Biological tissue-reinforcing material
A technology for reinforcing materials and biological tissues, which is used in textiles and papermaking, medical science, absorbent pads, etc., and can solve problems such as virus infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
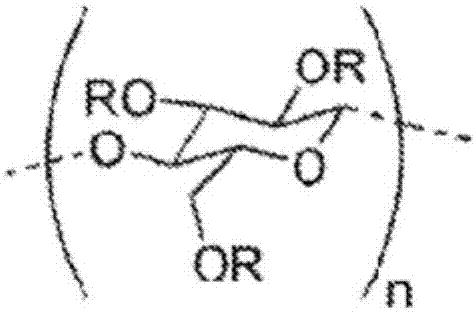
[0064] (1) Preparation of fiber structure made of hydroxyethylated cellulose
[0065] A 280-μm-thick single-knit fabric made of No. 80 cellulose yarn as a raw material was bleached by hydrogen peroxide bleaching.
[0066] Then, 3.55 g of the bleached knitted fabric was immersed in 140 mL of 10% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at 15° C. for 30 minutes to alkalize the cellulose. The alkalized knitted fabric was trodden flat by applying a load of 2.5 to 3.0 kg.
[0067] Next, 12.25 g of the obtained knitted fabric made of alkaline cellulose was immersed in 50 mL of a 0.8 mol / L ethylene oxide hexane solution at 25° C., and then reacted at 50° C. for 3 hours. The reacted knitted fabric was washed by immersing 70 mL of a mixture of methanol and methyl isobutyl ketone (methanol:methyl isobutyl ketone = 35:35) at 25°C for 5 minutes, and then washed by immersing 72.6 mL at 25°C Neutralize in a mixture of methanol, methyl isobutyl ketone and acetic acid (methanol: methyl isobutyl ke...
Embodiment 2
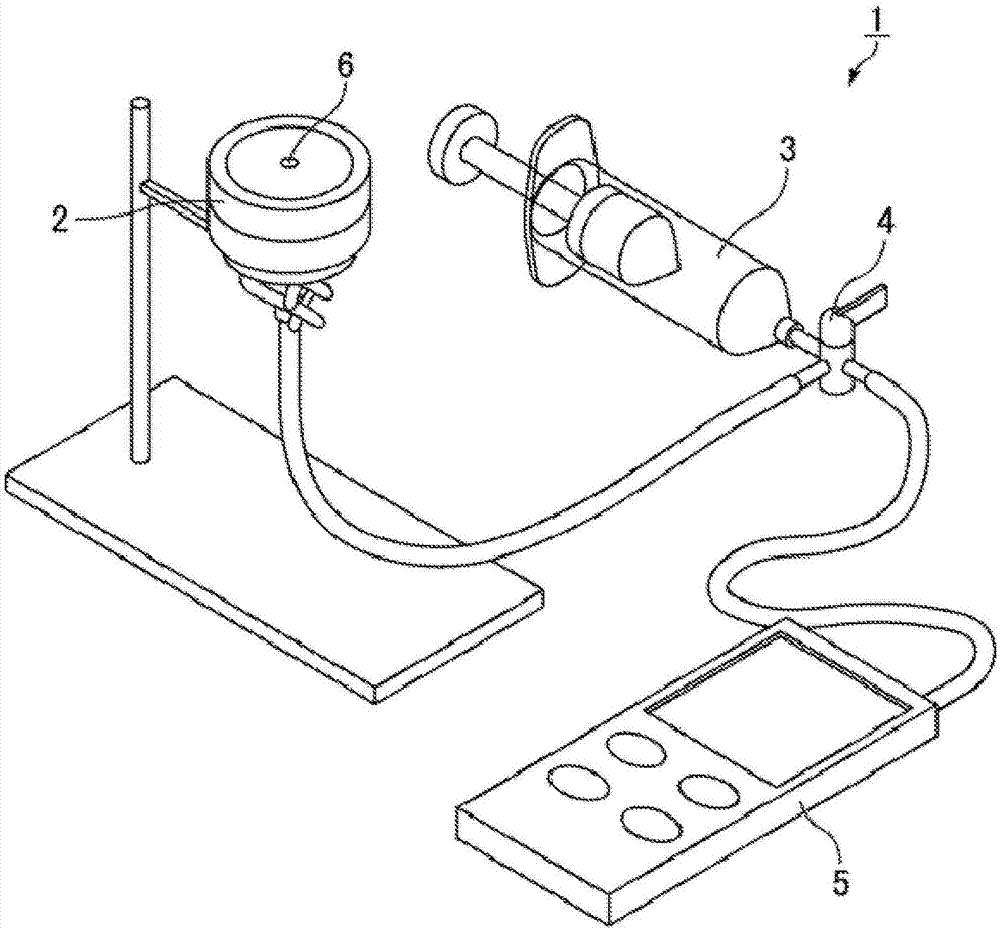
[0079] The prepared biological tissue reinforcement material was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the 200-μm-thick single-knit fabric made of 160-gauge cellulose yarn was used as a raw material to prepare the hydroxyethylated fiber fiber structure made of cellulose, and a combination of the three fiber structures made of hydroxyethylated cellulose / nonwoven made of polyglycolide / made of hydroxyethylated cellulose in the prescribed order The combination of the two fiber structures is laminated. Stress testing of biological tissue reinforcement materials. In the pressure test, the obtained test sample is placed in the center of the collagen membrane placed in the filter holder, so that the surface of the combined side of the three fibrous structures made of hydroxyethylated cellulose and the collagen membrane touch.
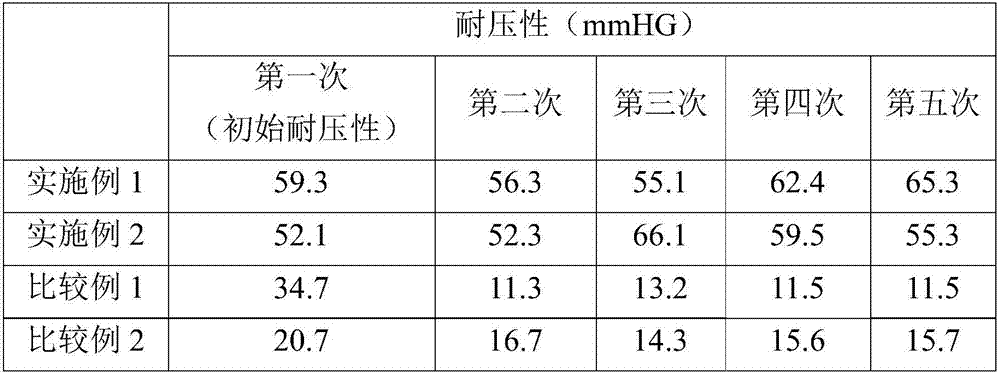
[0080] Table 1 shows the results of the stress test.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com