Wood modification to enhance fire retardancy
A fire-retardant, wood technology, used in wood treatment, wood heating, wood impregnation, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to achieve and meet durability, and achieve the effect of improving dimensional stability and increasing wood densification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (a) The operating pressure ranges from 50 to 3000 kPa depending on the various processing methods used.
[0031] (b) Also depending on the various processing methods used, the operating vacuum ranges from -10 to -90 kPa. These processes also require initial vacuum, final vacuum, extended vacuum, etc.,
[0032] (c) Depending on the process used, the pressure and vacuum cycle time will be from 2 to 120 minutes.
[0033] Heating (fixing) process.
[0034] Once the treated flame retardant "working solution" has been impregnated into the wood (via the treatment method), the wood must then undergo a heat (fixation) process based on a time / temperature scheme. The time / temperature protocol is based on a time range of 18 to 36 hours and a temperature range (in / out) of 80 to 130°C. The time / temperature range parameters are very critical to optimize chemical fixation without compromising wood strength.
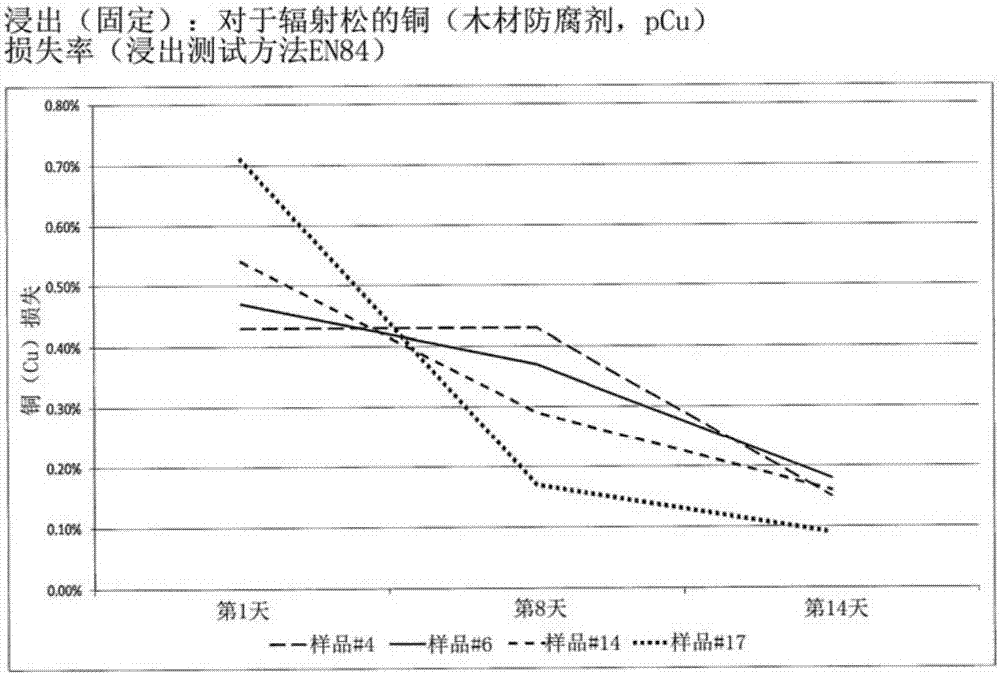
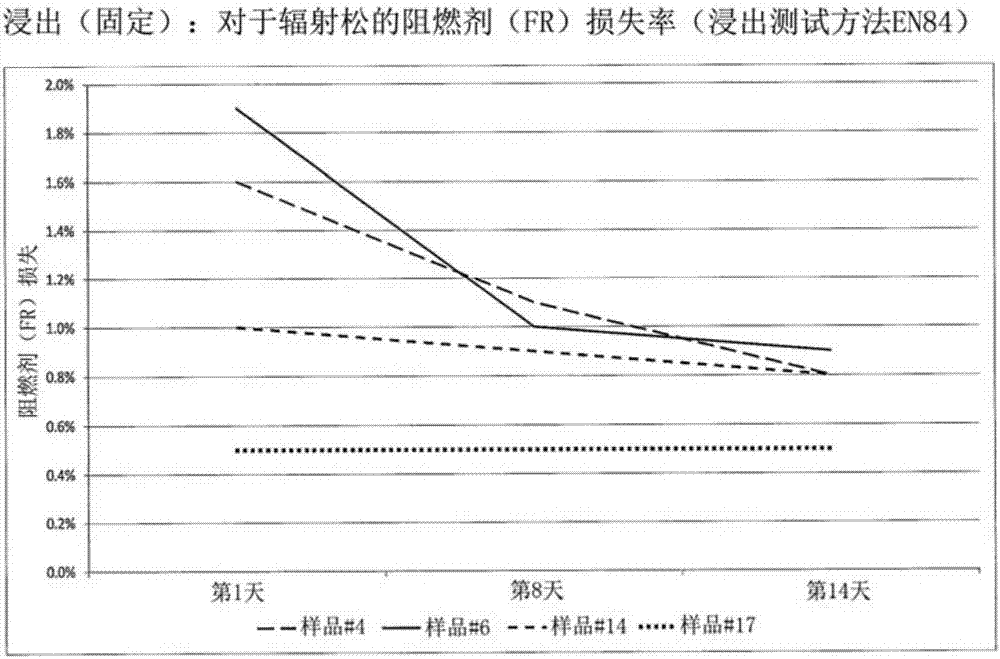
[0035] In order to evaluate and quantify the effectiveness of chemical fi...
