Method of rapidly degrading beta-lactam antibiotic in water
A lactam-based, rapid-degradation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as high energy consumption, weak selectivity, and susceptibility to other pollutants in water bodies. Achieve the effect of low energy consumption, fast degradation rate and wide application range of pH
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
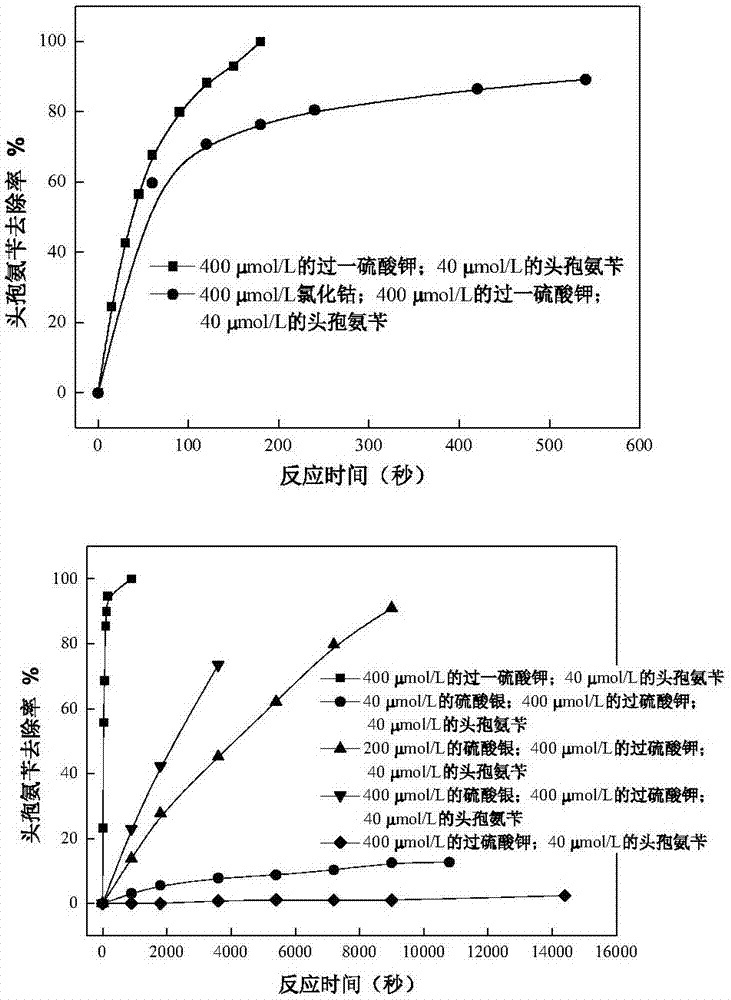
[0027] Prepare concentration of 0.01mol / L potassium persulfate, potassium persulfate, silver sulfate, cobalt chloride solution and 1000 μmol / L cephalexin solution. The first step, to 6 containing 40 μ mol / L cephalexin (0.01mol / L phosphate buffer pH=7), numbering is successively 1,2,3,4,5,6 reaction vials (volume 100ml, placed in On the stirrer) add reagents according to the following conditions: No. 1 bottle is added with 4ml of cobalt chloride (final concentration is 400 μmol / L); No. 2 to No. / L, 200μmol / L, 400μmol / L); in the second step, add 4ml of potassium persulfate solution (final concentration is 400μmol / L) to No. 1 and No. Add 4ml of the potassium persulfate solution prepared above into the bottle respectively, and stir and react for a certain period of time at room temperature. The removal rate of cephalexin in this example is respectively: permonosulfate alone degrades 3min 100%, cobalt chloride activates permonosulfate 3min 76.4%; Potassium persulfate alone degrade...
