Manufacturing method for hard micro-fluid chip
A technology of microfluidic chips and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test material strength, material inspection products, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as not being able to chip
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Embodiment 1, making epoxy resin microfluidic chip (substrate material is PDMS)
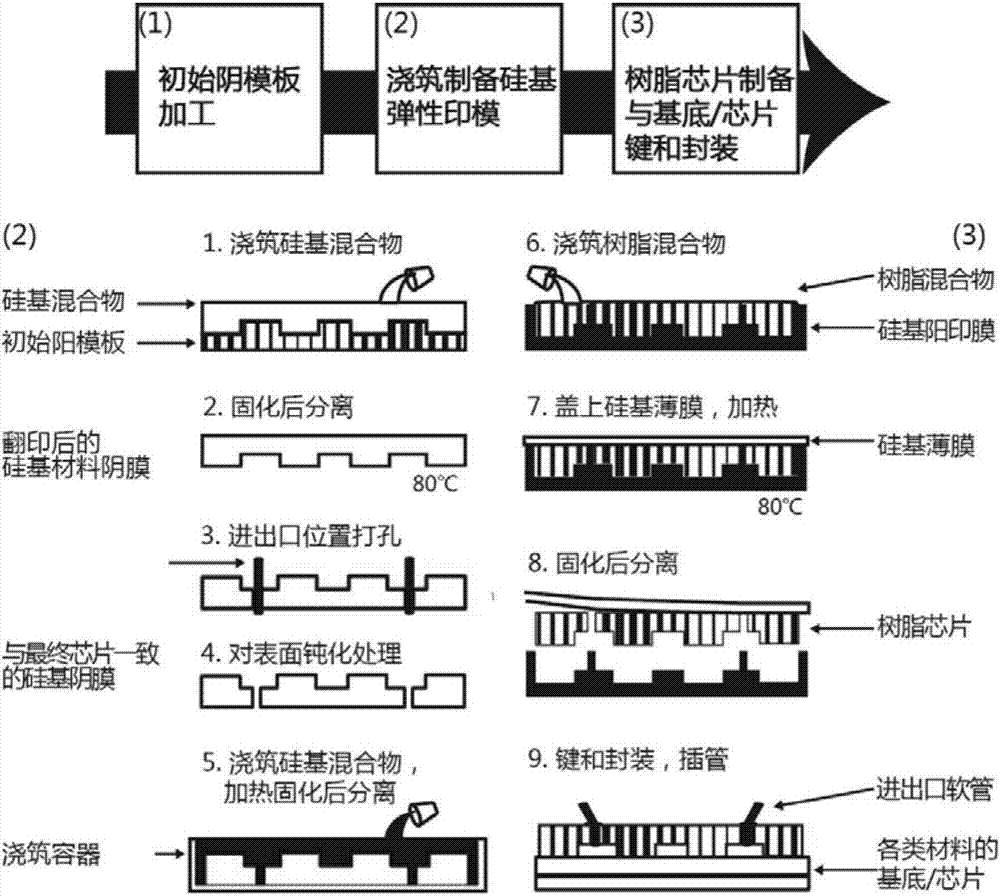
[0074] like figure 1 As shown, the microfluidic chip was fabricated according to the following steps:
[0075] (1) PDMS prepolymer and curing agent are mixed at a volume ratio of 10:1, and the mixture after removing air bubbles is poured onto a template / mold, which is a male master mold (such as a silicon wafer) containing a convex microchannel structure. SU-8 convex mold formed by photolithography).
[0076] (2) After the mold poured with the PDMS mixture in step (1) is dried at 80 degrees for 1 hour, the flash is removed and cleaned to become a microfluidic chip to be copied, which is a PDMS microfluidic chip corresponding to the concave microstructure chip.
[0077] (3) Use a hole puncher to punch through holes of appropriate size, such as 0.1mm, 0.2mm, 0.3mm, 0.4mm, etc., at the position of the sample inlet and outlet on the PDMS chip.
[0078] (4) Passivate the perforated PDMS chi...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2, making epoxy resin microfluidic chip (substrate material is PMMA)
[0087] like Figure 4 As shown, the microfluidic chip was fabricated according to the following steps:
[0088] (1) PDMS prepolymer and curing agent are mixed at a volume ratio of 10:1, and the mixture after removing air bubbles is poured onto the template / mold, which is a female master mold containing a concave micro-channel structure (such as laser engraving machine-cut PC material). Engraving can cut through holes of appropriate size at the position of the sample inlet and outlet on the female master mold at the same time, such as 0.1mm, 0.2mm, 0.3mm, 0.4mm, etc.
[0089] (2) After the mold poured with the PDMS mixture in step (1) is heated at 80 degrees for 1 hour, it is peeled off and cut off the flash, and cleaned to prepare a positive PDMS mold that is opposite to the pattern of the template / mold but contains micropillars entering and exiting the sample hole. The chip is a mold w...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Embodiment 3, making epoxy resin microfluidic chip (substrate material is glass)
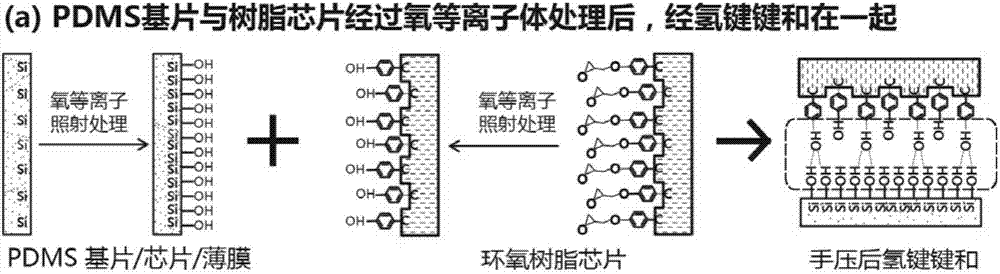
[0097] An epoxy resin microfluidic chip was prepared according to the steps in Example 2, only the substrate in step 9) was replaced with a glass substrate. In this embodiment, the XPS energy spectrum scanning result is as follows Figure 7 as shown, Figure 7 The upper two curves are the surface XPS scanning results of amino unmodified glass (samples 1 and 2), and the middle two curves are the surface XPS scanning results of amino modified glass (samples 3 and 4), where The peak of N element near the 401eV energy level increases significantly after modification, indicating that there is indeed an increase of amino groups on the glass surface after modification. Therefore by Figure 7 It can be seen that the amino groups are successfully modified on the surface of the glass substrate in this example.
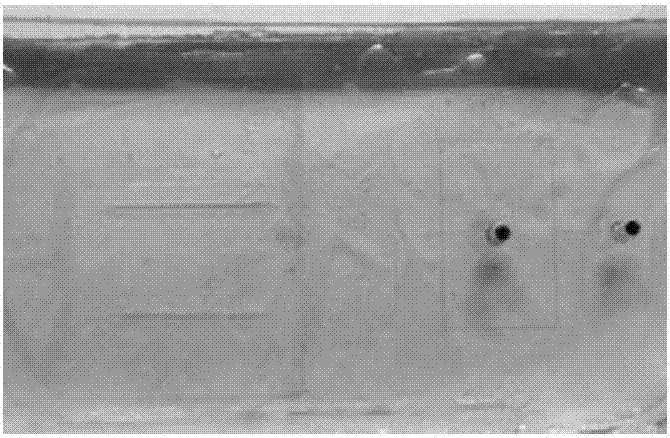
[0098] In the present embodiment, the photograph of the epoxy resin chip that prepa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com