Preparation method and application of soluble dietary fiber
A dietary fiber and soluble technology, applied in the fields of application, food science, tea, etc., can solve environmental pollution and other problems, achieve high-efficiency extraction, sweet and sour taste, and lower cholesterol
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
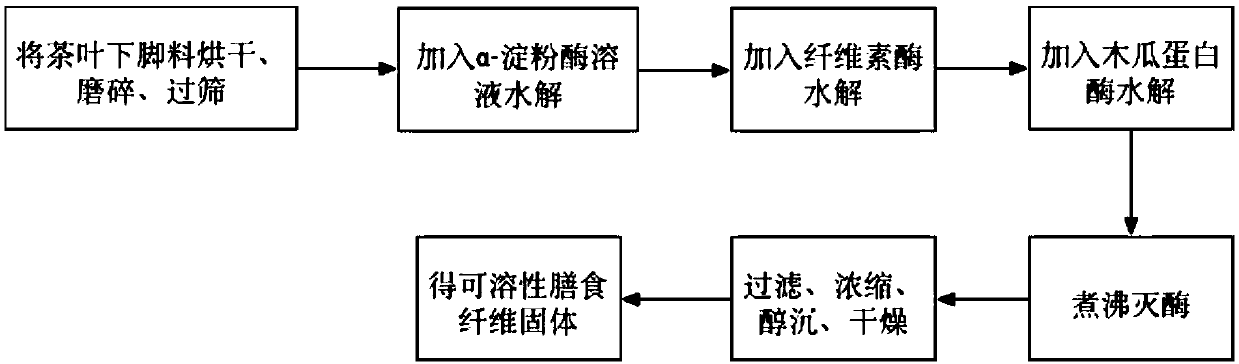
[0038] Example 1: 10 g of pulverized tea leaves were weighed and added to 200 mL of citric acid buffer solution (pH 6.4) containing 0.8 g of α-amylase, and enzymatically hydrolyzed in a water bath at 45° C. for 4 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 4.8, add 1.0 g of cellulase, and perform enzymolysis at 50° C. for 3 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 6.8, add 0.6 g of papain and perform enzymolysis at 60°C for 3 hours. After enzymolysis, the enzymolysis solution was boiled for 10 minutes, filtered, and the supernatant was concentrated, precipitated with 3 times the volume of 95% ethanol for 9 hours, and centrifuged at 4000 r / min for 10 minutes. Evaporate the precipitated part after centrifugation to near dryness, and then dry to obtain soluble dietary fiber solid. Take 0.4g compound stabilizer (sodium carboxymethylcellulose and xanthan gum mass ratio 3:1) and mix evenly with 12g white granulated sugar, add 6g of soluble dietary fiber solid pre...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: 100 g of pulverized tea leaves and 7 g of α-amylase were dissolved in 2000 mL of citric acid buffer (pH 6.4), and hydrolyzed in a water bath at 48° C. for 5 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 4.8, add 10 g of cellulase, and perform enzymolysis at 50° C. for 3 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 7.0, add 7 g of papain and perform enzymolysis at 56° C. for 2.5 hours. After enzymolysis, the enzymolysis solution was boiled for 10 minutes, filtered, the supernatant was concentrated, ethanol precipitation with 2 times the volume of 95% ethanol for 8 hours, and centrifugation at 4000r / min for 10 minutes. Evaporate the precipitated part after centrifugation to near dryness, and then dry to obtain soluble dietary fiber solid. Take 5g of compound stabilizer (mass ratio of sodium carboxymethylcellulose to xanthan gum: 2:1) and mix evenly with 100g of white granulated sugar, add 64g of soluble dietary fiber solids, add 3g of citric acid,...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: 100 g of pulverized tea leaves and 5 g of α-amylase were dissolved in 2000 mL of citric acid buffer (pH 6.6), and hydrolyzed in a water bath at 48° C. for 5 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 4.4, add 6 g of cellulase, and perform enzymolysis at 50° C. for 3 hours. Adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 7.0, add 9 g of papain and perform enzymolysis at 56°C for 2.5 hours. After enzymolysis, the enzymolysis solution was boiled for 10 minutes, filtered, and the supernatant was concentrated, precipitated with 4 times the volume of 95% ethanol for 8 hours, and centrifuged at 4000 r / min for 10 minutes. Evaporate the precipitated part after centrifugation to near dryness, and then dry to obtain soluble dietary fiber solid. Take 2g of compound stabilizer (mass ratio of sodium carboxymethylcellulose to xanthan gum: 2:1) and mix evenly with 50g of white granulated sugar, add 30g of soluble dietary fiber solids, add 1g of citric acid, 0.4g of vi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com