Oyster mushroom fermentation material cultivation medium taking beanstalks as raw material and oyster mushroom cultivation method
A technology of cultivation substrate and fermented material, which is applied in mushroom cultivation, cultivation, plant cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, environment, pollution, and failure to obtain reasonable and effective development and utilization, and achieve pollution reduction, cost reduction, and significant environmental protection. and economical effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
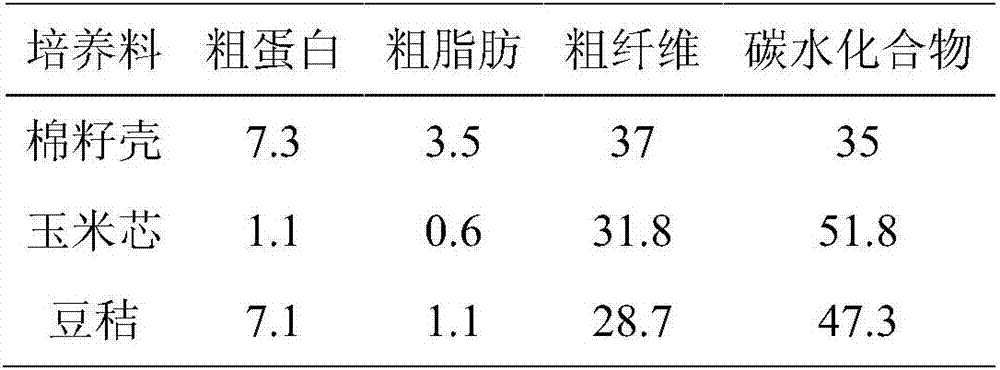
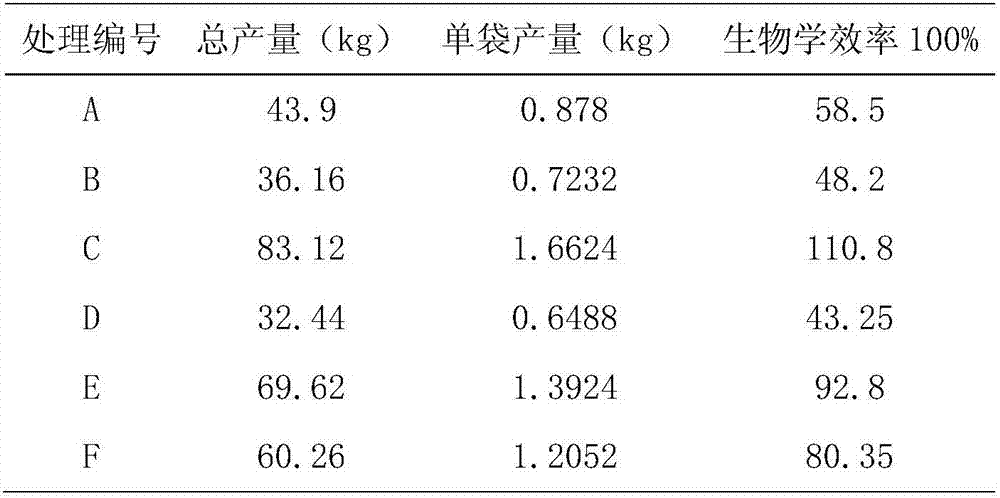
[0034] Comparison of Biological Efficiency of Different Cultivation Substrates of Pleurotus ostreatus Using Bean Straw as Part of Corncob or Cottonseed Hull
[0035] 1. Pleurotus ostreatus cultivation substrate formula
[0036] A: 32% corn cob, 62% bean straw, 1% urea, 2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 3% lime;
[0037] B: 47% corn cob, 47% bean straw, 1% urea, 2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 3% lime;
[0038] C: 64% corn cob, 30% bean straw, 1% urea, 2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 3% lime;
[0039] D: Cottonseed hulls 47%, soybean straw 47%, urea 1%, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer 2%, lime 3%;
[0040] E: Cottonseed hulls 64%, soybean straw 30%, urea 1%, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer 2%, lime 3%;
[0041] F: Cottonseed hulls 32%, soybean straw 62%, urea 1%, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer 2%, lime 3%.
[0042] 2. Test strain: 2026
[0043] 3. Experimental design: Randomized block design was adopted, and each formula...
Embodiment 2
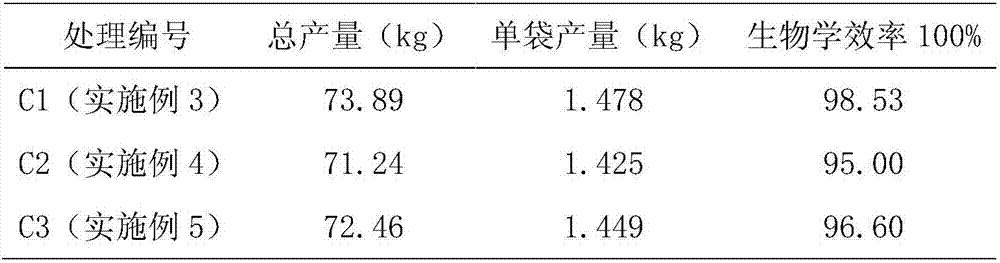
[0052] In order to reduce the raw material cost of using corncobs, and in order to improve the utilization rate of edible fungus waste, on the basis of the screened Pleurotus ostreatus fermentation material cultivation substrate (Group C), add fungus residues (Pleurotus eryngii fungus residues, Tremella fungus slag, enoki mushroom residue, etc.), and at the same time appropriately reduce the amount of corncobs used, and slightly adjust the amount of bean stalks used.
[0053] The oyster mushroom fermented material cultivation substrate with soybean stalks as raw material is composed of the following components in percentage by weight:
[0054] Group C1: corn cob 24%, fungus residue 40%, soybean straw 30%, urea 1%, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer 2%, lime 3%. Mushroom residue 13%, white fungus residue 13%, Flammulina velutipes residue 14%.
[0055] Group C2: 20% corn cob, 38% fungus residue, 36% soybean straw, 1% urea, 2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 3% lime. ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The flat mushroom cultivation method that adopts the flat mushroom fermented material cultivation substrate of C1 group, comprises the following steps:
[0059] 1) Crushing the bean straw into 3cm×0.2×0.2cm bean straw fragments;
[0060] 2) On the first day, mix the bean stalks, corncobs, and lime in proportion, add water to make a pre-wet pile; %;
[0061] 3) Stockpile fermentation: Drill air holes at intervals of 35m on the top of the stockpile, stack and ferment for 8 days, when the material temperature reaches 63°C, stack for 24 hours and then turn over the pile, after the fermentation ends, the pile is scattered to cool down, and the cultivation substrate is obtained;
[0062] 4) above-mentioned cultivation medium is packed into polyethylene cultivation bag and inoculated with Pleurotus ostreatus bacterial classification, makes Pleurotus ostreatus bacterium bag;
[0063] 5) Pleurotus ostreatus mushroom bags are placed in layers in the mushroom room for germinatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com