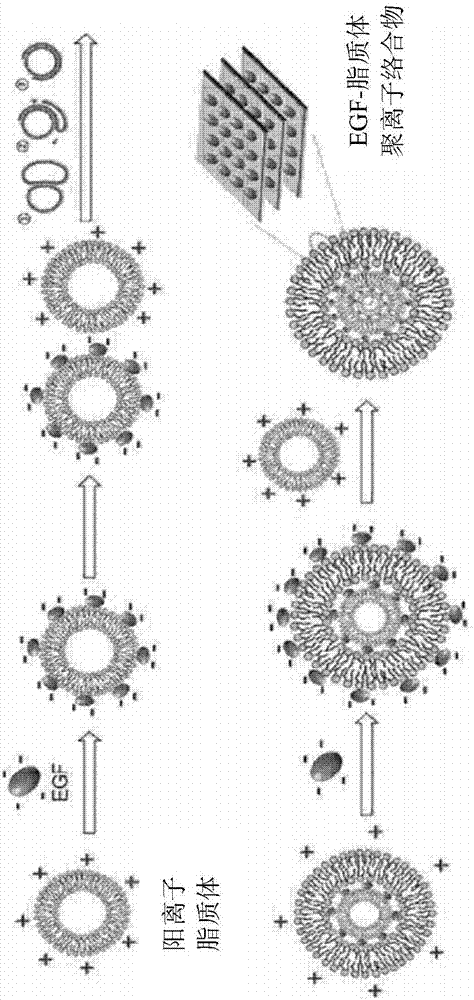
Hybrid-type multi-lamellar nanostructure of epidermal growth factor and liposome and method for manufacturing same
A technology of epidermal growth factor and nanostructure, which is applied in liposome delivery, skin care preparations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of low encapsulation efficiency of active ingredients and decreased protein physiological activity, etc., and achieve The effect of simple manufacturing process and high encapsulation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1: Preparation of EGF-DOTAP hybrid multilayer nanostructure
[0063] 1.1: Preparation of cationic empty monolamellar liposomes containing DOTAP
[0064] The cationic lipid DOTAP (20.96 mg, Avanti Polar Lipid, Inc.) was dissolved in 1 ml of chloroform and mixed in a round glass flask. Chloroform was removed by flushing the lipid solution with nitrogen gas at low speed in a rotary evaporator, and the lipid was dried to form a thin lipid layer. The formed lipid layer was further dried in vacuum for 12 h to completely remove the remaining chloroform. 1 ml of purified water was added to the prepared lipid layer, followed by stirring at 37°C for 2 hours, thereby preparing empty lipid vesicles. The obtained empty lipid vesicles were extruded through a polycarbonate membrane (polycarbonate membrane) (Avanti Polar Lipid, Inc.) with a pore size of 100 nm (Avanti Polar Lipid, Inc.) several times to prepare a cationic empty monolayer lipid containing DOTAP and havi...
experiment Embodiment 1
[0067] Experimental Example 1: Evaluation of Formation of EGF-DOTAP Hybrid Multilayer Nanostructures
[0068] 1.1: Confirmation of the formation of cationic empty unilamellar liposomes
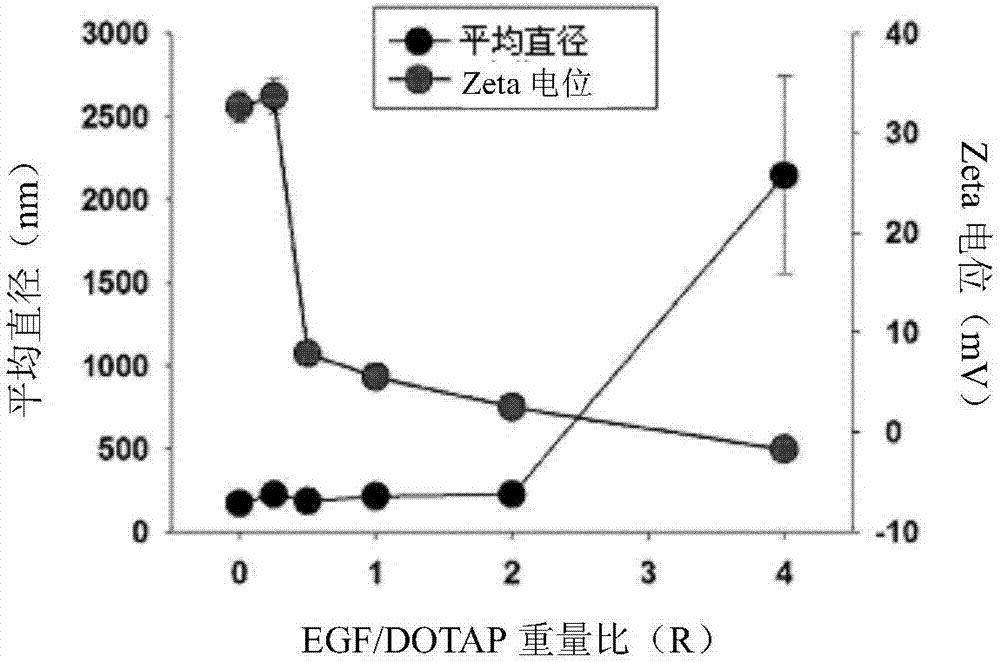
[0069] The particle size and zeta potential of the cationic empty unilamellar liposomes prepared in Example 1.1 were measured using dynamic light scattering (DLS, ELSZ-1000, Otsuka Electronics), and the measurement results are shown in Table 1 below. The measurement results showed that the prepared cationic empty monolamellar liposome had a particle size of 200nm and a positive surface charge.
