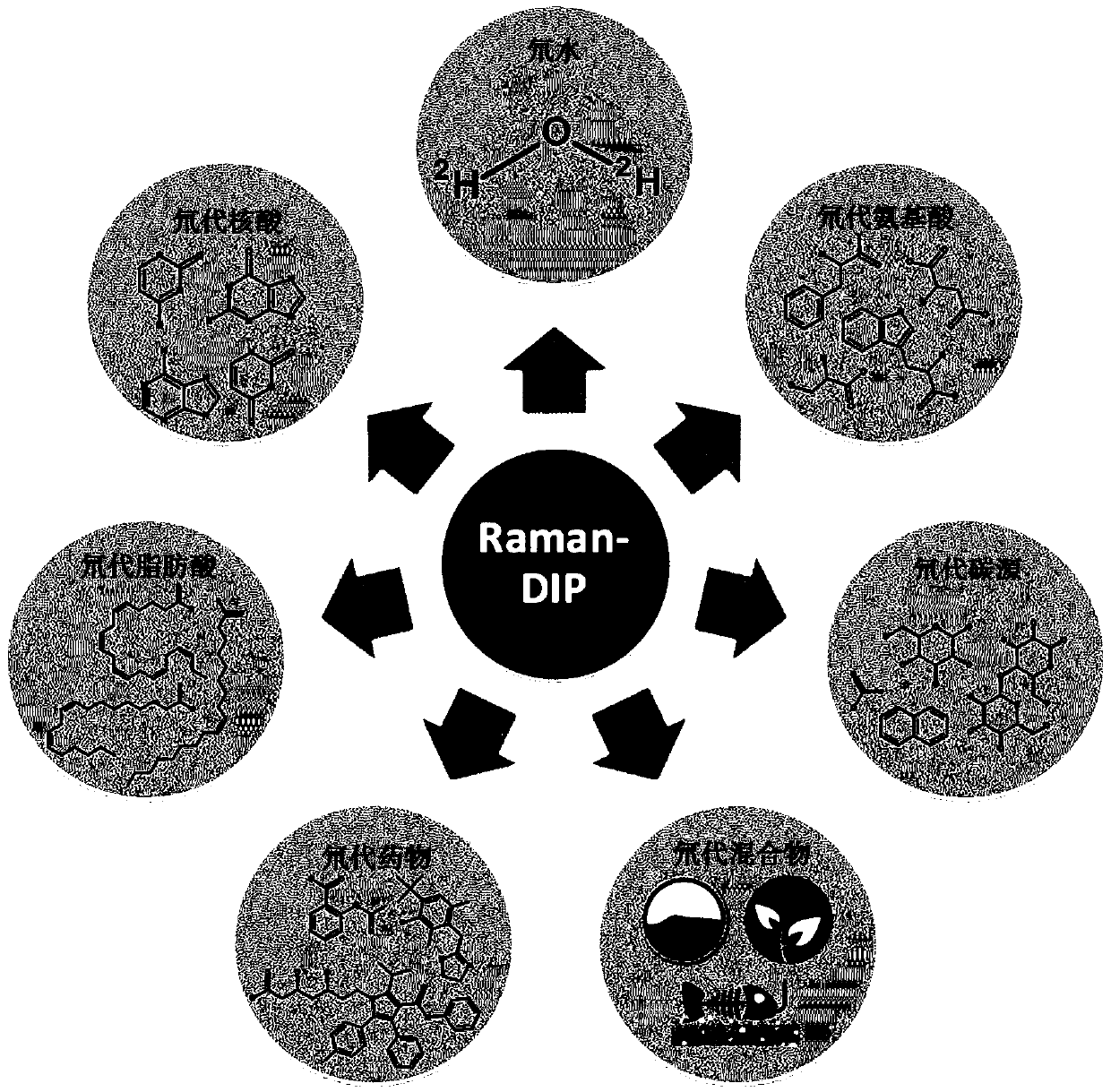
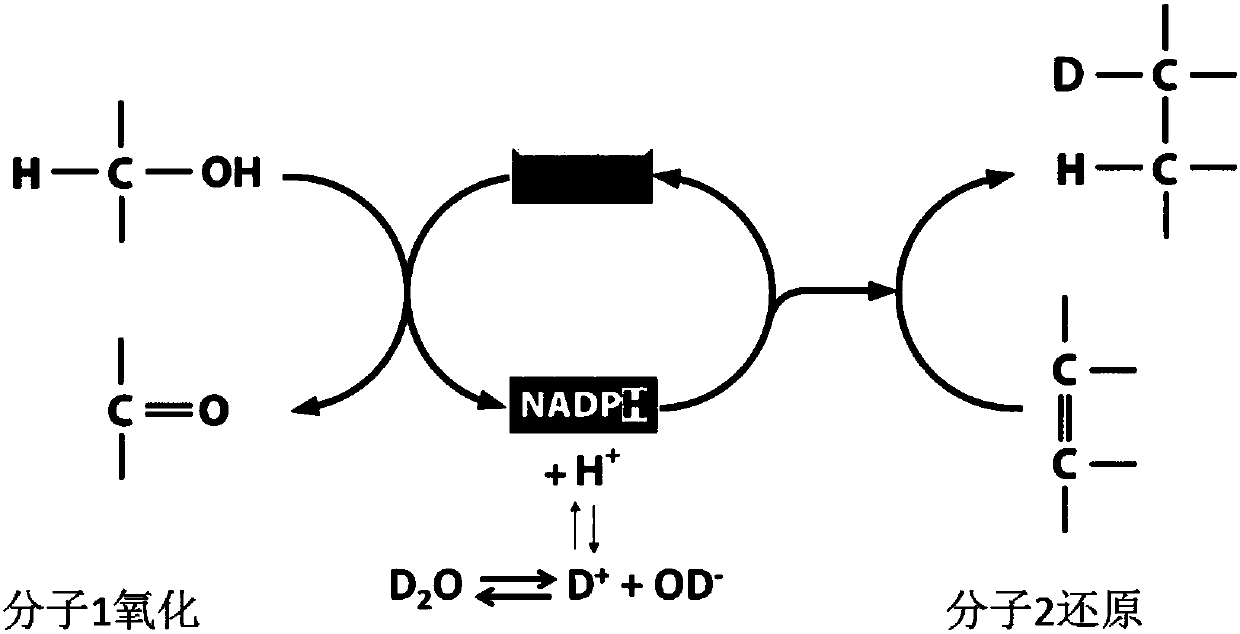
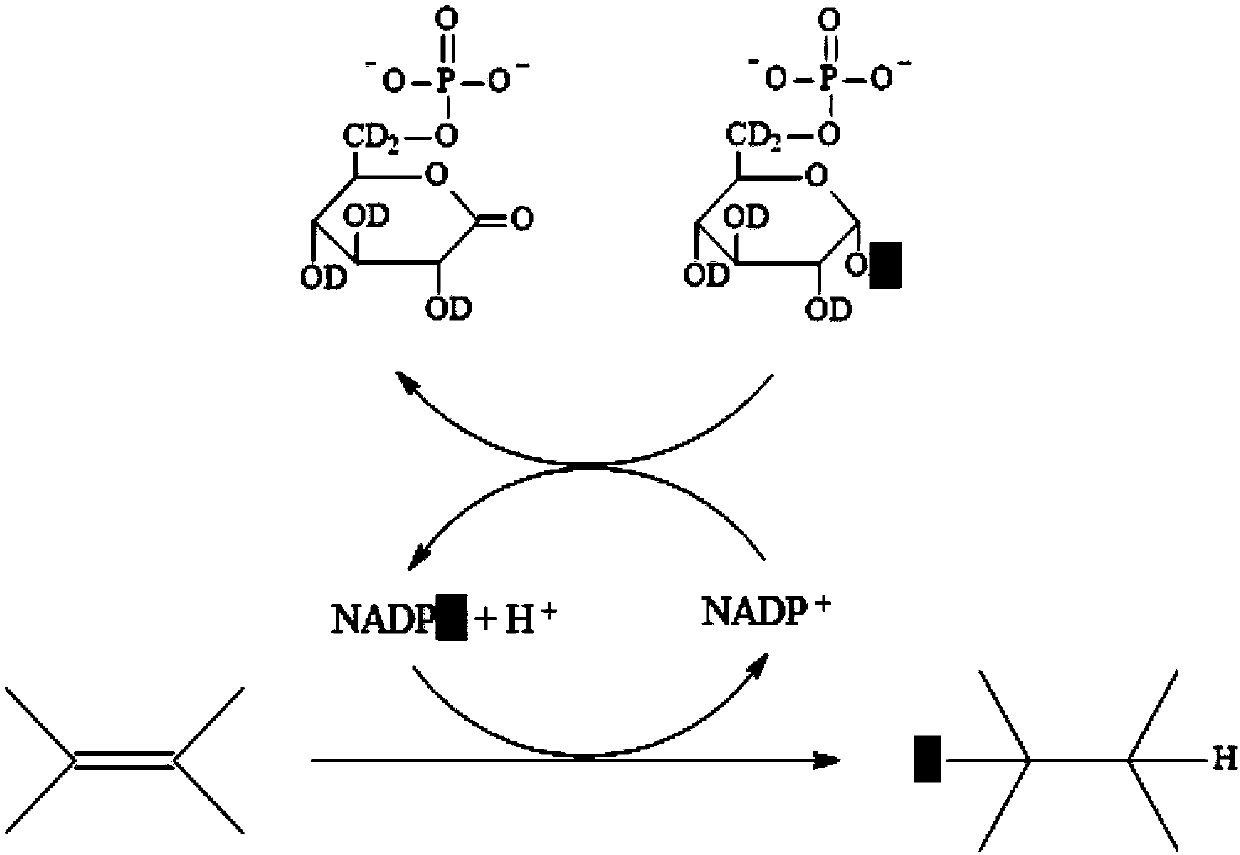
In-situ rapid detection method for cell biological process
A technology of cell biology and cell biology, which is applied in the field of rapid detection of cell biological processes in situ, and can solve problems such as not yet cultured and unable to reflect the living environment of cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0106] Embodiment 1: the impact of deuterated substrate on microbial growth
[0107] This example verifies that cells cannot distinguish undeuterated substrates from fully deuterated substrates during metabolism.
[0108] The specific implementation plan is as follows:
[0109] Escherichia coli DH5a, Pseudomonas putida UWC1, and Pseudomonas putida G7 were selected (these strains are common commercially available strains), the culture condition of Escherichia coli DH5a was 37°C, and Pseudomonas putida UWC1, Pseudomonas putida The culture condition of Monas G7 was 30°C. The bacterial solution cultured overnight in LB medium was inoculated into fresh MM medium at a ratio of 1:50. The only carbon source for the medium was glucose or naphthalene. The