Embodiment 2
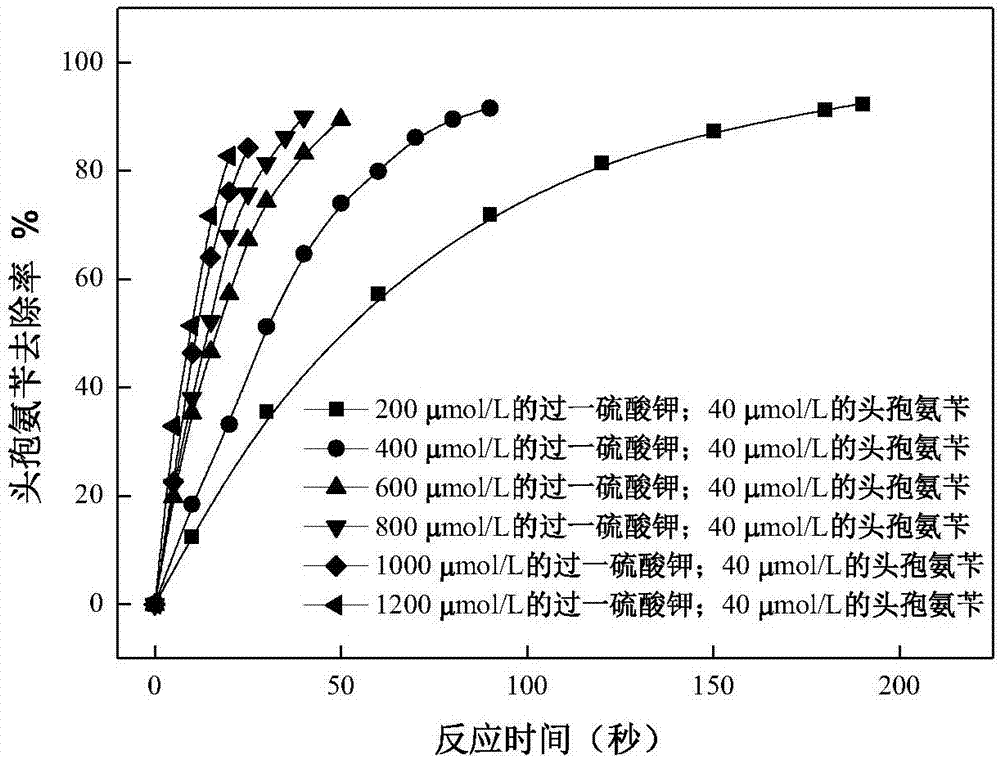
[0029] Add different amounts of potassium persulfate solution into 100ml ultrapure water (0.01mol / L phosphate buffer pH=7) containing 40 μmol / L cephalexin, so that the final concentrations of potassium persulfate are 200 μmol / L and 400 μmol / L respectively. L, 600μmol / L, 800μmol / L, 1000μmol / L, 1200μmol / L, placed on a stirrer and stirred evenly, after a certain period of reaction, the removal of cephalexin by potassium persulfate of different concentrations was completed. The removal rates of cephalexin in this example were 94.5%, 94.9%, 95.1%, 95.5%, 94.7%, 95.8%.
Embodiment 3
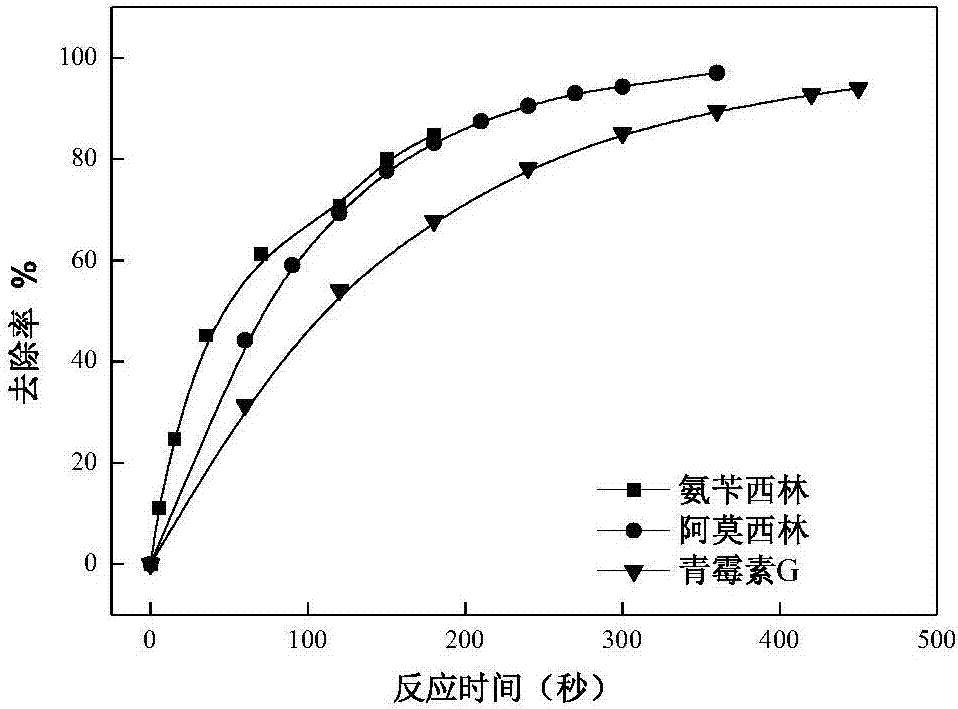
[0031] Take 4ml of the prepared potassium persulfate solution and add 40 μmol / L of cephalexin (CFX), cefapirin (cefapirin), cefradine (cefradine), penicillin G (PG), ampicillin (AMP), amoxicillin 100ml of ultrapure water from cillin (AMX) was placed on a stirrer at room temperature and stirred evenly, and samples were taken at a specified time. That is, the degradation of different beta-lactam antibiotics by potassium persulfate is completed. In this example, the removal rates of CFX, cefapirin, cefradine, PG, AMP, and AMX were 94.9%, 97.1%, 93.1%, 93.9%, 97%, and 84.8%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com