Fluorescence detection agent for p53 protein, and preparation method and application thereof
A fluorescent detection and protein technology, applied in the field of fluorescent detection agents for wild-type p53 protein, can solve the problems of high cost, complicated steps and the like, and achieve the effects of simple detection, simple operation and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Step (1) Dextran-modified Fc 3 o 4 Preparation of NPs:
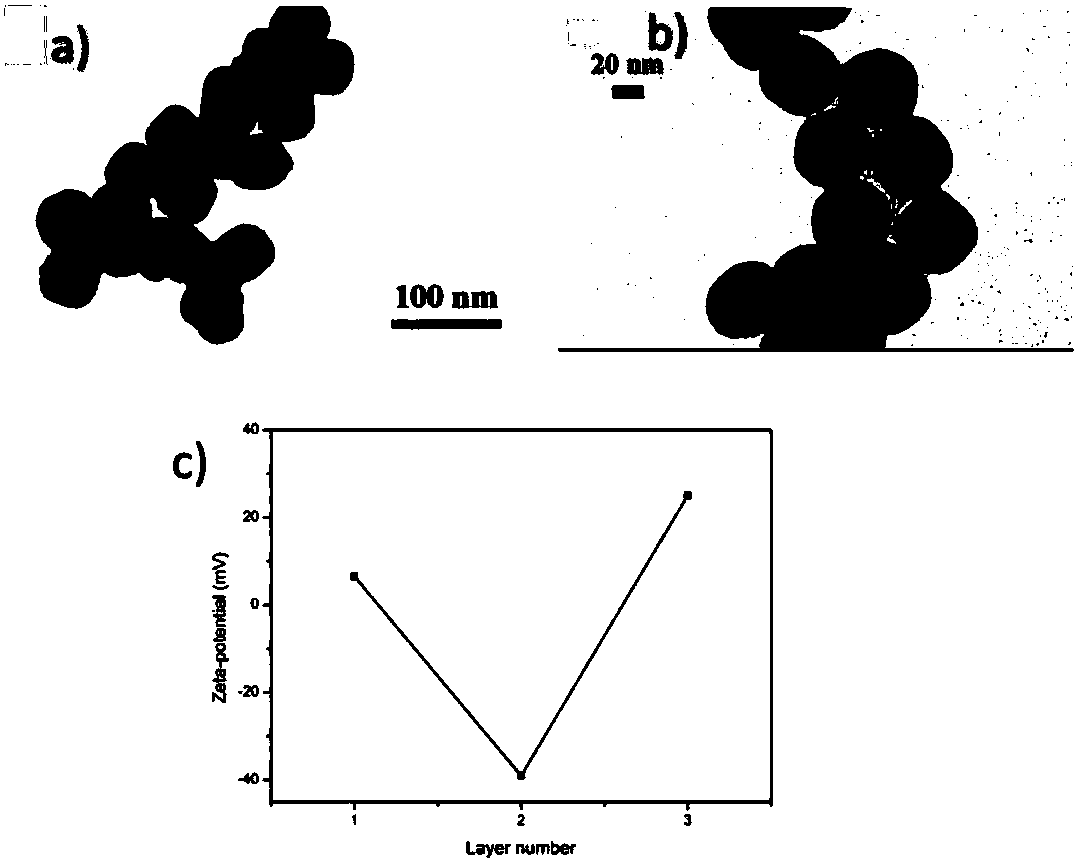
[0066] Fe 3 o 4 NPs were prepared by a hot solvent method. The specific process is as follows: 1.0g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in 20 mL of ethylene glycol solution, and then 3.0 g of sodium acetate and 0.7 g of polyethylene glycol were added. After stirring for 30 min, the mixture was transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene stainless steel autoclave, reacted at 200° C. for 8 h, and then cooled to room temperature. The precipitate was washed several times with ethanol and dried at 60°C to obtain Fe 3 o 4 NPs.