proportions of deuterated glucose were 0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100%, and the proportions of deuterated naphthalene were 0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100%. Use a pipette gun to pipette 200 μL of bacterial solution to a 96-well plate, and cul...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2: Identification of antibiotic resistance of unknown non-purely cultured microorganisms in river water without altering the in situ environment
[0113] The river water was collected in the Thames River, England in February 2016 (the coordinates of the sample collection point are 51°44'47.0"N, 1°15'21.0"W). Take 200mL surface river water samples and store them in glass sample bottles. Save it.
[0114] Take 2.4mL river water sample, add 1.6mL deuterium water, and add different concentrations of antibiotics (see Table 1 for specific concentrations), and incubate at room temperature for 24 hours at a rotation speed of 500rpm. The negative control is 2.4mL river water sample added with 1.6mL deionized water, cultured under the same conditions.
[0115] Table 1 Concentration of antibiotics in river water samples
[0116]
[0117] Label the 24-hour river water sample, centrifuge at 5000g for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, add 4 mL of deionized water and cen...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3: Identification of Bacterial Infection Resistance from Sputum of Patients with Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
[0123] The patient, male, 33 years old, had upper respiratory tract infection. Collect 2mL of its sputum and mix it with 2mL deuterium water. The mixed sample was divided into five equally, four of which were added with different antibiotics, including kanamycin (50 μg / mL), carbenicillin (100 μg / mL), tetracycline (12 μg / mL), chloramphenicol (6 μg / mL), and one without antibiotics was used as a control. Samples were incubated at 37°C for 7 hours.
[0124] Then the sample was centrifuged at 5000g for 5 minutes, the supernatant was removed, an equal volume of deionized water was added to mix, centrifuged at 5000g for 5 minutes, the supernatant was removed and resuspended in the same volume of deionized water. After drying 1 μL of cells on a calcium fluoride glass slide, the Raman spectrum of a single cell was measured with a Raman spectrometer. R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com