A non-migration antibacterial cellulose-based foam and its preparation method
A cellulose-based, cellulose-based technology, applied in the field of non-migration antibacterial cellulose-based foam and its preparation, can solve problems such as difficulty in reducing, and achieve the effect of simple preparation process, broad-spectrum and high-efficiency antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
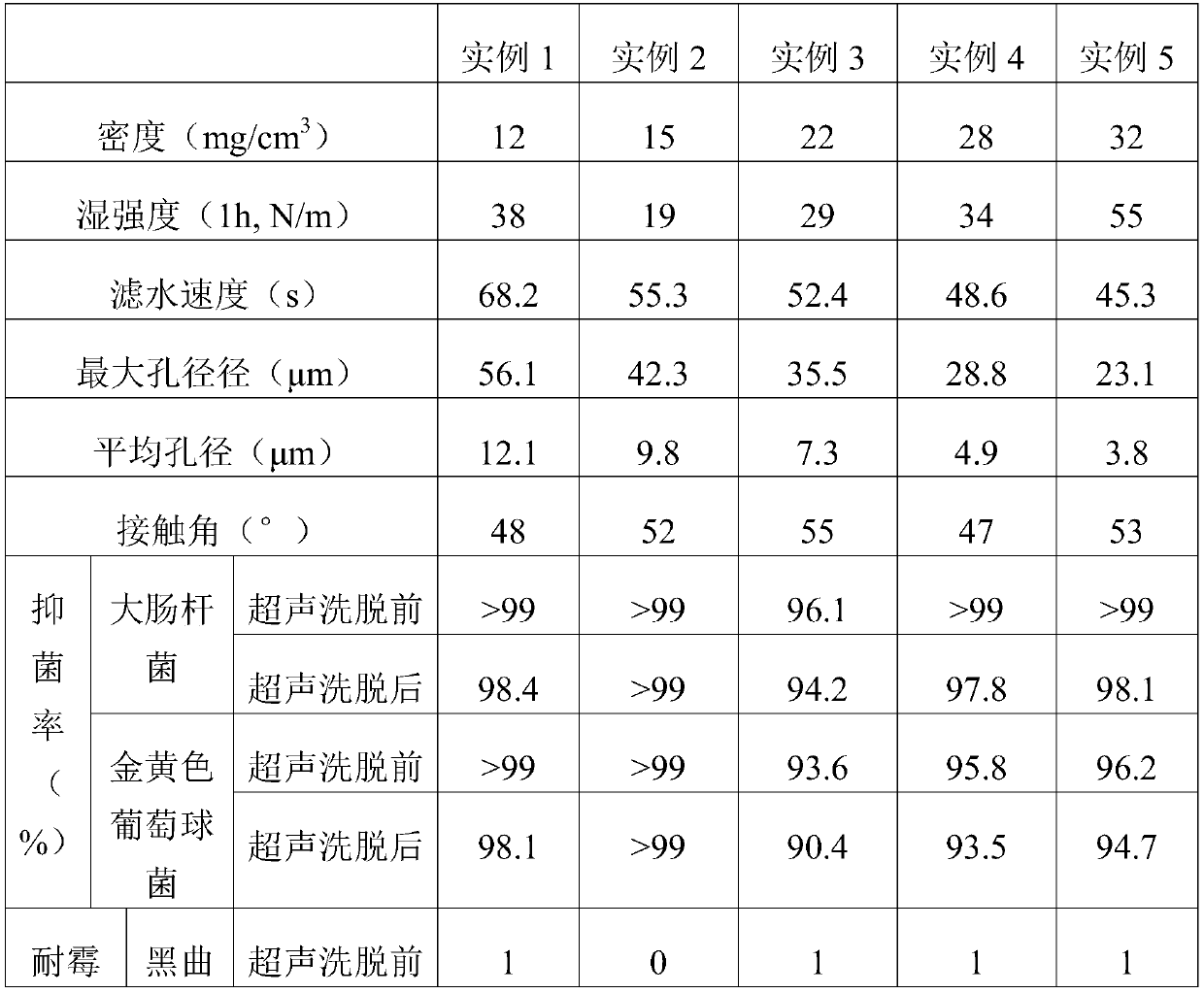
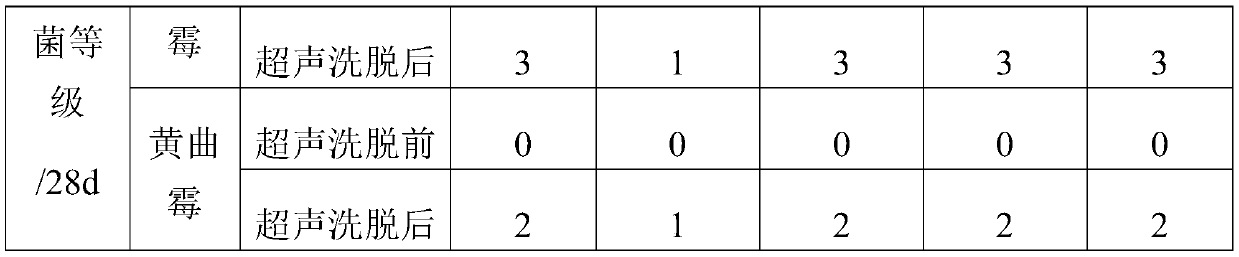
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) take the following components in g: water 1800g, 200g solid content are bleached eucalyptus fiber pulp (containing 20g wood cellulose in it) of 10wt% solid content, 2g wet strength agent CPAM, 2g surfactant AOS, 0.2g cross-linking agent MBA and 2g antibacterial agent antibacterial thermoplastic starch granules, then mix the bleached eucalyptus fiber pulp and water and place it in the pulp fiber disintegrator, and disintegrate it for 20min at a speed of 2000r / min until the eucalyptus fiber is evenly dispersed In the water;
[0028] (2) Weigh the obtained wet strength agent, surfactant, cross-linking agent and antibacterial agent in step (1) and add them to the material obtained after decomposing in step (1), and mix and stir at a speed of 1000r / min with a mechanical stirrer 30min, then quickly pour it into a Buchner funnel covered with filter paper, remove most of the water and foam by suction filtration under a pressure of 5kPa, and dry the obtained wet cellulose fo...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Take the following components in units of g: water 1800g, 200g solid content are 12wt% bleached bagasse fiber pulp (containing 24g wood cellulose), 2.4g wet strength agent PAE, 2.5g surfactant ABS , 0.3g cross-linking agent EGDMA and 0.6g guanidinium salt polymer macromonomer, then mix the bleached bagasse fiber pulp with water and place it in a pulp fiber disintegrating machine, and disintegrate it for 40min at a speed of 4000r / min until the bagasse fiber is evenly dispersed in water;
