Method for extremely fast preparing ferroferric oxide/graphene lithium ion battery composite negative electrode material
A technology for ferric oxide and lithium-ion batteries, which is applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., and can solve the problems of the electrochemical performance of ferric oxide-based composite materials that need to be improved, difficult industrial preparation and application, and complicated process flow and other issues to achieve the effect of ensuring long-term cycle stability, excellent cycle stability performance, and high reversible specific capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
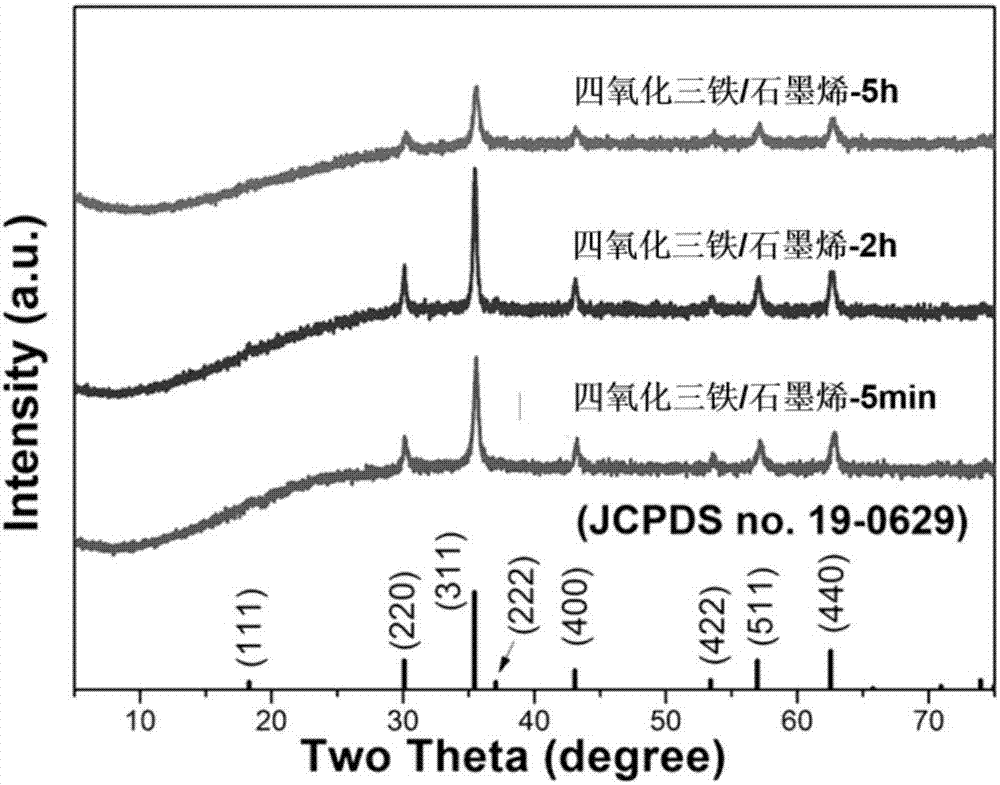
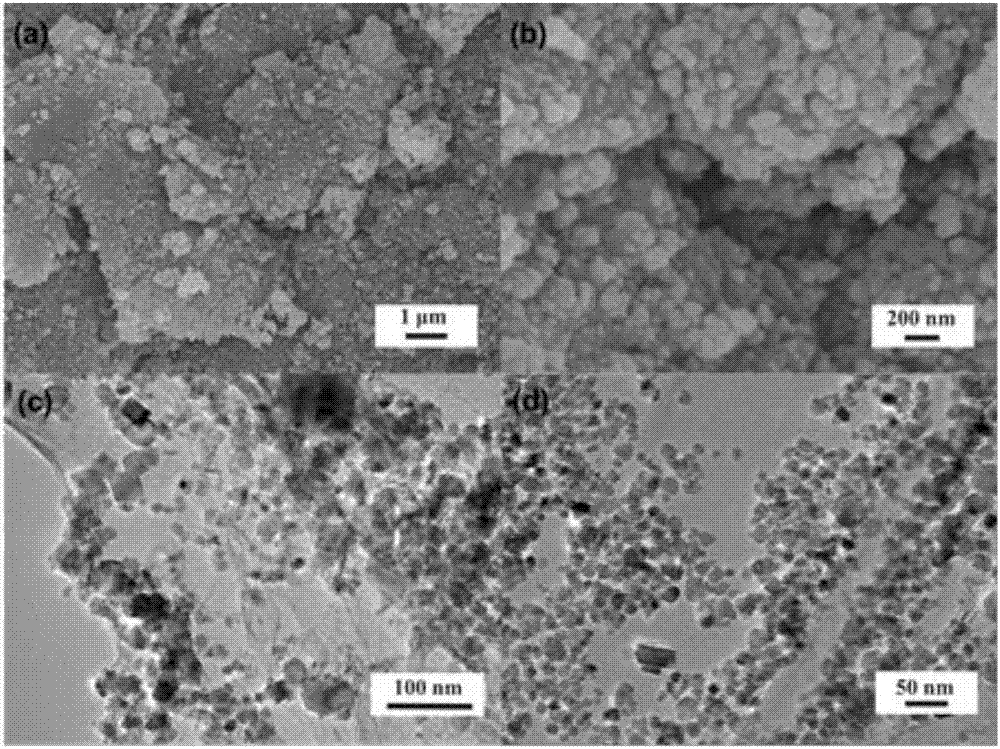
[0017] Measure 5 milliliters of graphene oxide solution (4 milligrams per milliliter), disperse it in 25 milliliters of deionized water, and disperse it completely by ultrasonication at 25 watts and 40 kHz for 0.5 hours. The obtained brown-yellow graphene oxide solution was heated up to 90 degrees centigrade, and mechanically stirred continuously. Weigh 140 mg of ferrous sulfate (0.5 mmol), dissolve it in 10 ml of deionized water to obtain a ferrous ion solution, and quickly add it to the graphene oxide solution. Measure 1 milliliter of ammonia water (28wt.%), add it dropwise in the mixed solution of ferrous ion and graphene oxide, with vigorous stirring, you can get magnetic ferric oxide / graphene composite material in 1 minute . The mixed system was continuously stirred at 90° C. for 5 minutes to stabilize its structure and further reduce the graphene. The obtained black solid was washed six times with deionized water, frozen, and dried in a lyophilizer to obtain a ferric o...
Embodiment 2
[0019] According to the main process method in Example 1, after adding excess ammonia water, the mixed system reacted at 90 degrees Celsius for 1 minute, and continued to stir at low temperature for 2 hours, changing the low temperature stability and reduction time, and the prepared trioxide The iron / graphene-5min-2h composite nano-carbon material was tested for electrochemical performance. After 200 cycles at a current density of 1 amp / g, the discharge specific capacity was 1024 mAh / g.
Embodiment 3
[0021] According to the main process method in Example 1, after adding excess ammonia water, after the mixed system reacted at 90 degrees Celsius for 1 min, it was continuously stirred at low temperature for 5 hours, and the low temperature stability and reduction time were changed, and the prepared ferric iron tetroxide was / Graphene-5h composite nano-carbon material was tested for electrochemical performance. After 200 cycles at a current density of 1 amp / g, the discharge specific capacity was 571 mAh / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com