[0067] Next, PAA was used to modify the Fe by layer-by-layer self-assembly technique 3 o 4 NP s . The specific process is as follows: 1mL Fe 3 o 4 NPs (1mg mL -1 ) solution was added to 10mL PAA (1mg mL -1 ) solution, ultrasonically incubated for 15mim, collected with a magnet and washed several times with water, and then collected the PAA-coated Fe with a magnet 3 o 4 NPs(PAA / Fe 3 o ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Step (1) dextran / PAA / Fe 3 o 4 The preparation of NPs: with the step 1 of embodiment 1
[0074] Step (2) DNA-2 / DNA-1 / dextran / PAA / Fe 3 o 4 The preparation of NPs: with the step 2 of embodiment 1
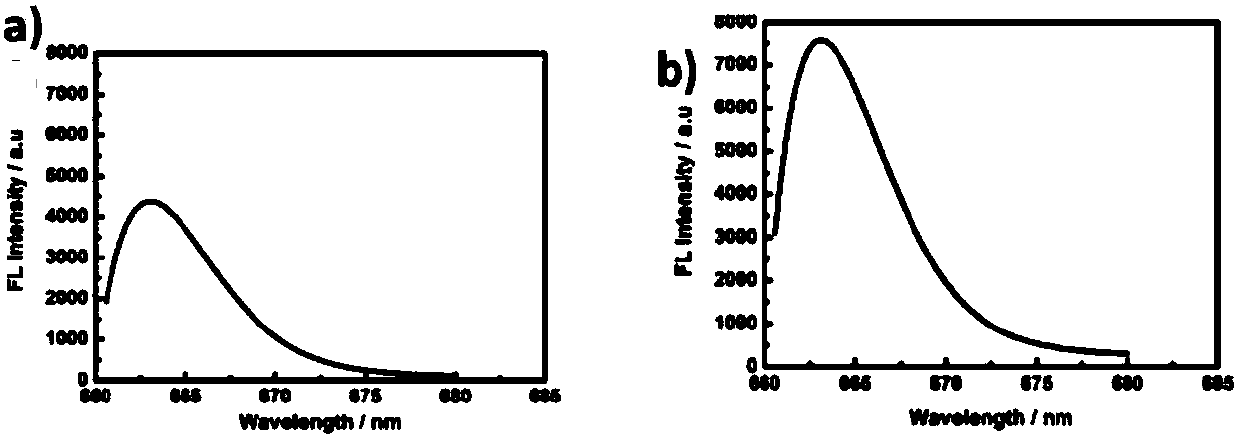
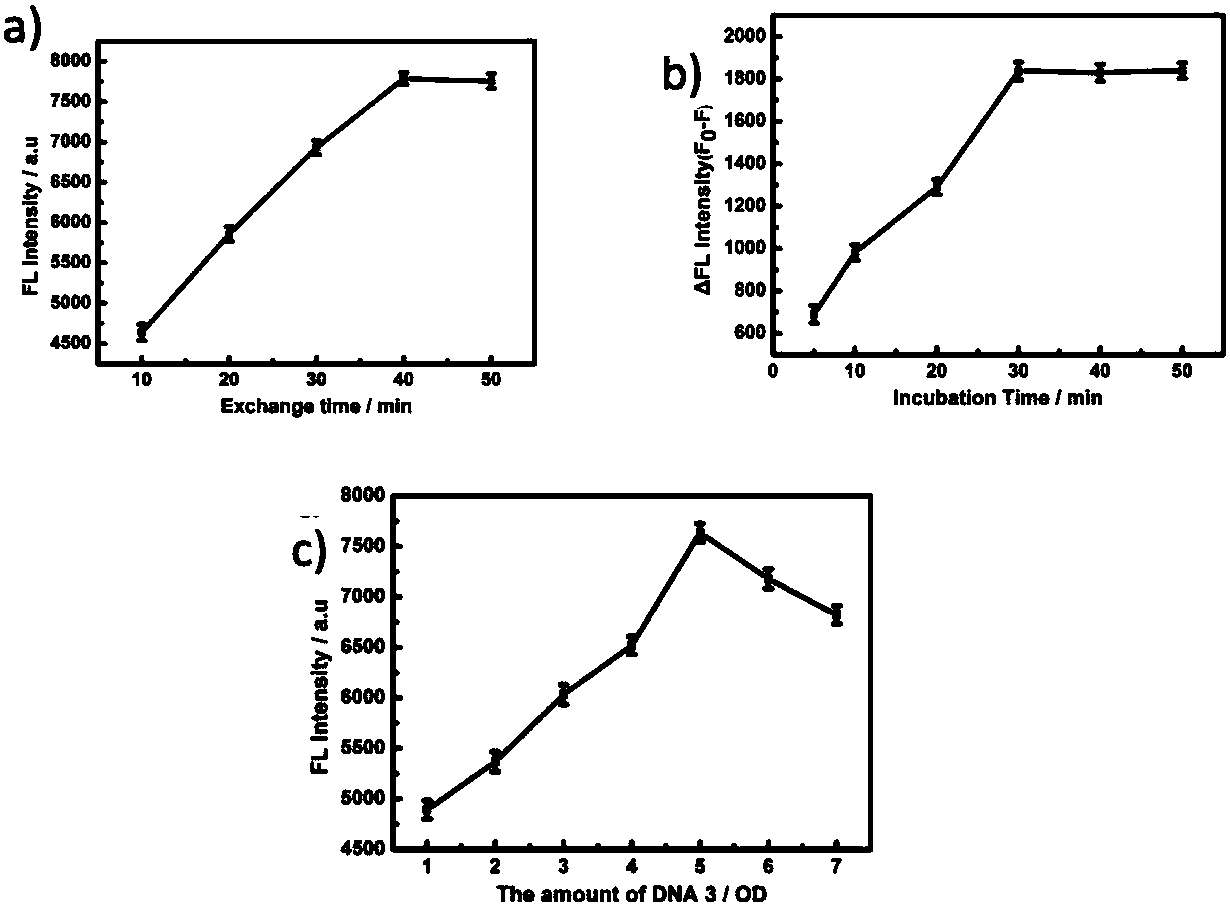
[0075] Step (3) Dilute p53 protein with PBS containing 20nM dithiothreitol (DTT), then add to DNA-2 / DNA-1 / dextran / PAA / Fe 3 o 4 In the NPs solution, after reacting for 30 minutes (incubation time), collect with a magnet and wash with PBS three times, and then collect nanoparticles that capture p53 protein with a magnet. Subsequently, Cy-5-labeled DNA-3 was added to replace DNA-2 (exchange reaction), and after heating at 37°C for 4 h (exchange reaction time), the nanoparticles (fluorescence detection agent) were collected and then redispersed in PBS solution, Test the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescence emission value at 663nm, such as figure 2 (b).
[0076] In order to explore the feasibility of using this strategy to detect p53 protein, 2nM p53 protein was added ...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Compared with Example 1, in order to investigate the influence of the DNA coverage on the surface of the magnetic nanoparticles on the detection sensitivity. Add DNA-1 with different concentration gradients from 1-7OD to 1mL dextran / PAA / Fe 3 o 4 NPs (1mg mL -1 ) solution, a total of 7 groups of magnetic nanoparticles modified by DNA-1 were obtained, and then DNA-2 corresponding to the amount of DNA-1 was added to each group to hybridize with DNA-1. Then, 1 nM p53 protein solution and the same amount of DNA-3 as DNA-1 were added to each group. The groups were then separated using a magnet, and the fluorescence intensity of the solution was measured. pass image 3 (c), inversely deduced that at 5OD, the DNA-1 load was the highest.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com