specific Embodiment approach
[0037] Example 1
[0038] wood impregnation process
[0039] The preservative treatment of wood by the pressure method is the preferred commercial method because it achieves a higher efficiency in controlling the conditions and effectiveness in achieving a more uniform, deeper penetration and greater absorption of the working solution. The processing equipment has doors at one or both ends to receive untreated lumber (charge) which is then loaded into containers for the processing to take place. The facility has various auxiliary equipment such as working tanks, flood lines, controls, vacuum pumps and pressure pumps to provide various treatment options.
[0040] There are two types of treatment pressure methods; the first is the "empty cell process" where compressed air is applied to the wood prior to the application of the wood preservative "working solution". The wood preservative was added from the equalizing tank into the container where air was exchanged with the prese...
Embodiment 2
[0052] heat (fixing) treatment
[0053] Once the treated fire retardant wood has been treated it has a high moisture content (%mc) in the range of 60-100% which needs to be dried to bring the moisture below 18%mc for resale. During the drying process, various kiln schemes are used to control temperature (set point), air flow (fan) and relative humidity at predetermined times. The kiln scheme calls for an inlet temperature (wet bulb) in the temperature range of 70-100°C and an outlet temperature (dry bulb) in the temperature range of 100-130°C. Initial time-temperature 1-2 hours, continue 18-36 hours, then return to ambient temperature. Pre-steaming can also be used in the initial stages. Other heat sources such as steam, radio frequency and microwaves can also be used.
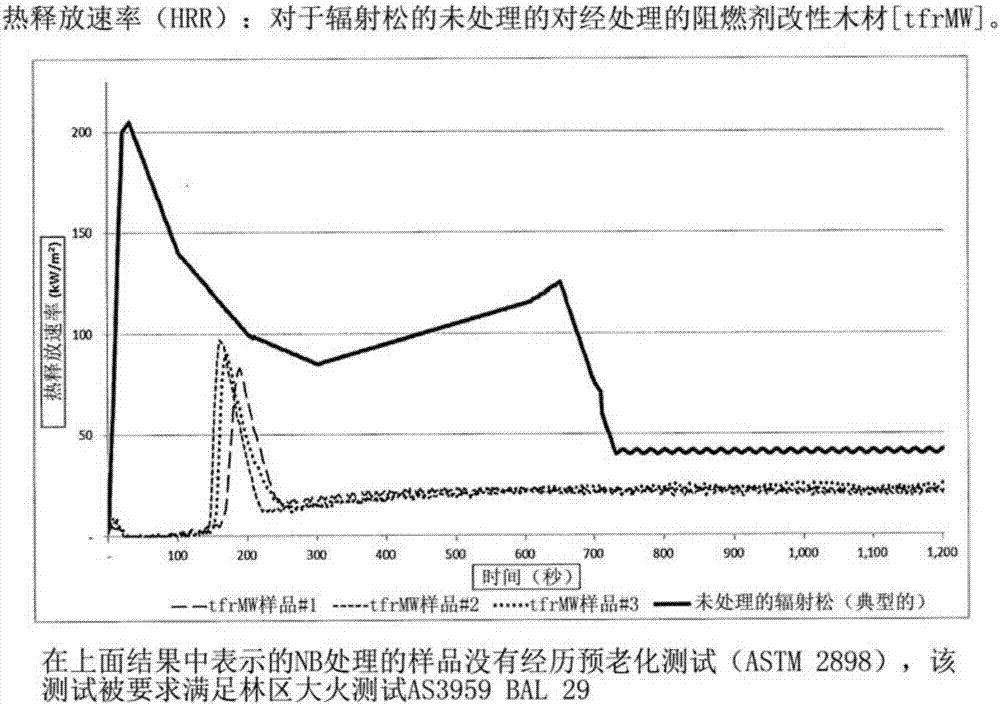
[0054] The heating (fixation) process and the conditions required to achieve this are critical as it achieves two important processes, firstly reducing the moisture content (%mc) and secondly providing ener...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com