight of the raw material, see Table 1 below for details; see Table 1 below for the grinding fineness and the culture substrate.
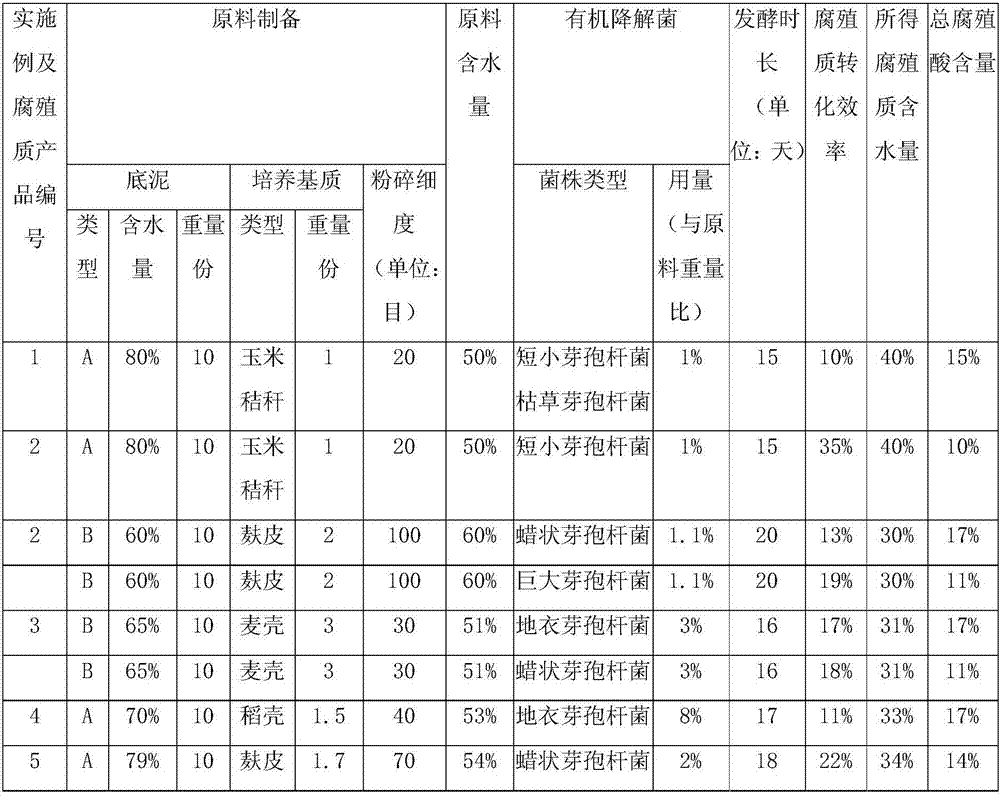
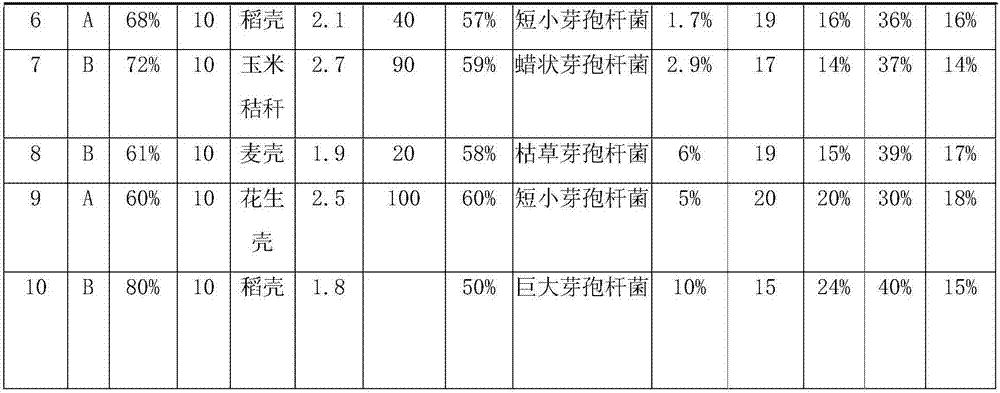
[0048] Table 1
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] The bottom mud of type A is ordinary bottom mud; the bottom mud of type B is the bottom mud that meets the national "soil envi...