[0070] [Table 1]
[0071] Empty unilamellar liposomes
[0072] Empty unilamellar liposomes
Particle size (nm)
Zeta potential (mV)
DOTAP
197.7±4.9
56.5±2.5
[0073] 1.2: Confirmation of the formation of EGF-DOTAP hybrid multilayer nanostructures
[0074] Use DLS to measure the particle size and zeta potential of the EGF-DOTAP hybrid multilayer nanostructure p...
experiment Embodiment 2
[0077] Experimental Example 2: Evaluation of EGF Encapsulation Efficiency in EGF-DOTAP Hybrid Multilayer Nanostructures
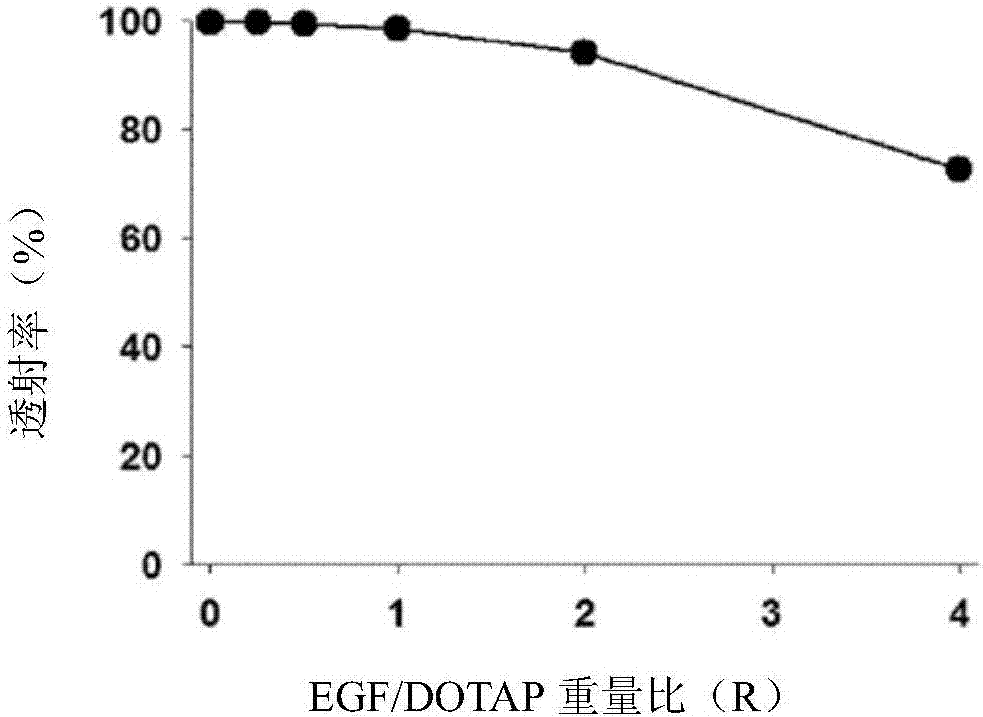
[0078] In order to measure the amount of EGF encapsulated in the EGF-DOTAP hybrid multilayer nanostructures, the EGF-DOTAP hybrid multilayer nanostructures prepared in Example 1.2 were subjected to an ultracentrifuge (200,000 x g, 2 hours, 4°C, Beckman). Layer nanostructures (1 ml) were centrifuged to separate unencapsulated free EGF. The amount of isolated free EGF was measured using a micro BCA assay and an ELISA assay. The measurement results are shown in Figure 4 .
[0079] From Figure 4 As can be seen in , high encapsulation efficiencies of 60% or higher occur at most EGF / DOTAP weight ratios, which vary slightly depending on the method used to quantify EGF. Thus, it can be seen that the encapsulation efficiency in the structures according to the invention is significantly higher than in conventional liposomes (only 10-20%).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com