Fluorescent/phosphorescent mixed white light OLED
A phosphorescence and fluorescence technology, which is applied in the field of white light OLED and fluorescent/phosphorescence mixed white light OLED, can solve the complex device structure of multi-emitting layer mixed white light OLED, limit the mass industrial production of white light OLED, and affect the stability of the device, etc., to achieve Effects of cost reduction, color stability balance, and preparation cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0059] During the preparation process of the device, the evaporation rate of the material and the thickness of the evaporation film layer are monitored by a quartz crystal frequency meter connected outside the vacuum chamber. Among them, organic materials, MoO 3 The evaporation rates of LiF, LiF, and Al are about 1Å / s, 0.3Å / s, 0.1Å / s, and 3Å / s, respectively. The overlapping part of the ITO glass and the aluminum cathode is used as the effective light-emitting layer of the device, and the effective light-emitting area is 3mm×3mm.
[0060] The detailed process of preparing the white light OLED device of the embodiment of the present invention by thermal evaporation is as follows.
[0061] First, a layer of MoO was deposited on the ITO glass substrate under high vacuum 3 As a hole injection layer (HIL), the thickness is maintained at a certain value between 2 and 8 nm. Second, in MoO 3 A layer of organic layer is continuously thermally deposited in high vacuum on the film lay...
Embodiment 1
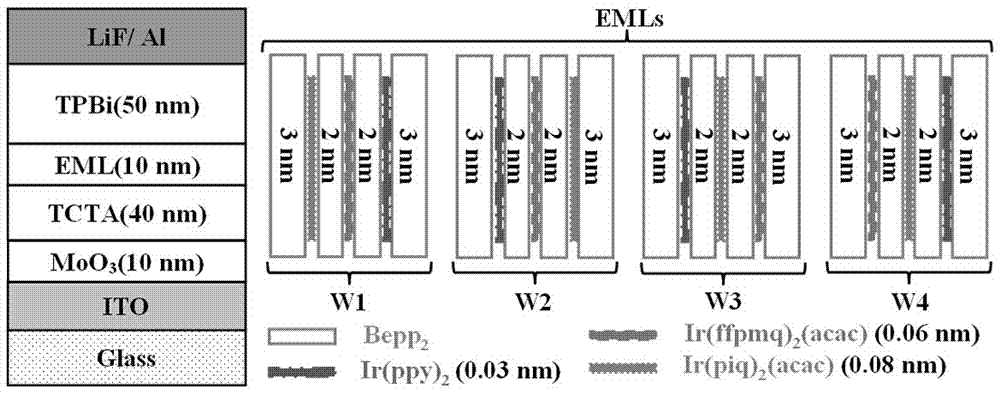
[0068] Prepare white light device W1 according to the above specific embodiment, the device structure is ITO / MoO 3 (3nm) / TCTA(40nm) / Bepp 2 (3nm) / Ir(piq) 2 (acac) (0.08nm) / Bepp 2 (2nm) / Ir(ffpmq) 2 (acac)(0.06nm) / Bepp 2 (2nm) / Ir(ppy) 3 (0.03nm) / Bepp 2 (3nm) / TPBi (50nm) / LiF (1nm) / Al (200nm).
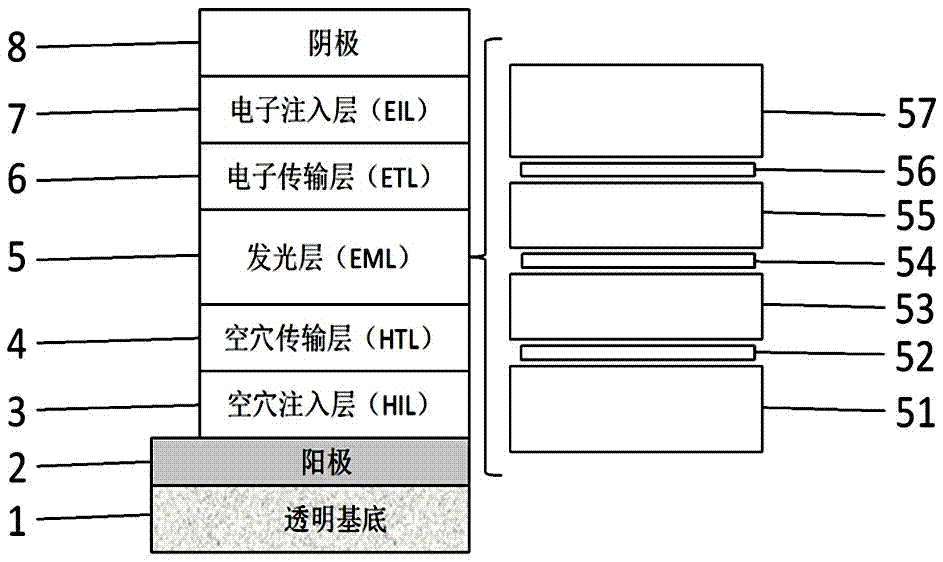
[0069] figure 2 A schematic diagram of the structure of the white light device W1 is given. ITO correspondence figure 1 The middle anode 2 has an area resistance of 15 Ω / □, and the transparent substrate 1 is a transparent glass substrate with a thickness of 1.1mm. MoO 3 correspond figure 1 The hole injection layer 3 has a thickness of 3nm. TCTA correspondence figure 1 The hole transport layer 4 has a thickness of 40nm. TPBi correspondence figure 1 The middle electron transport layer 6 has a thickness of 50nm. LiF correspondence figure 1 The middle electron injection layer 7 has a thickness of 1 nm. Al correspondence figure 1 In the cathode 8, the thickness is 2...
