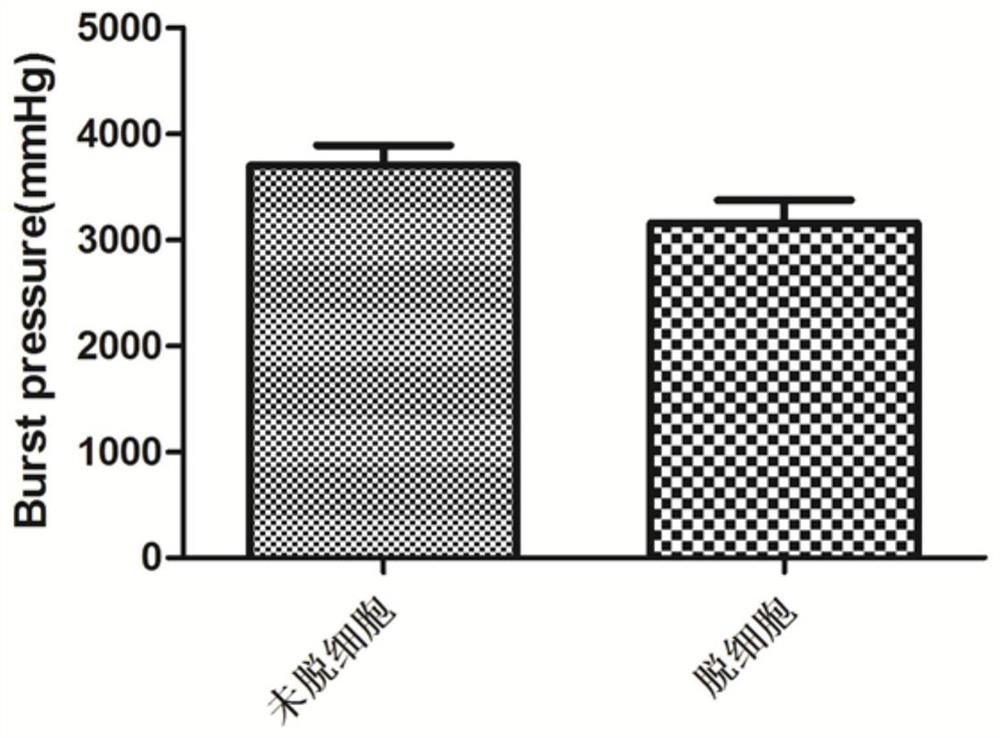
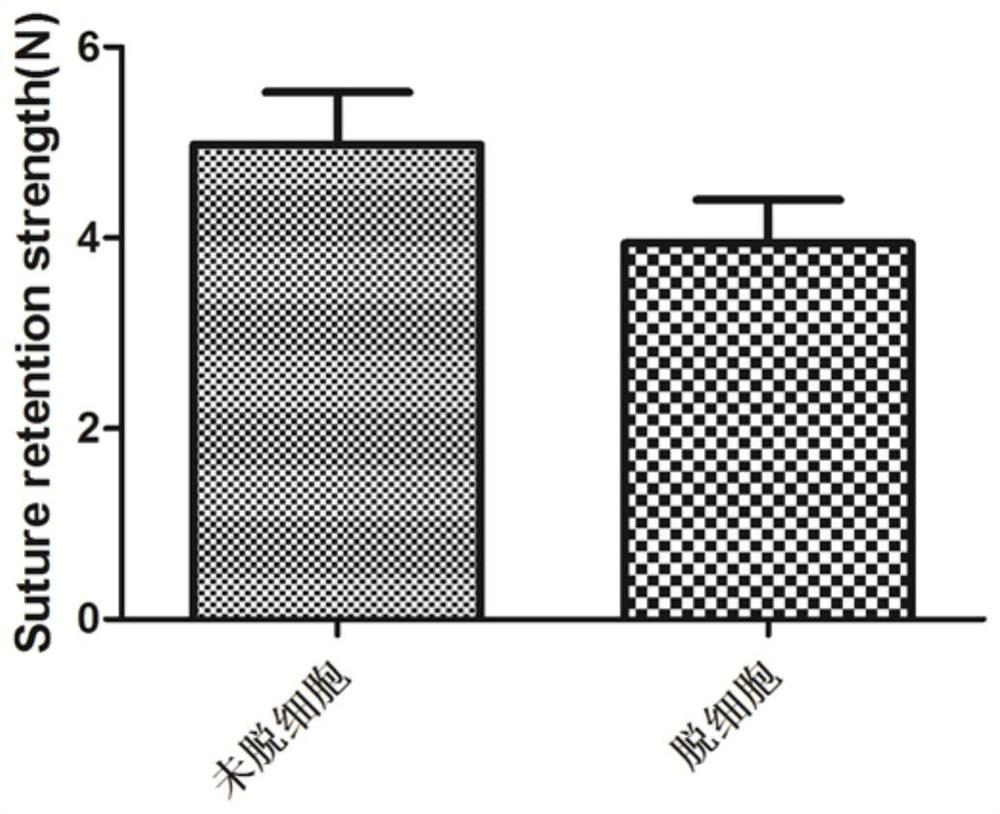
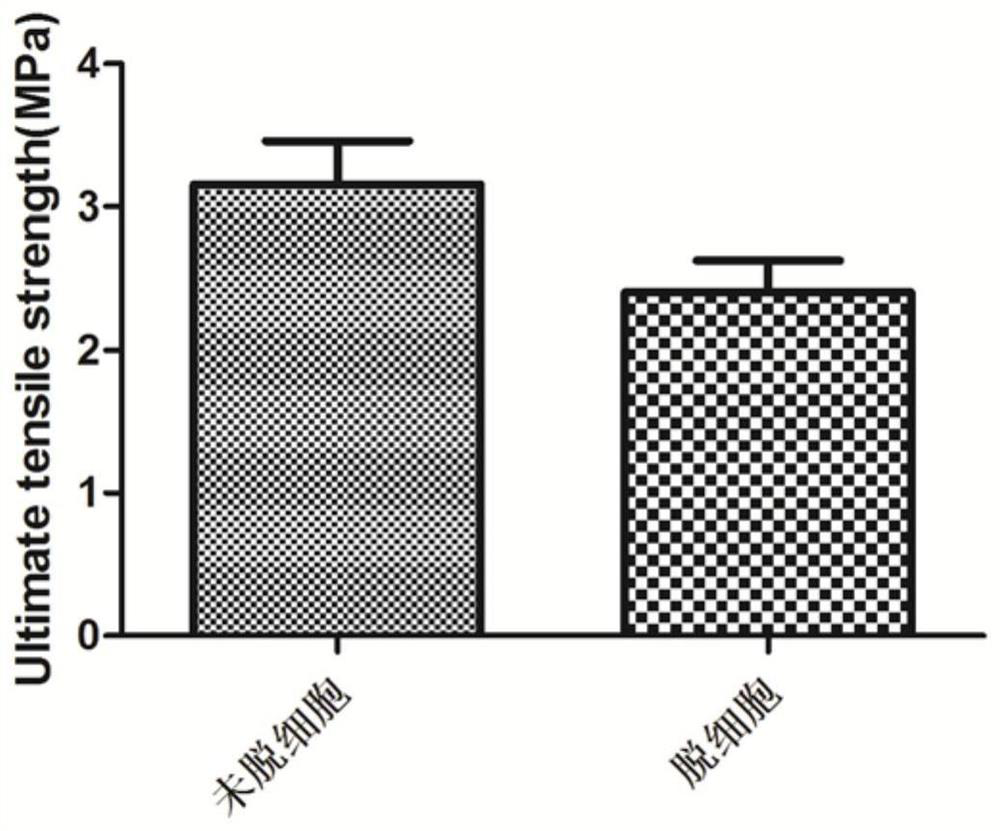
A kit and method for durable patency of artificial blood vessels
An artificial blood vessel and kit technology, applied in the field of tissue materials, can solve the problems of weak mechanical properties, complex preparation process, intimal hyperplasia, etc., and achieve improved mechanical properties and patency rate, mild structure and mechanical properties, and durable anti-blocking performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1) Preparation of artificial tubular tissue
[0035] Cut the Teflon tube (1 / 16 inch outer diameter, about 1.59mm) with the diameter that matches the inner diameter of the blood vessel to be replaced to a suitable length, sterilize with 75% alcohol for 30 minutes, place it in the human subcutaneous tissue, and take out the subcutaneous Teflon after 4 weeks The tube and the surrounding new tissue are taken out, and the Teflon tube is removed to obtain an artificial tubular tissue with a thickness of 324.1±57.4 microns (n=6, n is the number of samples to be tested, and n has the same meaning below).
[0036] 2) Decellularization treatment
[0037] Configure decellularization reagents according to Table 1 below
[0038] Table 1 Components of decellularization reagents
[0039]
[0040] Add the accurately weighed reagents into a clean wide-mouth glass bottle, shake on a shaker for 2-3 hours to fully dissolve the reagents, at this time the solution becomes clear and prepare it as a de...
Embodiment 2
[0051] 1) Preparation of artificial tubular tissue