[0031] (2) Weigh the obtained wet strength agent, surfactant, cross-linking agent and antibacterial agent in step (1) and add them to the material obtained after decomposing in step (1), and mix and stir at a speed of 2000r / min with a mechanical stirrer 10min, and then quickly pour it into a Buchner funnel covered with filter paper, and remove most of the water and water foam by suction filtration under a pressure of 10kPa, and dry the obtained wet cellulose foam at 40°C for 24h, an...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Take the following components in units of g: 1700g of water, 300g of sisal fiber pulp (containing 48g of wood cellulose) with a solid content of 16wt%, 2.4g of wet strength agent PEI, and 2.5g of surfactant AES , 0.3g cross-linking agent DCP and 2.5g quaternary ammonium salt polymer, then mix the sisal fiber slurry with water and place it in the pulp fiber disintegrator, and disintegrate it for 50min at a speed of 5000r / min until the sisal fiber is evenly dispersed In the water;
[0034](2) Weigh the obtained wet strength agent, surfactant, cross-linking agent and antibacterial agent in step (1) and add them to the material obtained after decomposing in step (1), and mix and stir at a speed of 2000r / min with a mechanical stirrer 25min, then quickly pour it into a Buchner funnel covered with filter paper, and remove most of the water and water foam by suction filtration under a pressure of 10kPa, and dry the obtained wet cellulose foam at 40°C for 24h, and the result...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com