Embodiment 2
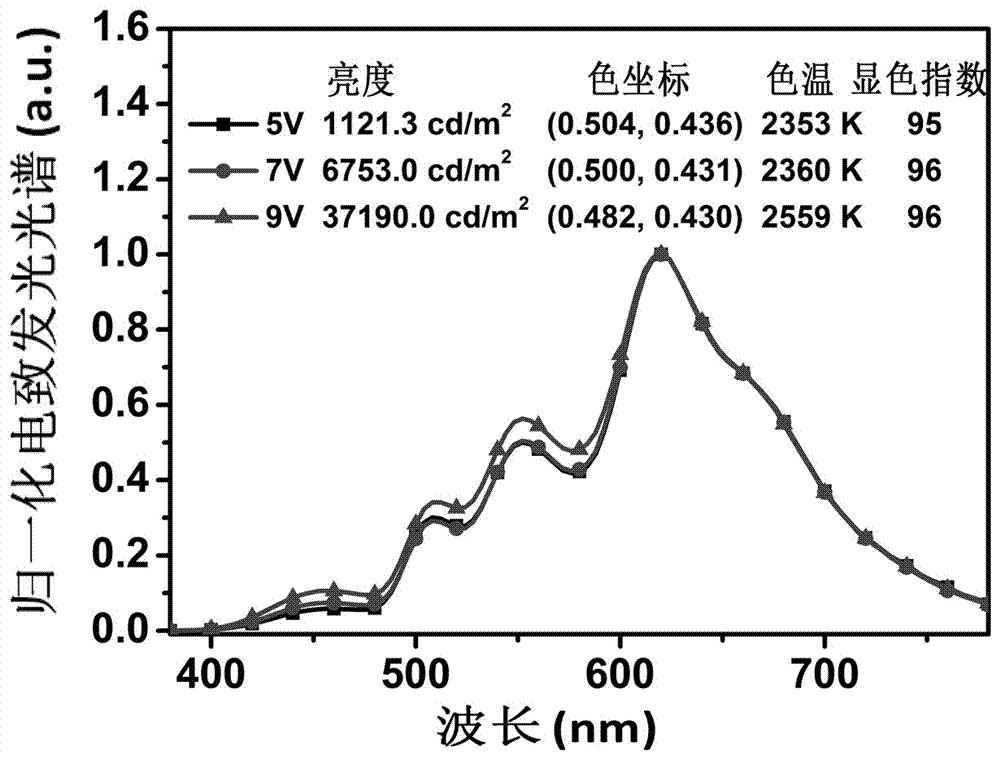
[0073] Keep the structure and device preparation materials of the white light device W1 unchanged, and change the ultra-thin red (0.08nm Ir(piq) 2 acac layer), yellow (0.06nm Ir(ffpmq) 2 acac layer), green (0.03nm Ir(ppy) 3 layer) phosphorescent emitting layer embedded in a 10nm thick blue fluorescent emitting layer (Bepp 2 Layer) in the embedding order, the embedding order from the anode to the cathode is green / yellow / red, and the white light device W2 is prepared, and the device structure is ITO / MoO 3 (3nm) / TCTA (40nm) / Bepp 2 (3nm) / Ir(ppy) 3 (0.03nm) / Bepp 2 (2nm) / Ir(ffpmq) 2 acac (0.06nm) / Bepp 2 (2nm) / Ir(piq) 2 acac(0.08nm) / Bepp 2 (3nm) / TPBi (50nm) / LiF (1nm) / Al (200nm), the device structure is as figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com