[0052] Cut the Teflon tube (1 / 16 inch outer diameter, about 1.59mm) with the diameter that matches the inner diameter of the blood vessel to be replaced to a suitable length, sterilize with 75% alcohol for 30 minutes, and place it in the subcutaneous tissue of the pig. After 2 weeks, remove the subcutaneous Teflon. The tube and the surrounding new tissue were taken out, and the Teflon tube was removed to obtain an artificial tubular tissue with a thickness of 154.3±56.4 microns (n=6).
[0053] 2) Decellularization treatment
[0054] Configure decellularization reagents according to Table 3 below
[0055] Table 3 Components of decellularization reagents
[0056]
[0057] Add the accurately weighed reagents into a clean wide-mouth glass bottle, shake on a shaker for 2-3 hours to fully dissolve the reagents, at this time the solution becomes clear and prepare it as a decellularized reagent, and store it at 4°C for later use.
[0058] Put...
Embodiment 3
[0068] 1) Preparation of artificial tubular tissue
[0069] Cut the Teflon tube (outer diameter 1.59mm) that matches the inner diameter of the blood vessel to be replaced to a suitable length, sterilize with 75% alcohol for 30 minutes, and place it under the skin of humans (also can be implanted in other mammals such as mice, pigs, etc.) Subcutaneous) tissue, removed after 5 weeks, remove the subcutaneous Teflon tube together with the surrounding new tissue, and remove the Teflon tube to obtain an artificial tubular tissue with a thickness of 352.1±43.2 microns (n=6).
[0070] 2) Decellularization treatment
[0071] Configure decellularization reagents according to Table 5 below
[0072] Table 5 Components of decellularization reagents
[0073]
[0074] Add the accurately weighed reagents into a clean wide-mouth glass bottle, shake on a shaker for 2-3 hours to fully dissolve the reagents, at this time the solution becomes clear and prepare it as a decellularized reagent, and store it a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com