Embodiment 11-30
[0054] Embodiment 11-30, using the method of the present invention to further prepare the cultivation substrate
[0055] In this series of embodiments, the auxiliary material formula used is specifically shown in Table 2 below:
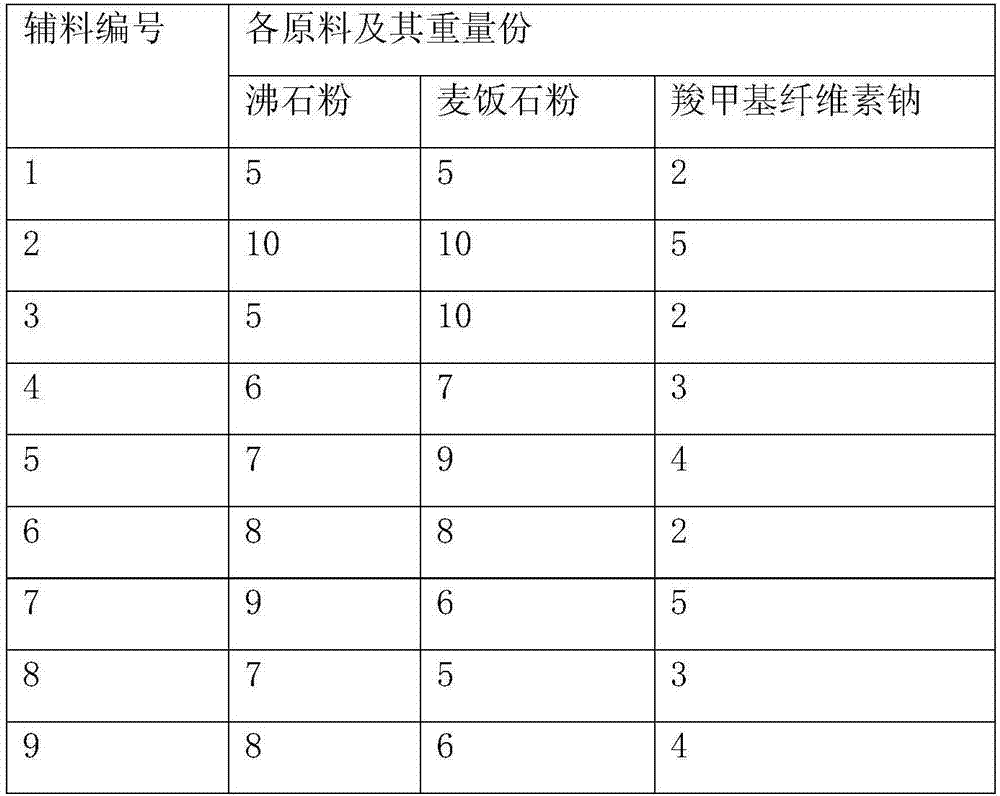
[0056] Table 2
[0057]
[0058]
[0059] The specific operating parameters of the method provided by this series of embodiments, and the corresponding cultivation substrate product performance values obtained are shown in Table 3 below:
[0060] table 3
[0061]
[0062]
[0063] The methods in the above-mentioned embodiments all include this step: mixing the auxiliary material and the humic substance in the weight ratio listed in the above table.
[0064] The types of cultivated plants involve: aquatic plants, such as: dry grass, dwarf dry grass, snapdragon, foxtail, water lily; non-aquatic plants, such as: coleus, pothos, asparagus, rose.
[0065] During the cultivation effect testing process, 100 plants were cultivated for each pl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com