Wet rubbing fastness improver for dyed fabrics
A technology for wet rubbing fastness and improving agent, which is applied in the field of textile auxiliary preparation, can solve the problems of poor fastness improving effect of wet rubbing fastness improving agent, affecting the color index of fabrics, etc. Capacitance, the effect of reducing adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
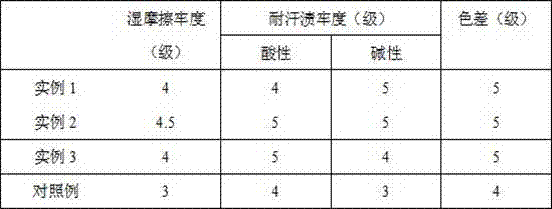
example 1
[0020] First take successively by weighing 20g polyaspartic acid, 20g citric acid, 15g sucrose, 40g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, pour in the beaker that fills 400mL deionized water, stir and mix with glass rod for 20min, get mixed solution, and The obtained mixed solution was transferred to a three-necked flask, and then the three-necked flask was moved into a digital display velocity measuring constant temperature magnetic stirrer, and at a temperature of 32°C and a rotating speed of 500r / min, 40 mL of activated yeast liquid, 20 gL -Ascorbic acid; After the activated yeast liquid and L-ascorbic acid are added, continue to stir and react at a constant temperature for 4 hours, then filter the material in the three-necked flask to obtain a filter residue, and wash the filter residue 5 times with deionized water, and then transfer the washed filter residue to vacuum drying box, at a temperature of 85°C, dry for 5 hours to obtain a dry filter residue; then weigh 30g of sodium dode...
example 2
[0022]First take successively by weighing 10g polyaspartic acid, 10g citric acid, 10g sucrose, 30g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, pour in the beaker that fills 300mL deionized water, stir and mix with glass rod for 10min, get mixed solution, and The obtained mixed solution was transferred into a three-necked flask, and then the three-necked flask was moved into a digital display velocity measuring constant temperature magnetic stirrer, and at a temperature of 28°C and a rotating speed of 300r / min, 30 mL of activated yeast liquid, 10 gL -Ascorbic acid; after the addition of the activated yeast liquid and L-ascorbic acid is completed, continue to stir and react at a constant temperature for 2 hours, then filter the material in the three-necked flask to obtain a filter residue, and wash the filter residue 3 times with deionized water, and then transfer the washed filter residue to vacuum drying box, at a temperature of 75°C, dry for 3 hours to obtain a dry filter residue; then weig...
example 3
[0024] First take successively by weighing 15g polyaspartic acid, 15g citric acid, 12g sucrose, 35g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, pour in the beaker that fills 350mL deionized water, stir and mix with glass rod for 15min, get mixed solution, and The obtained mixed solution was transferred into a three-necked flask, and then the three-necked flask was moved into a digital display velocity measuring constant temperature magnetic stirrer, and at a temperature of 31°C and a rotating speed of 400r / min, 40 mL of activated yeast liquid, 15 gL -Ascorbic acid; after the activated yeast liquid and L-ascorbic acid are added, continue to stir and react at a constant temperature for 3 hours, then filter the material in the three-necked flask to obtain a filter residue, wash the filter residue 4 times with deionized water, and then transfer the washed filter residue to vacuum drying box, at a temperature of 80°C, dry for 4 hours to obtain a dry filter residue; then weigh 25g of sodium dodecy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com